Access Class 9 Science Chapter 1 With Our Detailed Solutions and Questions
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matters In Our Surroundings (2025-26)
1. Where can I find accurate, step-by-step NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 as per the 2025-26 syllabus?
You can find detailed and accurate NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1, 'Matter in Our Surroundings,' on educational platforms like Vedantu. These solutions are updated for the CBSE 2025-26 session and provide a step-by-step methodology for solving all the in-text and exercise questions from the NCERT textbook, which are available for free online access.
2. What is the structure of the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 are structured to cover all questions in the textbook. This includes solutions for all sets of in-text questions found within the chapter and the final comprehensive chapter-end exercise. In total, there are four sets of in-text questions and one main exercise, with solutions provided for every question to ensure complete syllabus coverage.
3. How do the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 explain the characteristics of different states of matter?
The NCERT solutions explain the characteristics of solids, liquids, and gases by focusing on the properties of their constituent particles. Answers are structured around key parameters like:
- Intermolecular space: The distance between particles.
- Intermolecular force: The force of attraction between particles.
- Kinetic energy of particles: The energy of motion.
This approach helps in correctly answering questions about why solids have a fixed shape while gases do not.
4. How should I approach solving numerical problems on temperature conversion and latent heat from Chapter 1?
To solve numericals using the NCERT solution method, follow these steps:
- Identify the given data: Note down the values for temperature, mass, or heat provided in the question.
- Select the correct formula: Use K = °C + 273 for Celsius to Kelvin conversion or Q = m × L for latent heat calculations.
- Substitute values correctly: Place the given values into the chosen formula, ensuring units are consistent.
- State the final answer with units: Clearly write the result with the appropriate unit (e.g., Kelvin, Joules).
5. What common mistakes do students make when answering questions about evaporation vs. boiling, and how do NCERT solutions clarify this?
A common mistake is confusing the two processes. NCERT solutions clarify this distinction by highlighting that evaporation is a surface phenomenon that can occur at any temperature below the boiling point, while boiling is a bulk phenomenon that happens at a specific temperature (the boiling point). Solutions emphasize writing these distinct definitions to secure full marks.
6. Why is it important to provide reasons for phenomena like 'a gas fills its container completely' as per the NCERT question pattern?
