Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Wastewater Story (2025-26)
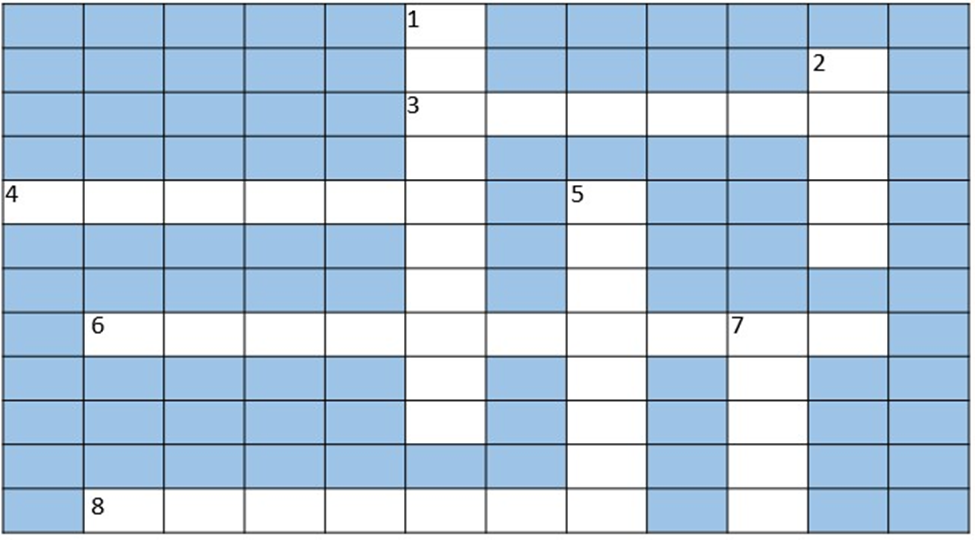
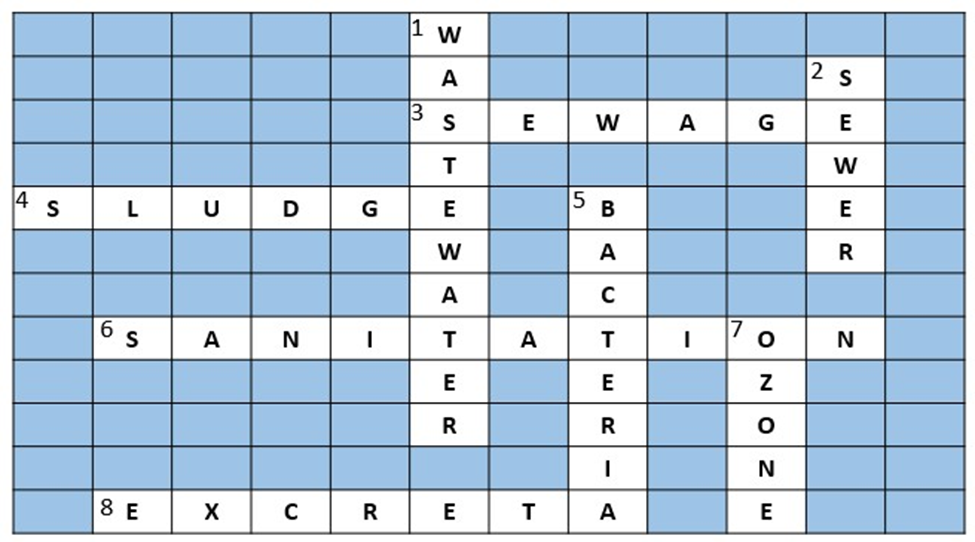
1. What is the correct solution for the crossword puzzle in NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 13?
The NCERT solutions provide the correct answers for the crossword puzzle based on the chapter's key terms. The solutions are:
- Across: 3. Sewage, 4. Sludge, 6. Sanitation, 8. Excreta.
- Down: 1. Wastewater, 2. Sewer, 5. Bacteria, 7. Ozone.
