Step-by-Step Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 In Hindi - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers (2025-26)
1. What is the recommended stepwise approach for solving NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers as per CBSE 2025–26 guidelines?
The ideal approach involves the following steps:
- Read each exercise question carefully and identify the concept type—structural, nomenclature, mechanism, or property-based.
- Recall relevant definitions and concepts from your NCERT textbook before attempting the solution.
- For chemical mechanisms and conversions, write every step sequentially, showing reagents and intermediates.
- Use correct nomenclature and justify your answers with logical chemical reasoning.
- Review your work to check for completeness and correctness as per CBSE marking scheme.
2. How does the Lucas test help distinguish between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols in Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers?
The Lucas test uses a mixture of concentrated HCl and ZnCl2 to identify alcohol types based on reactivity:
- Tertiary alcohols react instantly, forming turbidity within seconds.
- Secondary alcohols give turbidity in a few minutes.
- Primary alcohols react very slowly or not at all at room temperature.
3. What are the key IUPAC naming rules for organic compounds in Chapter 11 and common errors students should avoid in NCERT Solutions?
While applying IUPAC nomenclature:
- Find the longest carbon chain containing the functional group.
- Number the chain to give the lowest possible number to the functional group.
- List and number all substituents accurately.
- Use correct suffixes like '-ol', '-phenol', or '-oxy' where needed.
- Avoid skipping numbers, misplacing substituents, or using trivial names in final answers.
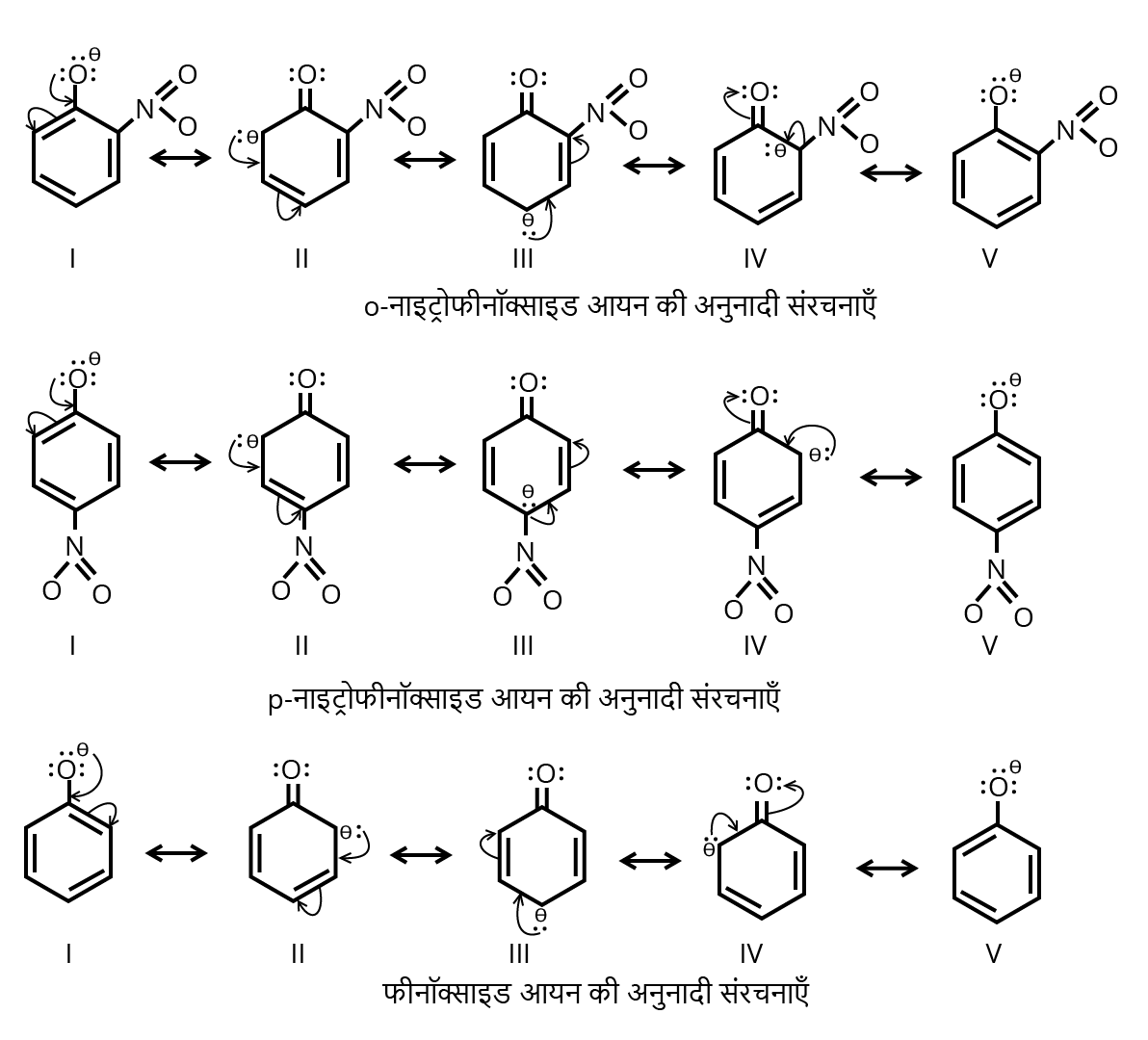
4. Why are o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol more acidic than phenol according to CBSE Chemistry Guidelines?
