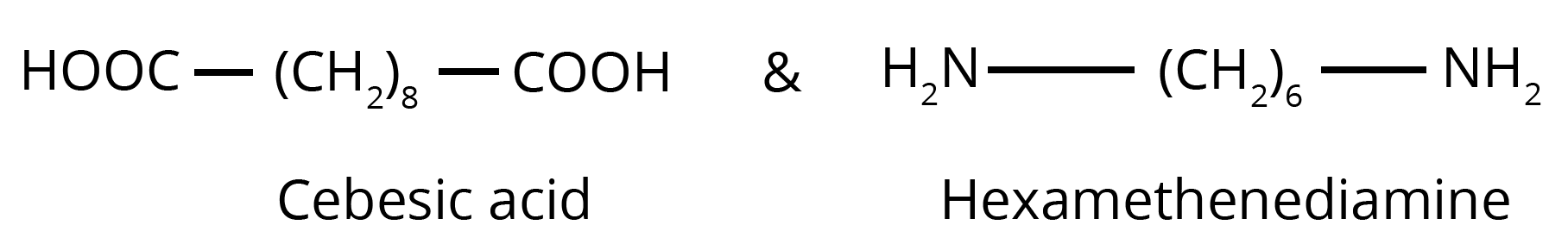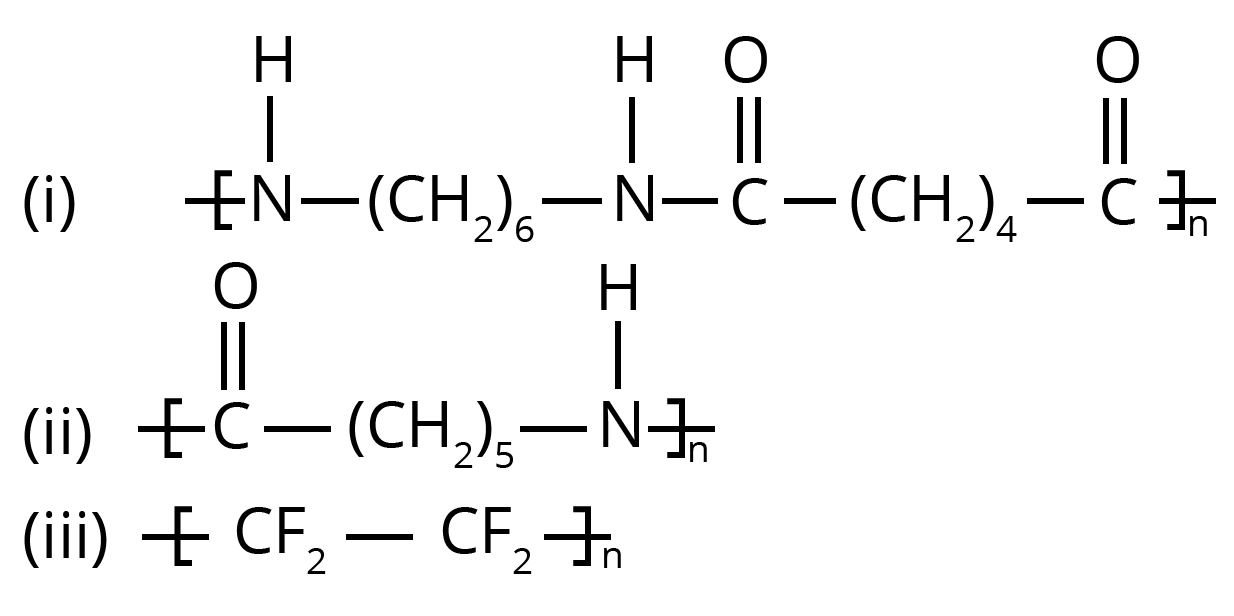Step-by-Step Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 In Hindi - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Polymers In Hindi Mediem in Hindi - 2025-26
1. Where can I find reliable, step-by-step NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 (Polymers)?
Vedantu provides comprehensive NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15, developed by subject matter experts. These solutions feature detailed, step-by-step explanations for all in-text and exercise questions, fully aligned with the latest CBSE 2025-26 syllabus, to help students build a strong conceptual foundation and solve problems accurately.
