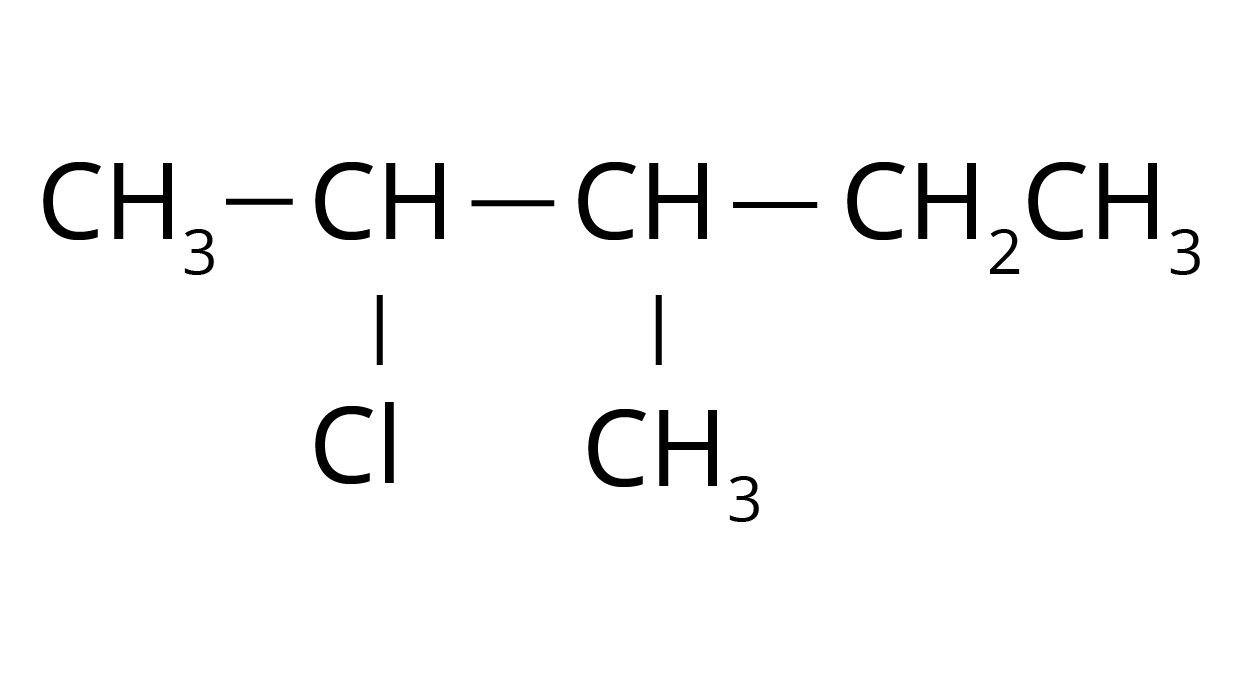Solved NCERT Questions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 In Hindi - Free PDF
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry In Hindi Chapter 10 Haloalkanes And Haloarenes - 2025-26
1. Where can I find the correct, step-by-step NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10, updated for the 2025-26 syllabus?
You can find reliable and detailed NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10, Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, fully updated for the CBSE 2025-26 session. These solutions provide the correct methodology and step-by-step answers for all in-text and exercise questions, helping you understand how to approach each problem as per the board's guidelines.
2. What is the systematic method to solve IUPAC nomenclature questions for haloalkanes and haloarenes from the NCERT textbook?
To correctly solve IUPAC naming problems as per the NCERT solutions, follow these steps:
- Identify the longest continuous carbon chain containing the halogen atom to determine the parent alkane or arene.
- Number the chain starting from the end that gives the carbon atom bonded to the halogen the lowest possible number (locant).
- Name the halogen as a prefix (e.g., fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, iodo-).
- Identify all other substituents, assign them locants, and list them in alphabetical order before the parent name.
- For haloarenes, use locants 1,2- (ortho), 1,3- (meta), or 1,4- (para) for disubstituted benzenes.
3. Why do NCERT solutions show that reacting an alkyl halide with aqueous KOH gives an alcohol, while using alcoholic KOH results in an alkene?
