Solved NCERT Questions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 In Hindi - Free PDF
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry In Hindi Chapter 16 Chemistry In Everyday Life - 2025-26
1. Where can I find complete, step-by-step NCERT Solutions for all questions in Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16, Chemistry in Everyday Life?
You can find comprehensive and accurate NCERT Solutions for all in-text and end-of-chapter exercise questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16. These solutions are prepared by subject matter experts and are fully aligned with the latest CBSE 2025-26 syllabus, ensuring you learn the correct methodology for answering board exam questions.
2. How should one correctly classify drugs with examples when solving an NCERT exercise question?
To answer correctly, you must first identify the basis of classification mentioned in the question. The main classifications to include in your solution are:
- Pharmacological effect: This describes the drug's effect on the body. Example: Analgesics are painkillers.
- Drug action: This refers to the action of a drug on a specific biochemical process. Example: Antihistamines inhibit the action of histamine.
- Chemical structure: Drugs with similar structures and activity. Example: Sulphonamides.
- Molecular targets: This is based on the macromolecules the drug interacts with. Example: Enzyme inhibitors.
3. Why is it incorrect to use the terms 'drug' and 'medicine' interchangeably when writing NCERT solutions?
Using the correct terminology demonstrates a precise understanding. The fundamental difference lies in their purpose and safety at a given dose. A drug is any chemical that produces a biological response in the body, which can be beneficial or harmful. A medicine, however, is a drug that has been identified as safe and effective for treating or preventing a specific disease when used in a recommended dose. Therefore, all medicines are drugs, but not all drugs are medicines.
4. What key points are essential for a perfect answer distinguishing between antiseptics and disinfectants?
Your solution must highlight the primary difference in their application. A well-structured answer should include:
- Antiseptics: These are chemical agents applied to living tissues such as skin and wounds to kill or prevent the growth of microorganisms. They are safe for human tissue. Examples include Dettol and Savlon.
- Disinfectants: These are antimicrobial agents applied to inanimate objects like floors, surgical instruments, and surfaces. They are generally toxic to living tissues. Examples include phenol and chlorine solutions.