2. How do you correctly solve the NCERT question asking for the monomers of Nylon 6 and Nylon 6,6?
To solve this question as per NCERT guidelines, you must identify the distinct monomer units for each polymer.
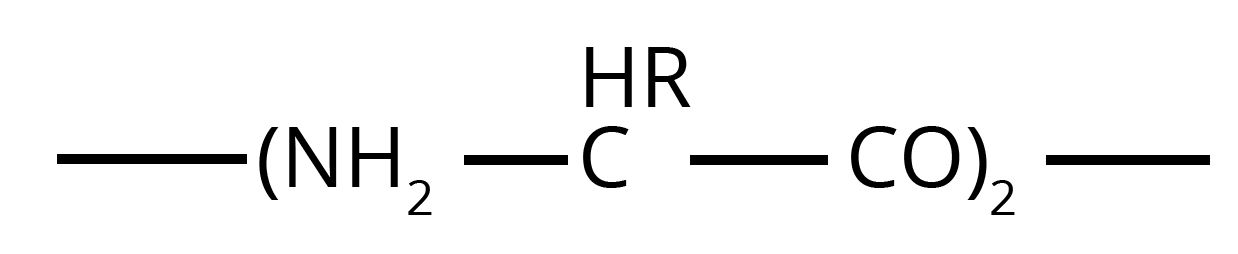
- For Nylon 6,6, the two monomers are hexamethylenediamine (H₂N−(CH₂)₆−NH₂) and adipic acid (HOOC−(CH₂)₄−COOH). It is formed through condensation polymerization.
- For Nylon 6, the single monomer is caprolactam, which undergoes ring-opening polymerization to form the polymer.
3. What is the correct method to differentiate between thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers as per the NCERT syllabus?
The primary method to differentiate them is based on their structural differences and their response to heat.
- Thermoplastic polymers consist of linear or slightly branched long chains. They soften on heating and harden on cooling, and this process is reversible. Examples include polythene, PVC, and polystyrene.
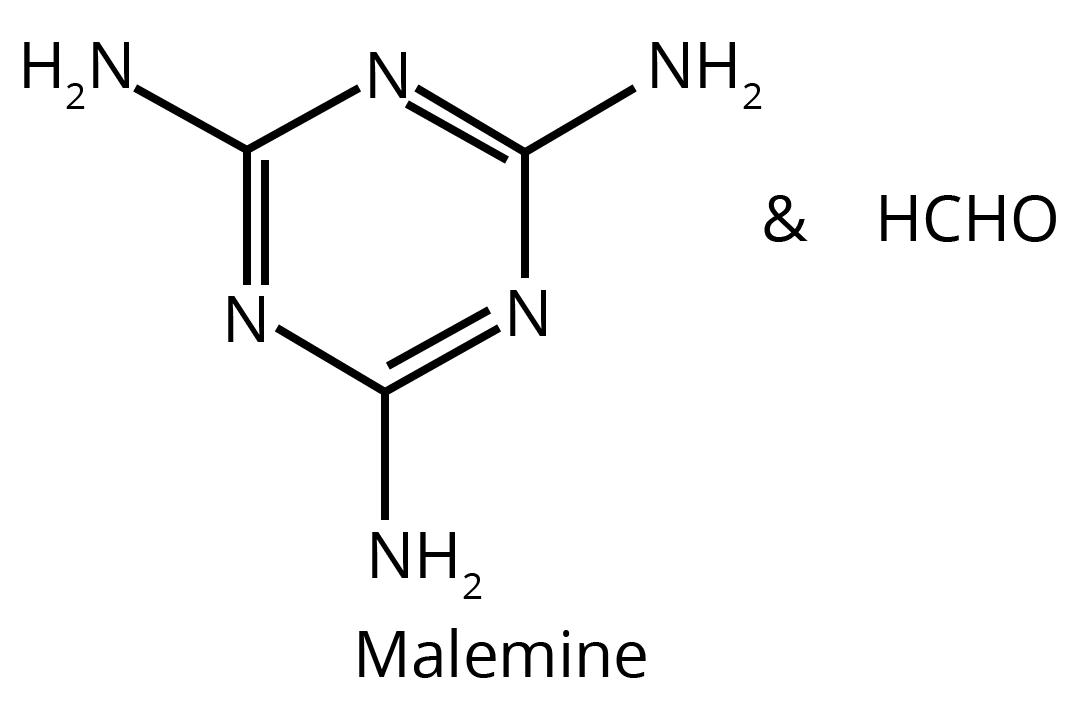
- Thermosetting polymers have a cross-linked or heavily branched structure. On heating, they undergo extensive cross-linking in moulds and become infusible and permanently hard. This process is irreversible. Examples include Bakelite, urea-formaldehyde resin, and melamine.
4. Why is the 'functionality' of a monomer crucial in determining the final structure of a polymer?