This is a critical distinction based on the reaction type favoured by the solvent. In an aqueous solution, KOH provides hydroxide ions (OH⁻), which act as strong nucleophiles, leading to a nucleophilic substitution (Sₙ) reaction to form an alcohol. In an alcoholic solution, the medium contains alkoxide ions (RO⁻), a much stronger base. This strong base promotes an elimination reaction by abstracting a proton from the β-carbon, forming an alkene as the major product.
4. How do the NCERT solutions explain the key differences in reaction mechanisms for Sₙ1 and Sₙ2 pathways?
The NCERT solutions differentiate the two mechanisms based on their kinetics and intermediates:
- Sₙ2 (Bimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution): This is a single-step, concerted reaction where the nucleophile attacks as the leaving group departs. It is favoured by primary (1°) alkyl halides due to less steric hindrance and results in an inversion of configuration.
- Sₙ1 (Unimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution): This is a two-step reaction. The first step involves the formation of a stable carbocation intermediate. This mechanism is favoured by tertiary (3°) alkyl halides because they form the most stable carbocations. The product is usually a racemic mixture.
5. What is the step-by-step method to determine the major product in a dehydrohalogenation reaction using Saytzeff's rule?
The NCERT solutions apply Saytzeff's rule, which states that the more substituted alkene is the major product. The correct method is:
- Identify the α-carbon (bonded to the halogen) and all adjacent β-carbons with hydrogen atoms.
- Visualize removing the halogen from the α-carbon and a hydrogen atom from each unique β-carbon.
- Draw the structures of all possible alkene products formed by creating a double bond.
- The alkene with the greatest number of alkyl groups attached to the double-bonded carbons is the most substituted and, therefore, the major product.
6. When solving NCERT problems with ambident nucleophiles like KCN, why is an alkyl cyanide the major product and not an isocyanide?
The cyanide ion (CN⁻) is an ambident nucleophile, capable of attacking from either carbon or nitrogen. As explained in the NCERT solutions, the product depends on the reagent's nature. KCN is predominantly ionic, providing free cyanide ions in solution. The attack occurs through the carbon atom because the resulting C-C bond is more stable than the C-N bond, leading to the formation of an alkyl cyanide (nitrile) as the major product.
7. Why are haloarenes much less reactive than haloalkanes towards nucleophilic substitution reactions, as explained in the NCERT textbook?
The NCERT solutions explain this low reactivity of haloarenes due to several factors:
- Resonance Effect: The C-Cl bond acquires a partial double bond character due to resonance, making it stronger and harder to break.
- Hybridisation: The carbon atom in a haloarene is sp² hybridised, which is more electronegative and holds the electron pair of the C-X bond more tightly than the sp³ hybridised carbon in a haloalkane.
- Instability of Phenyl Cation: The phenyl cation formed after the loss of the halide ion is highly unstable.
- Repulsion: The electron-rich nucleophile is repelled by the electron-rich benzene ring.
8. What is the correct method for solving the conversion of Toluene to Benzyl alcohol as shown in NCERT exercises?
The correct two-step method solved in NCERT solutions for this conversion is:
- Step 1: Free Radical Halogenation: Toluene is first treated with chlorine (Cl₂) in the presence of ultraviolet (UV) light or heat. This selectively halogenates the side-chain (methyl group) to form benzyl chloride (C₆H₅CH₂Cl), leaving the benzene ring untouched.
- Step 2: Nucleophilic Substitution: The resulting benzyl chloride is hydrolysed using an aqueous solution of KOH, where the hydroxide ion (OH⁻) substitutes the chloride ion to form the final product, benzyl alcohol (C₆H₅CH₂OH).
9. How are problems involving the Finkelstein reaction solved in the NCERT exercises for preparing alkyl iodides?
The Finkelstein reaction is a halogen exchange method solved in the NCERT textbook by reacting an alkyl chloride or bromide with sodium iodide (NaI) in dry acetone as the solvent. The key to solving this is understanding Le Chatelier's principle: NaI is soluble in acetone, but the by-products NaCl or NaBr are not. They precipitate out of the solution, shifting the equilibrium forward and ensuring a high yield of the desired alkyl iodide.