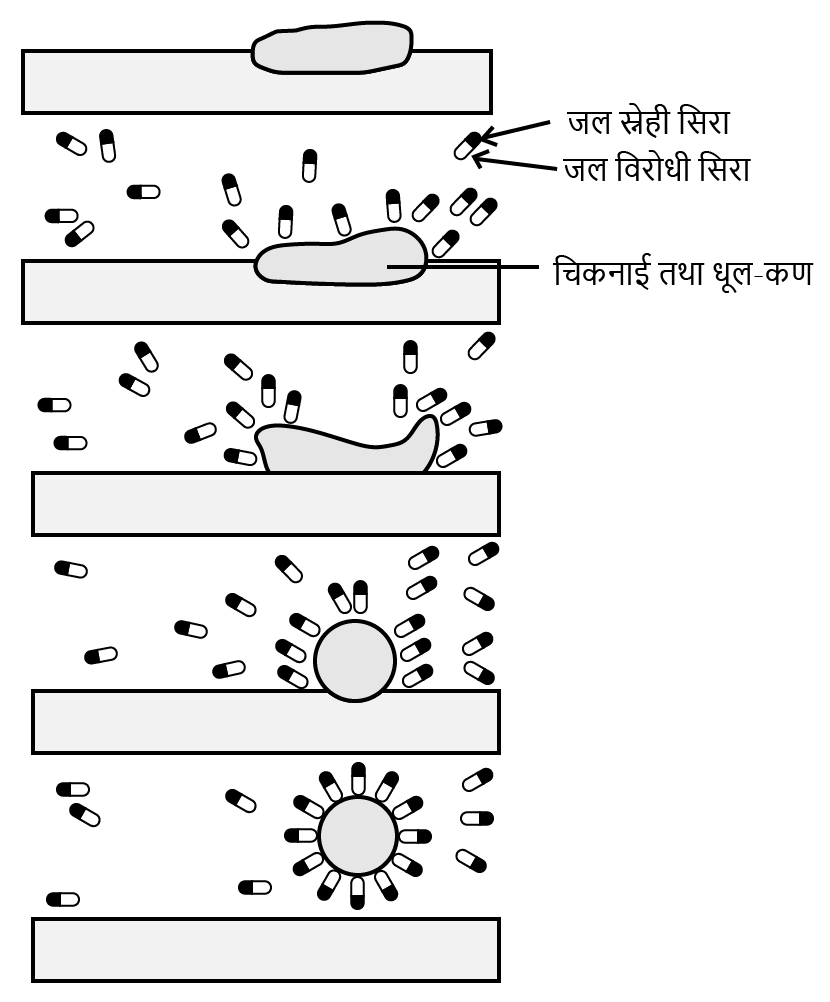
5. When an NCERT question asks for the cleansing action of soap, what is the best method to explain micelle formation?
To correctly explain the cleansing action of soap, you must describe the formation and function of micelles in a step-by-step manner:
1. Define the structure of a soap molecule, noting its two parts: a long non-polar hydrophobic (water-repelling) tail and a polar hydrophilic (water-attracting) head.
2. Explain that in water, soap molecules aggregate to form spherical structures called micelles.
3. Describe the orientation within the micelle: the hydrophobic tails point inwards, creating an oily core, while the hydrophilic heads face outwards, interacting with the surrounding water.
4. Detail the cleansing process: The hydrophobic tails trap oily dirt and grease in the micelle's core. The entire micelle, with the dirt encapsulated, is then easily washed away by water because its outer hydrophilic surface is water-soluble.
6. How should I structure an answer for an NCERT question on artificial sweetening agents?
A comprehensive answer on an artificial sweetener should cover three main points:
- Name and Sweetness Level: Mention the name of the sweetener (e.g., Aspartame, Saccharin, Sucralose) and its relative sweetness compared to cane sugar.
- Stability and Application: Specify its stability under heat. For example, Aspartame is unstable at cooking temperatures and is limited to cold foods and drinks, whereas Sucralose is stable.
- Purpose: Explain that it provides sweetness without adding significant calories, making it ideal for diabetic patients and for weight control.
7. Why are synthetic detergents considered superior to soaps in hard water? How should this be explained in an NCERT solution?
Your explanation must focus on their different reactions with the mineral ions present in hard water (Ca²⁺ and Mg²⁺).
• Soaps: In hard water, soaps react with calcium and magnesium ions to form an insoluble, sticky precipitate called scum. This scum reduces the soap's cleansing ability and leaves a residue on fabrics.
• Synthetic Detergents: Detergents are salts of sulphonic acids or alkyl hydrogen sulphates. Their calcium and magnesium salts are soluble in water. As a result, they do not form scum and can produce lather and cleanse effectively, even in hard water. This is their primary advantage.
8. What is the fundamental difference between broad-spectrum and narrow-spectrum antibiotics, and why is this distinction important?
The fundamental difference lies in the range of bacteria they affect. This distinction is crucial for effective and targeted medical treatment.
• Broad-spectrum antibiotics (e.g., ampicillin, chloramphenicol) are effective against a wide variety of both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
• Narrow-spectrum antibiotics (e.g., Penicillin G) are effective only against a specific type or limited group of bacteria.
The distinction is important because using a narrow-spectrum antibiotic, when the infectious agent is known, helps prevent the destruction of beneficial bacteria in the body and reduces the risk of developing antibiotic resistance.
9. How do you solve NCERT questions asking for examples of tranquilizers and their uses?
To solve these questions, first define tranquilizers as a class of neurologically active drugs used to treat stress and mental diseases by inducing a sense of well-being. Then, provide specific examples as mentioned in the NCERT textbook:
- For relieving tension and anxiety: Chlordiazepoxide and Meprobamate.
- For controlling depression and hypertension: Equanil.
- As sleep-inducing agents (hypnotics): Derivatives of barbituric acid like veronal and luminal.