Stepwise Answers & Key Tips for Class 7 Climates of India
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3 Climates Of India - 2025-26
1. What are NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3 Climates of India?
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3 Climates of India are step-by-step answers to all textbook questions, designed to help students understand key concepts and score full marks in CBSE exams.
Key features include:
- Detailed explanations for each exercise question
- Exam-focused definitions, diagrams, and examples
- Based on the latest CBSE 2025–26 syllabus
- Teacher-reviewed and easy to follow for revision
- Helps clarify important topics like monsoon, climate diversity, and seasonal patterns
2. How can I score full marks in Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3 using NCERT Solutions?
To score full marks in Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3, follow these steps:
- Write stepwise answers as shown in NCERT Solutions
- Include important keywords and definitions
- Draw clear diagrams or maps where required
- Structure long answers into clear points (introduction, main body, conclusion)
- Revise using summary notes and complete all back exercise questions
3. Which topics are most important in Class 7 Climates of India for CBSE exams?
The most important topics in Class 7 Chapter 3 Climates of India include:
- Definition of climate and weather
- Factors affecting the climate of India
- Types of seasons in India (summer, winter, monsoon, retreating monsoon)
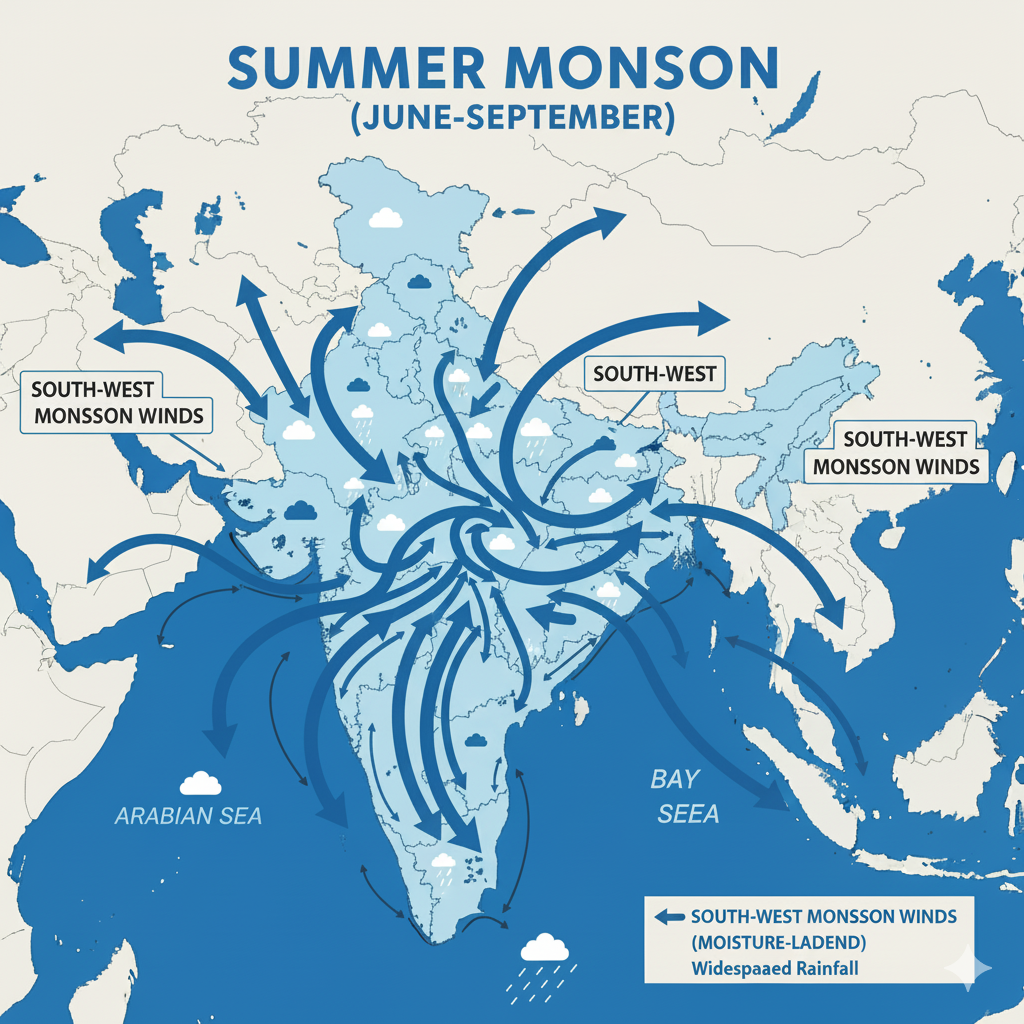
- Monsoon winds and their importance
- Diversity of India's climate, with examples
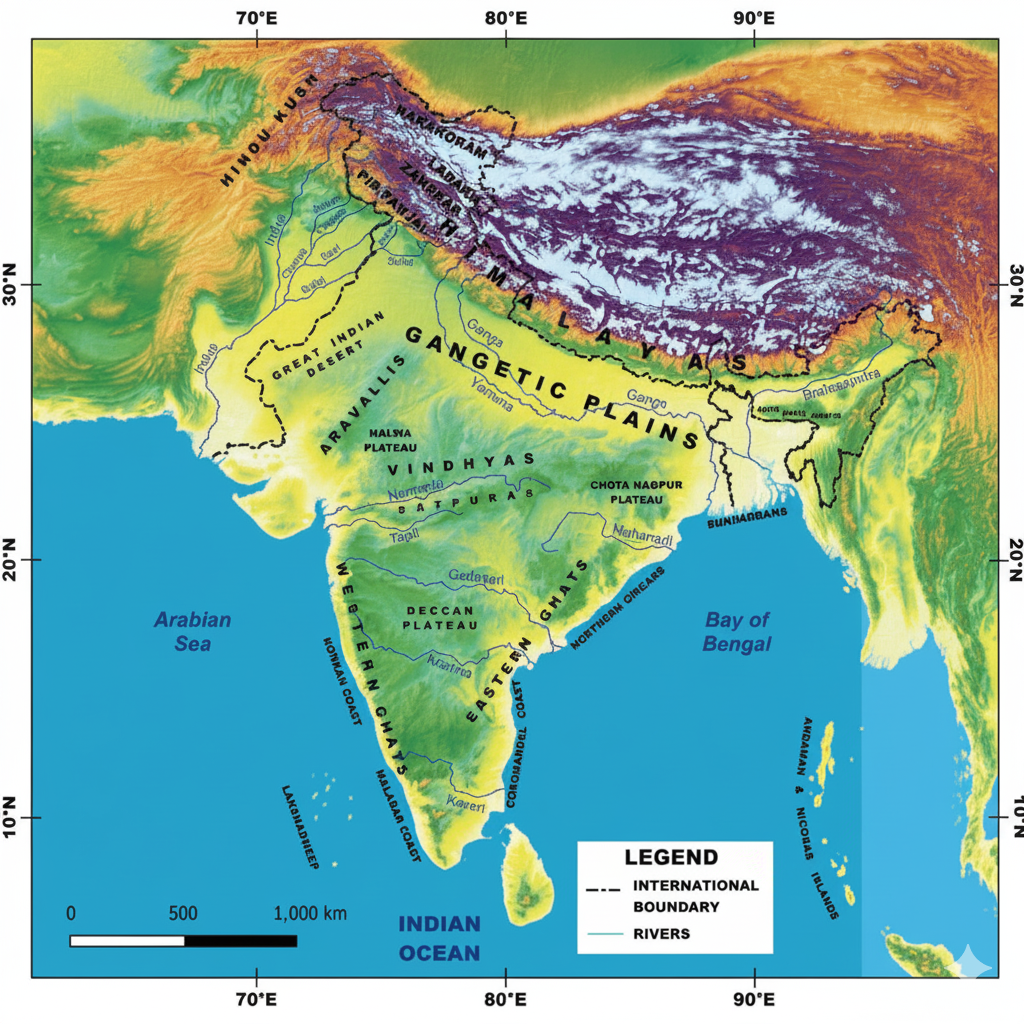
- Diagrams/maps showing rainfall patterns and climate zones
4. Where can I download the PDF of Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3 NCERT Solutions?
You can download the free PDF of Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3 NCERT Solutions from trusted educational websites like Vedantu or the official NCERT app.
Steps:
- Visit the NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science page
- Locate Chapter 3: Climates of India
- Click on the Download PDF button for offline access
5. Are diagrams or definitions compulsory in answers for Class 7 SST Chapter 3?
Including diagrams and definitions is highly recommended and sometimes compulsory for full marks in CBSE exams.
Tips:
- Always label diagrams and maps clearly
- Start answers with exam-ready definitions of terms like 'monsoon,' 'climate,' etc.
- Use neat and simple sketches where asked
6. How should I structure long answers in Class 7 Social Science exams?
To structure long answers effectively:
1. Start with a brief introduction on the topic.