The functionality of a monomer, which is the number of bonding sites it has, is a critical factor that dictates the polymer's structure and properties. A monomer with a functionality of two, like ethene, can only form linear chains (e.g., polythene). In contrast, a monomer with a functionality of three or more, like phenol or formaldehyde, can form cross-linked or network polymers. This cross-linking results in rigid, infusible, and hard materials, such as the thermosetting polymer Bakelite.
5. How are polymers classified based on intermolecular forces according to the NCERT textbook?
According to the Class 12 NCERT textbook, polymers are classified into four main categories based on the magnitude of their intermolecular forces:
- Elastomers: These have the weakest intermolecular forces, allowing them to stretch and return to their original shape. Example: Buna-S.
- Fibres: These possess strong intermolecular forces like hydrogen bonds, which give them high tensile strength. Example: Nylon 6,6.
- Thermoplastic Polymers: Their intermolecular forces are intermediate between those of elastomers and fibres. Example: Polythene.
- Thermosetting Polymers: These are characterized by strong covalent bonds that form a rigid 3D network. Example: Bakelite.
6. How do these NCERT Solutions for Chapter 15 help in preparing for the CBSE 2025-26 board exam?
These NCERT Solutions are designed not just to provide answers but to serve as a comprehensive preparation tool. They help by:
- Illustrating the correct step-by-step method for solving problems, which is crucial for scoring full marks.
- Explaining the mechanisms of reactions like addition and condensation polymerization with clear examples.
- Ensuring complete coverage by including solutions for both in-text and end-of-chapter exercises.