Ortho- and para-nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol because the nitro group is an electron-withdrawing group. When this group is at the ortho or para position, it stabilizes the negative charge on the phenoxide ion via resonance and inductive effect. This increases acidity compared to unsubstituted phenol.
5. What is the correct method to write the mechanism for the Reimer–Tiemann reaction in Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Solutions?
Present the mechanism stepwise as follows:
- Show the formation of phenoxide ion from phenol and NaOH.
- Depict the reaction of phenoxide with chloroform to generate the dichlorocarbene intermediate.
- Illustrate the electrophilic substitution at the ortho position to phenol's ring.
- Conclude with hydrolysis resulting in formation of salicylaldehyde.
6. What are common mistakes students should avoid when balancing chemical equations in Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers NCERT Solutions?
Watch out for:
- Omitting coefficients in front of molecules, especially in redox reactions.
- Not balancing hydrogen and oxygen atoms completely.
- Confusing structural formulas (e.g., writing CH3O instead of CH3OH).
7. How does the Williamson ether synthesis proceed and what are the key points to include in solutions for this method?
Williamson ether synthesis involves:
- Reacting a primary alkyl halide with a sodium alkoxide (R-O−).
- The alkoxide acts as a nucleophile, attacking the carbon of the alkyl halide (SN2 mechanism).
- This forms an ether and sodium halide as byproduct.
- Students should highlight that primary halides are preferred to avoid elimination and ensure a good yield of ether.
8. How do NCERT Solutions for Chapter 11 help students understand the difference between alcohols, phenols, and ethers effectively?
The solutions support conceptual clarity in the following ways:
- They show how to identify functional groups: alcohols (–OH on sp3 C), phenols (–OH on aromatic ring), and ethers (R–O–R').
- Stepwise answers explain differences in properties and reactivity through solved examples and mechanisms.
- Relevant structures and CBSE-aligned marking scheme are used for visual and logical understanding.
9. What role does resonance play in phenol derivatives and how should students represent it in NCERT Solutions?
Resonance in phenol derivatives allows the lone pair on the oxygen atom to delocalize into the aromatic ring, increasing reactivity towards electrophilic substitution. Substituents like nitro or alkyl groups influence the position and reactivity due to their electron-withdrawing or donating effects. Answers should include relevant resonance structures and clear stepwise representation in line with the syllabus.
10. Can students using Hindi Medium NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry expect similar performance as those using English Medium for CBSE 2025–26 exams?
Yes, both Hindi Medium and English Medium NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry strictly follow the CBSE curriculum and exam pattern. The stepwise solutions, concepts covered, and marking scheme are identical in both languages, ensuring that students from either medium are equally prepared for the exam.
11. How can students avoid common misconceptions while using NCERT Solutions for Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers exercises?
To avoid misunderstandings:
- Pay close attention to structure when identifying alcohols, phenols, or ethers by checking the functional group position.
- Follow the correct order in reaction mechanisms instead of skipping intermediates.
- Always double-check nomenclature and balancing in equations before finalizing answers.
- Justify every step with chemical reasoning as required by the CBSE marking guideline.
12. What if a multi-step organic conversion question is asked from Chapter 11 in the Class 12 Chemistry exam? How should students approach it in NCERT Solutions?
For multi-step conversions:
- Break the problem into small steps, writing every reaction and intermediate clearly.
- Label all reagents and conditions used in each transformation.
- Draw structural formulas for each compound involved.
- Connect the starting material to the final product logically, following CBSE standards for conversion questions.
13. How should students demonstrate understanding of electrophilic substitution in ethers and phenols using NCERT Solutions?
Students should:
- Show how electron-donating or withdrawing substituents affect the aromatic ring's reactivity and orientation of incoming groups.
- Provide resonance diagrams and briefly explain why ortho/para positions are favored in phenols and alkoxybenzenes.
- Present the complete set of products formed, indicating the major and minor ones based on steric and electronic factors in solution steps.