2. Use main body paragraphs with bullet points or subheadings for clarity.
3. Include important terms, definitions, and diagrams if relevant.
4. End with a concise conclusion or summary statement.
This stepwise approach matches CBSE's marking scheme and maximises marks.
7. What are the stepwise answering tips for NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3?
Writing answers in steps helps you earn marks for each part of the solution, even if the final answer is incomplete.
Best practices:
- Break the answer into logical steps
- Use numbered or bullet points
- Highlight keywords from the chapter
- Draw diagrams/maps if asked
- Follow the sequence given in NCERT Solutions
8. How does practising with NCERT Solutions help for CBSE Class 7 SST exams?
Practising with NCERT Solutions boosts your scores by:
- Covering every important question likely to appear in exams
- Helping you learn correct answer presentation and keywords
- Familiarising you with the CBSE exam pattern
- Building confidence in writing long/short answers with diagrams
- Providing ready-made revision notes and definitions
9. Are these NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3 teacher-reviewed and updated?
Yes, these NCERT Solutions are teacher-reviewed, based on the latest CBSE 2025–26 syllabus, and regularly updated for accuracy.
Benefits:
- Aligned with the current CBSE marking scheme
- Reviewed for exam relevance
- Fact-checked by CBSE subject experts
- Include model answers, definitions, and diagrams
10. What mistakes should I avoid when writing answers for Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3?
To avoid losing marks in Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3:
- Don’t skip definitions for key terms
- Draw neat diagrams/maps where asked
- Avoid incomplete or one-line answers for descriptive questions
- Don’t write essays—use bullet points for clarity
- Always answer using exam keywords
- Follow the sequence/steps as shown in model NCERT Solutions
11. What is the difference between weather and climate as defined in Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3?
The difference between weather and climate:
- Weather refers to the day-to-day atmospheric conditions at a place, e.g., temperature, rainfall.
- Climate is the average weather conditions of a place observed over a longer period (30 years or more).
This definition is important for CBSE exams and should be clearly stated in answers.
12. Do examiners award partial marks for correct steps even if the final answer is wrong?
Yes, in CBSE Social Science exams, you can earn partial marks for writing correct steps, keywords, or diagrams—even if the final answer is incomplete or partially incorrect. Always attempt to show your working and reasoning clearly to maximise your score.