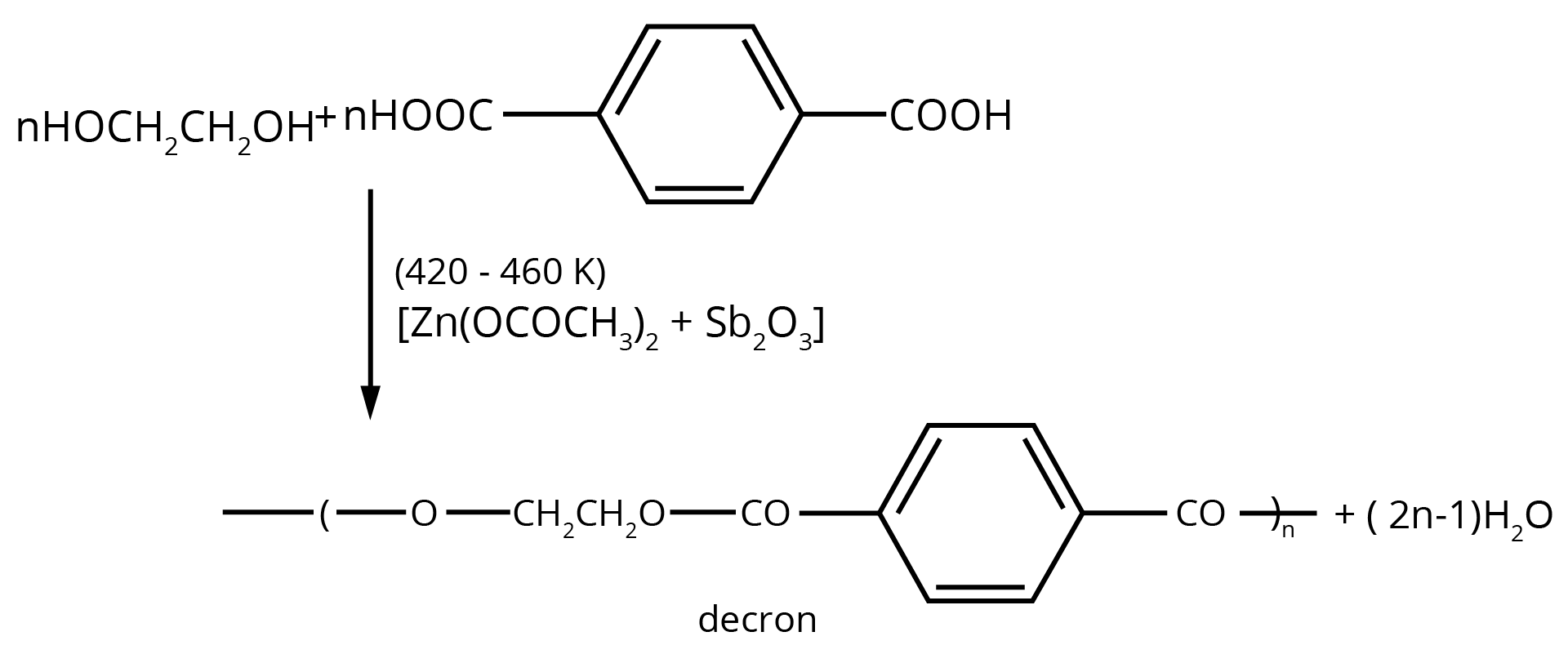
- Clarifying the structures and uses of important polymers like Dacron, Teflon, and PHBV, which are frequently asked about in exams.
7. What are biodegradable polymers, and what is the correct NCERT example to use in an exam?
Biodegradable polymers are polymers that can be broken down by microbial action over a period of time, thus offering a solution to environmental pollution. The most important example from the NCERT Class 12 Chemistry textbook is PHBV (Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate-co-β-hydroxyvalerate). It is a copolymer of 3-hydroxybutanoic acid and 3-hydroxypentanoic acid and is used in specialty packaging and orthopedic devices.
8. Why is the vulcanization of natural rubber necessary, and what is the key chemical change involved?
Natural rubber has limited practical use because it is soft, sticky, and has low tensile strength. Vulcanization is necessary to enhance its physical properties. The process involves heating raw rubber with sulphur. The key chemical change is the formation of sulphur cross-links between the linear cis-polyisoprene chains. This network structure prevents the chains from slipping past one another, making the rubber harder, stronger, and more elastic.
9. How do the NCERT solutions for Chapter 15 correctly explain the difference between Buna-N and Buna-S?
The NCERT solutions explain that both Buna-N and Buna-S are synthetic rubbers made by copolymerization, but they differ in one of their monomers:
- Buna-S is a copolymer of 1, 3-butadiene and styrene. The 'S' stands for styrene. It is used in making automobile tyres and footwear.
- Buna-N is a copolymer of 1, 3-butadiene and acrylonitrile. The 'N' stands for acrylonitrile. It is resistant to the action of petrol and oils and is used in making oil seals and tank linings.