What are the steps and significance of the photosynthesis process?
Photosynthesis is a vital biological process that sustains almost all life on Earth by converting light energy into chemical energy. This process occurs in plants, algae, and some bacteria, enabling them to create organic molecules like glucose from simple inorganic substances. By releasing oxygen, photosynthesis also supports animal and human life, playing a major role in ecological balance and global food supply.
Photosynthesis Definition
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and certain bacteria transform light energy, usually from the sun, into chemical energy stored in glucose. The reaction uses carbon dioxide and water as reactants and produces oxygen as a byproduct. This definition is fundamental to biology and is covered in detail in photosynthesis class 12 resources.
Historical Development and Discovery
The study of photosynthesis began in the 18th century. Joseph Priestley discovered that plants could restore air spoiled by burning a candle, and Jan Ingenhousz found that this process needed light and green plant parts. Later, researchers proved that the oxygen released comes from water, not carbon dioxide, fundamentally shaping our understanding of plant biology and environmental science.
Overall Photosynthesis Process: Explanation and Stages
Photosynthesis is a two-stage process, involving both light-dependent and light-independent reactions. These steps occur inside the chloroplasts, mainly in the leaves of plants. Understanding this process helps students answer many photosynthesis questions and attempt related photosynthesis mcqs.
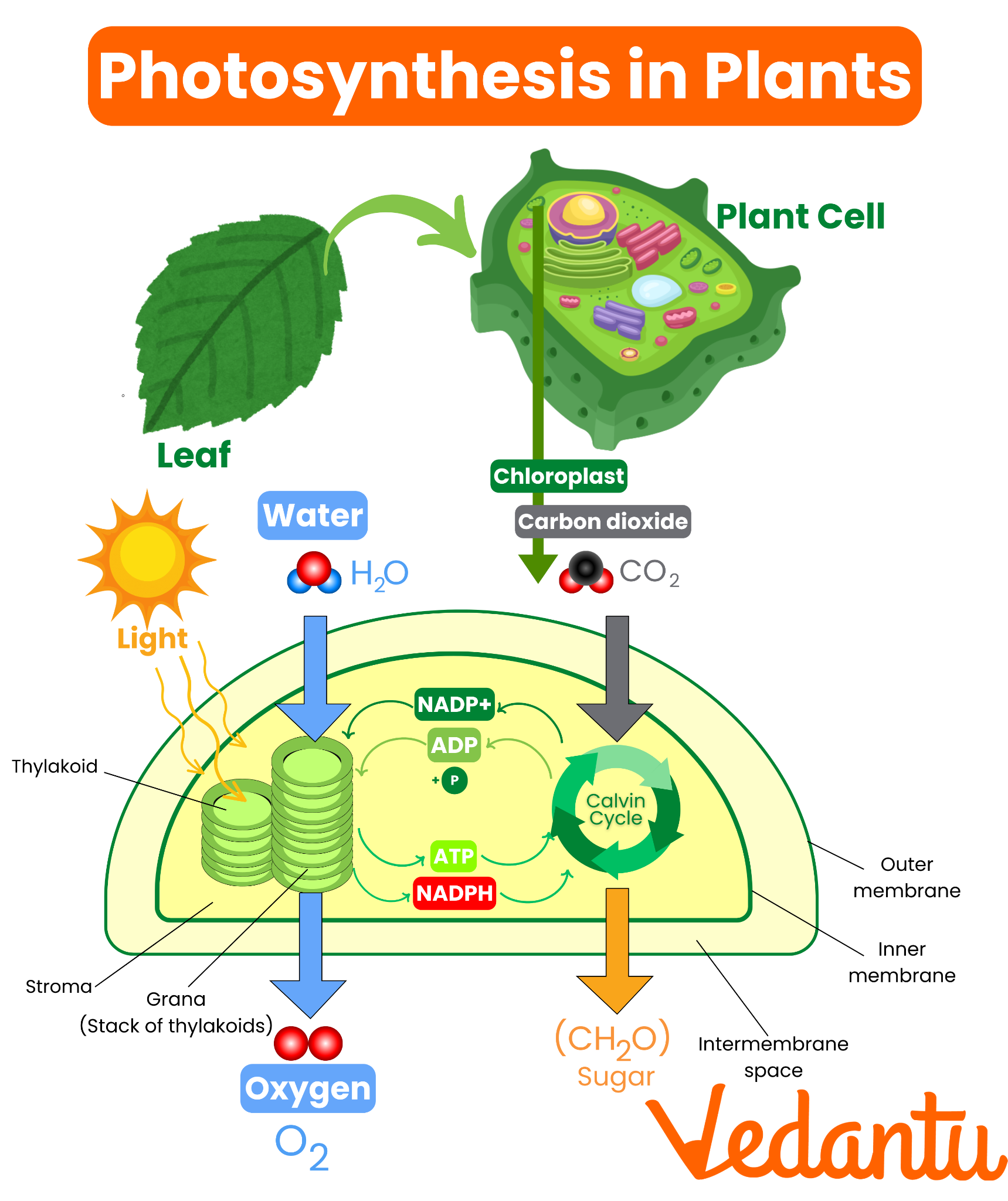
- Light-dependent reactions: These happen in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast. Solar energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments, splitting water molecules into oxygen, protons, and electrons. This also produces ATP and NADPH, crucial molecules for the next stage.