2. How do the NCERT solutions explain the harmful effects of discharging untreated sewage?
The NCERT solutions for Chapter 13 explain that untreated sewage is harmful because it contains dangerous chemicals and disease-causing organisms. When discharged into rivers or seas, the nutrients in the sewage can cause excessive algal growth (eutrophication). This depletes the dissolved oxygen in the water, which can kill fish and other aquatic life, severely damaging the ecosystem.
3. According to the NCERT textbook, why should oils and fats not be released into drains?
The NCERT solutions clarify that oils and fats should not be poured down the drain because they are not soluble in water. They harden and accumulate inside pipes, causing severe blockages. If they reach a water body, they form a layer on the surface, which prevents oxygen from dissolving into the water and harms aquatic organisms.
4. What are the key steps to get clarified water from wastewater, as explained in the Chapter 13 solutions?
The NCERT solutions for "Wastewater Story" outline a multi-step process for wastewater treatment to get clarified water:
- Physical Filtration: Wastewater is first passed through bar screens to remove large objects like rags, plastics, and cans.
- Grit and Sand Removal: The water then flows into a tank where the speed is reduced to allow sand, grit, and pebbles to settle down.
- Sedimentation: In a large settling tank, solid waste like faeces, called sludge, settles at the bottom and is removed with a scraper. Floatable materials like oil and grease are removed with a skimmer. The water at this stage is called clarified water.
5. How can students access the complete NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 for the 2025-26 session?
Students can find detailed, step-by-step NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13, "Wastewater Story," on the Vedantu website. These solutions are prepared by subject matter experts and are fully aligned with the latest CBSE 2025-26 syllabus, helping you understand the correct methods to answer all textbook questions.
6. Why is untreated human excreta considered a major health hazard in the NCERT solutions?
The NCERT solutions explain that untreated human excreta is a significant health hazard because it contains millions of harmful microorganisms, including bacteria and viruses. When this waste contaminates soil or water sources (like groundwater), it can spread serious water-borne diseases such as cholera, typhoid, and dysentery to a large population that may consume the contaminated water.
7. What is the scientific reason for using chemicals like chlorine and ozone to disinfect water, as mentioned in the NCERT solutions?
The NCERT solutions identify chlorine and ozone as key disinfectants. The scientific reason they are used is that they are powerful oxidising agents. They effectively kill or inactivate harmful pathogenic microorganisms (like bacteria and viruses) present in the water by destroying their cell walls or disrupting their reproductive processes. This makes the water safe for human consumption and prevents the spread of disease.
8. Beyond just filtering, what is the specific function of bar screens in the initial stage of a wastewater treatment plant as per the NCERT solutions?
According to the NCERT solutions, the specific function of bar screens is not just general filtration but the crucial first step of primary treatment. They are designed to remove large, solid objects such as rags, sticks, plastic bags, and cans from the incoming wastewater. This is essential to prevent damage and clogging of the pumps and other equipment in the later stages of the treatment plant.
9. How do the NCERT solutions for Chapter 13 help students understand their role as active citizens in promoting sanitation?
The NCERT solutions for this chapter encourage students to become active citizens by highlighting their responsibilities. They explain that students can contribute by:
- Not throwing waste, oils, or chemicals down the drain.
- Ensuring their home and school sanitation systems work correctly.
- Spreading awareness about the importance of clean water and proper waste disposal.
- Reporting any open drains or leaking sewer lines to the local authorities.
This helps connect textbook knowledge to practical, responsible actions.
10. What is the difference between sludge and sewage, and how are they treated differently in a wastewater treatment plant?
The NCERT solutions clarify the key differences between these two terms:
- Sewage is the total liquid wastewater released from homes, industries, and hospitals. It is the incoming raw material for the treatment plant.
- Sludge is the semi-solid residue that settles at the bottom of sedimentation tanks after primary and secondary treatment of sewage.
Their treatment methods are also different. Sewage undergoes the full treatment process (screening, settling, aeration), while the collected sludge is transferred to a separate tank called a digester. Here, anaerobic bacteria decompose it, producing useful biogas and nutrient-rich manure.