Providing reasons is crucial because it demonstrates a deep understanding of the underlying scientific principles, which is a key focus of the CBSE evaluation pattern. For a question like 'a gas fills its container,' the correct method involves explaining that gas particles have high kinetic energy and negligible intermolecular forces, allowing them to move randomly and occupy all available space. Simply stating the fact is not enough for a complete answer.
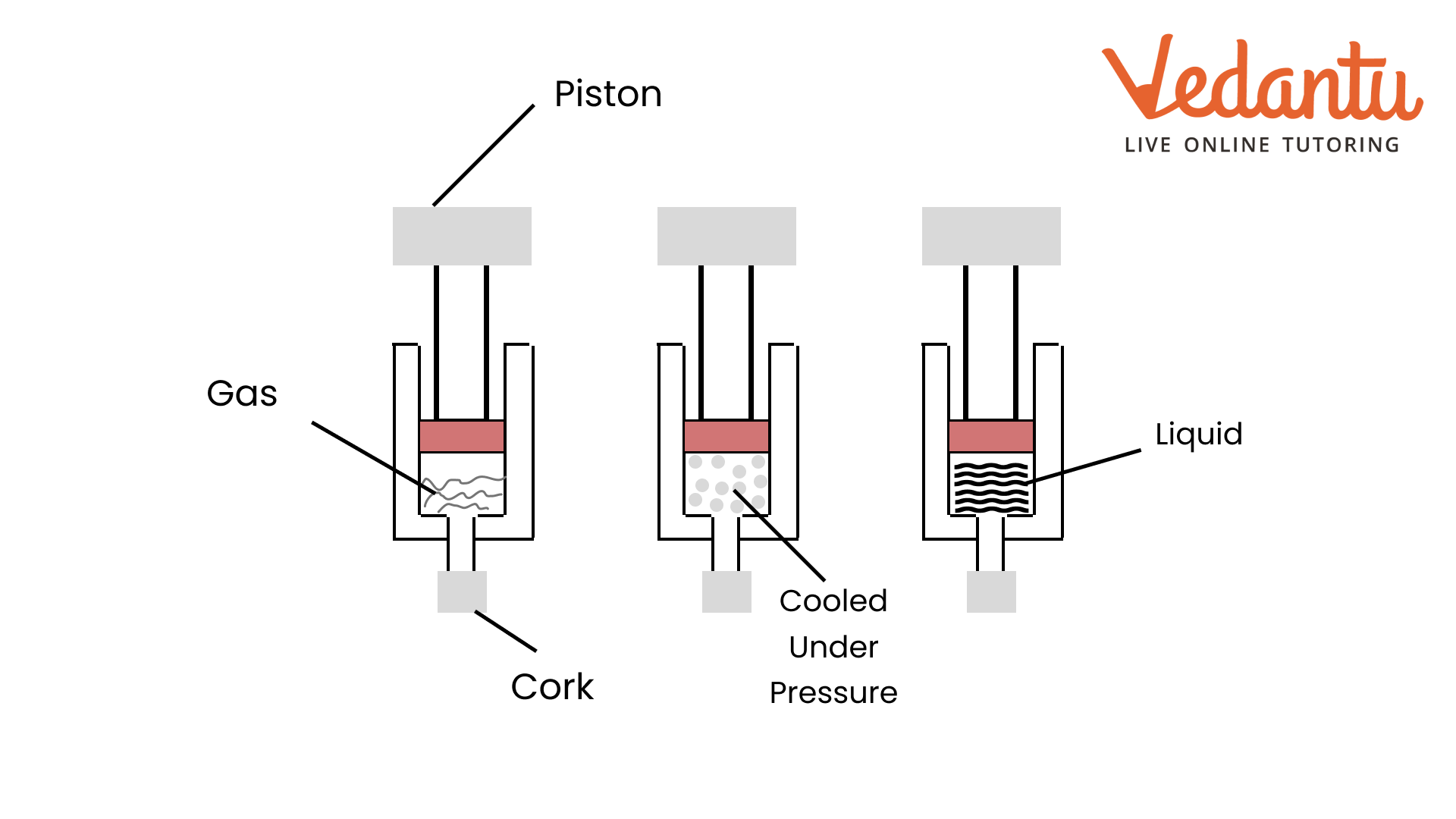
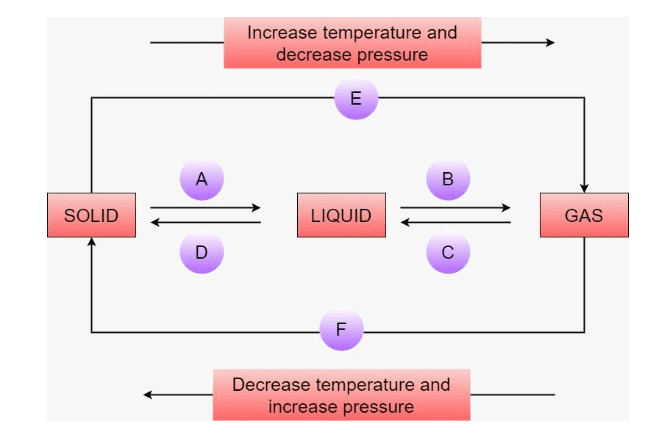
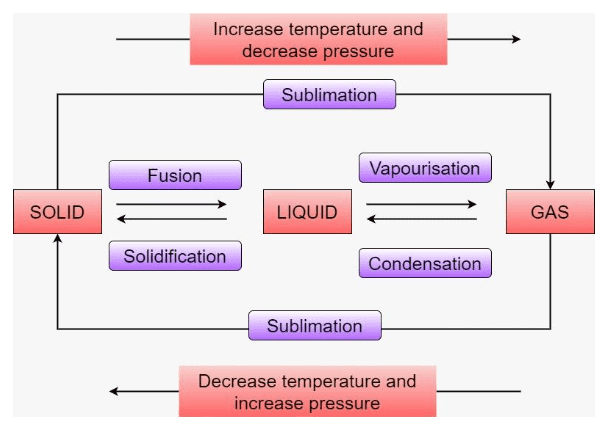
7. How are questions about the interconversion of states of matter solved in the NCERT Solutions?
Questions on the interconversion of states are solved by clearly defining each process and stating the condition required. The solutions explain:
- Melting (Fusion): Solid to liquid, by increasing temperature.
- Freezing (Solidification): Liquid to solid, by decreasing temperature.
- Boiling (Vaporisation): Liquid to gas at boiling point.
- Condensation: Gas to liquid, by decreasing temperature.
- Sublimation: Solid directly to gas, e.g., camphor or ammonium chloride.
8. When solving questions about factors affecting evaporation, what key points must be included for a full-marks answer?
For a complete answer on factors affecting evaporation, as per the CBSE pattern, you must list the factor and explain its effect. The four key factors are:
- Surface Area: An increase in surface area increases the rate of evaporation.
- Temperature: An increase in temperature increases the kinetic energy of particles, thus increasing the evaporation rate.
- Humidity: A decrease in humidity (amount of water vapour in the air) increases the evaporation rate.
- Wind Speed: An increase in wind speed carries away water vapour, increasing the rate of evaporation.
9. How do NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 address questions on diffusion?
The solutions address diffusion questions by explaining it as the intermixing of particles of different substances on their own. The key concepts used in the answers are the continuous motion (kinetic energy) of particles and the presence of intermolecular spaces. For example, when explaining the smell of hot food reaching from a distance, the solution would state that at high temperatures, particles have higher kinetic energy and diffuse faster through the air.
10. What key topics from 'Matter in Our Surroundings' are covered in the NCERT exercise solutions for Chapter 1?
The NCERT exercise solutions for Chapter 1 cover all major topics from 'Matter in Our Surroundings'. This includes solving problems and answering questions related to the physical nature of matter, characteristics of particles, the three states of matter (solid, liquid, gas), the effect of temperature and pressure on state change (including latent heat), and the process of evaporation and the factors that affect it.