- Light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle): These processes occur in the stroma of the chloroplast. Using the ATP and NADPH generated in the previous stage, carbon dioxide is converted into glucose through a series of enzyme-driven steps. This is also known as carbon fixation.
Many biology courses, such as photosynthesis process topics, explain these steps using labeled diagrams and practical experiments.
Photosynthesis Equation and Chemical Formula
The general chemical equation for photosynthesis is:
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
This means six molecules of carbon dioxide combine with six molecules of water, using sunlight, to produce one molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen. The detailed mechanism also involves intermediate compounds and various enzymes, as explored in biomolecules studies.
Structure and Role of Chloroplasts and Chlorophyll
The key organelle for photosynthesis is the chloroplast. Inside it, chlorophyll pigments absorb sunlight, making the entire process possible. The arrangement of membranes and pigments ensures efficient light harvesting and conversion to chemical energy.
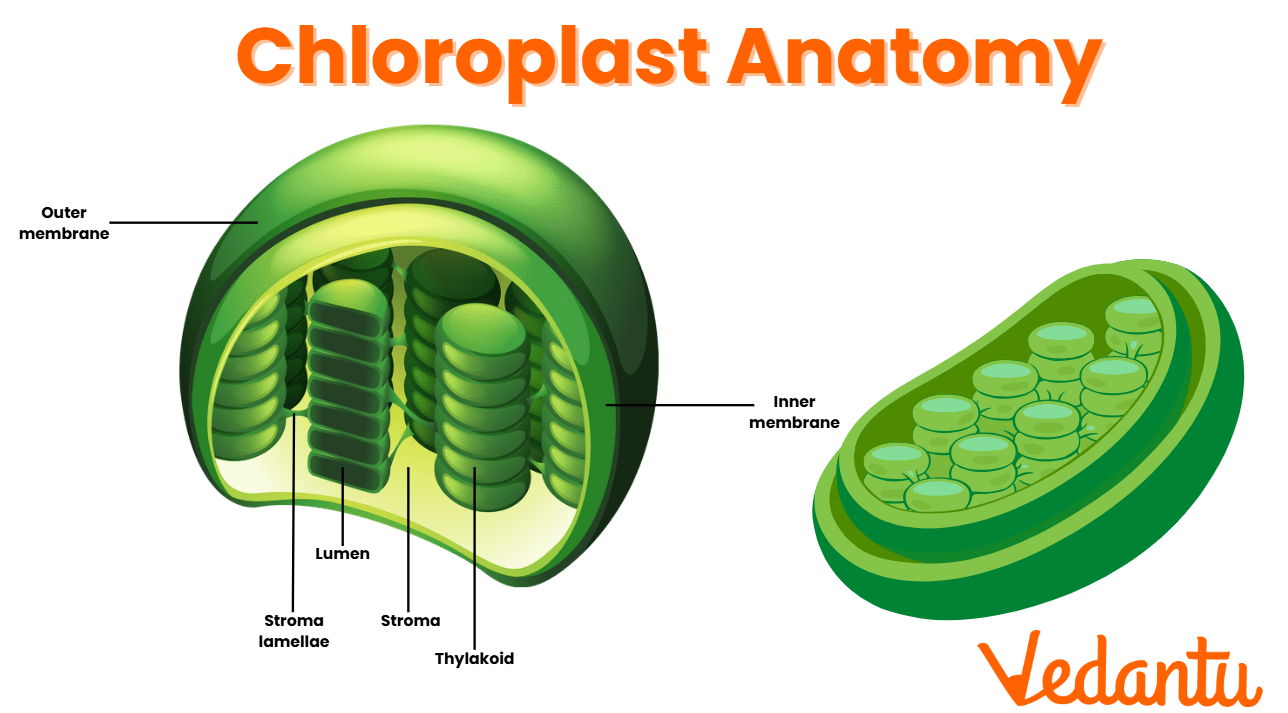
For a detailed structure, see the plant cell and chloroplasts sections.
Photosynthesis Examples in Everyday Life
Examples of photosynthesis surround us:
- Leaves of trees and plants making food in gardens or forests
- Algae in ponds producing oxygen for aquatic life
- Crops like wheat, rice, and maize that humans rely on for food
- Phytoplankton in oceans that serve as the base of marine food chains
To explore more plant adaptations and diversity, visit adaptations in plants and tree leaves.
Photosynthesis Diagram
A well-labeled diagram can clarify the complex process of photosynthesis. Key elements shown include sunlight, chloroplasts, stomata for gas exchange, and pathways for water and carbon dioxide. These diagrams are often included in classroom biology diagrams and photosynthesis PPT presentations.
Reactants and Products in Photosynthesis
