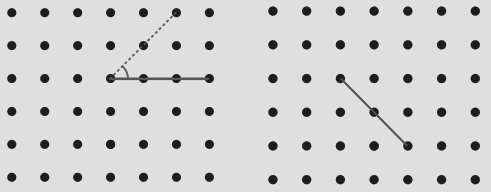
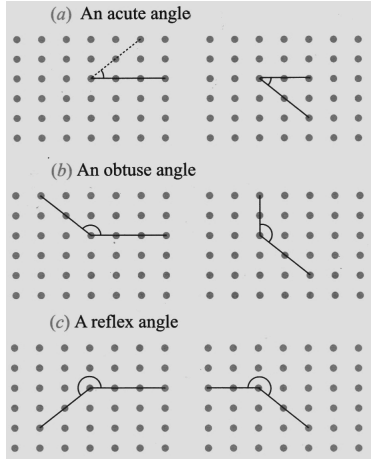
Lines And Angles Class 6 Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Lines And Angles Exercise 2.11 (2025-26)
1. Where can I find reliable, step-by-step NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 (Whole Numbers)?
You can find comprehensive and reliable NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2, Whole Numbers, right here on Vedantu. Our solutions are crafted by subject matter experts to provide a clear, step-by-step methodology for solving every problem in the textbook, ensuring they align perfectly with the latest CBSE 2025-26 guidelines.
2. How do the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2 explain the method to find the predecessor and successor of a given whole number?
The NCERT Solutions provide a very straightforward method for this. To find the successor of a whole number, you simply add 1 to it. For example, the successor of 99 is 99 + 1 = 100. To find the predecessor, you subtract 1 from the number. For example, the predecessor of 100 is 100 - 1 = 99. The solutions clarify that the whole number 0 does not have a predecessor in whole numbers.
3. What is the correct process to solve problems using the distributive property as shown in the Chapter 2 solutions?
The solutions explain the distributive property of multiplication over addition with clear steps to simplify calculations. The method involves breaking down one of the numbers into a sum. For example, to calculate 24 x 105, you would:
Rewrite 105 as (100 + 5).
Apply the property: 24 x (100 + 5).
Distribute the multiplication: (24 x 100) + (24 x 5).
Solve the simpler products: 2400 + 120.
Add the results to get the final answer: 2520.
4. How do the solutions demonstrate the representation of whole number operations on a number line?
The NCERT solutions clearly illustrate how to use a number line for operations. For addition (e.g., 3 + 4), you start at 3 and make 4 jumps to the right, landing on 7. For subtraction (e.g., 7 - 5), you start at 7 and make 5 jumps to the left, landing on 2. This visual method helps in understanding how numbers are ordered and manipulated.
5. Are the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 provided by Vedantu updated for the 2025-26 academic year?
Yes, all our NCERT Solutions, including those for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2, are meticulously updated to align with the official CBSE/NCERT syllabus for the 2025-26 academic session. You can rely on them for accurate and current methods for your homework and exam preparation.
6. Why is division of a whole number by zero considered 'not defined' in the NCERT syllabus?
The NCERT syllabus explains that division by zero is undefined because it leads to a mathematical contradiction. Division is the inverse of multiplication. For example, 8 ÷ 2 = 4 because 4 x 2 = 8. If we try to calculate 8 ÷ 0, we would be looking for a number that, when multiplied by 0, gives 8. However, any number multiplied by 0 is 0, not 8. Since no such number exists, the operation is not defined.
7. What is the significance of '0' (zero) and '1' (one) as identity elements for whole numbers?
The NCERT solutions explain their significance as follows:
Zero (0) is the additive identity: Adding 0 to any whole number does not change its value (e.g., 5 + 0 = 5). This property is fundamental in algebra for solving equations.
One (1) is the multiplicative identity: Multiplying any whole number by 1 does not change its value (e.g., 5 x 1 = 5). This is a key principle used in simplifying fractions and algebraic expressions.
8. Why don't the closure and commutative properties apply to the subtraction of whole numbers?
The solutions explain this with clear examples. Closure property means performing an operation on two whole numbers results in a whole number. Subtraction is not closed because 3 - 5 = -2, and -2 is not a whole number. Commutative property means the order of numbers does not affect the result. Subtraction is not commutative because 5 - 3 = 2, but 3 - 5 = -2. Since 2 is not equal to -2, the order matters, and the property does not hold.