Reactants: Carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and sunlight are the starting materials.
Products: Glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2) are formed.
- Glucose serves as energy for plants and as food for animals and humans.
- Oxygen is released into the atmosphere, supporting life on Earth.
These details are essential for understanding climate effects, as explained in effects of climate changes.
Significance of Photosynthesis for Environment and Life
Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen and builds organic matter forming the base of the food chain. It mitigates carbon dioxide, reducing greenhouse gases. Without this process, there would be no food for herbivores or humans, and oxygen levels would drop. This topic is linked with environmental issues and food and health.
Key Facts about Photosynthesis
- Occurs primarily in leaves but also in some stems.
- Supports all heterotrophic life, including humans.
- Can happen under artificial light in greenhouses.
- Certain bacteria perform photosynthesis without producing oxygen.
For high-yield crops and food security, modern agriculture relies on maximizing photosynthetic efficiency.
Real-World Applications and Connections
Understanding photosynthesis helps in improving crop yields, addressing climate change, and designing renewable energy solutions (like artificial photosynthesis and solar panels). This knowledge underlies biotechnology, nature conservation, and research into the effects of environmental stress on plants. In medicine, oxygen produced is vital for survival treatments.
Learn further about food science, life science, and biological science at Vedantu.
Page Summary
Photosynthesis is the cornerstone of life, providing food and oxygen for all living beings. Its detailed stages, reactants, and significance connect biology with agriculture, medicine, and environmental sustainability. Understanding this topic helps us better appreciate nature and solve global challenges using science, as explored deeply in Vedantu’s learning resources.


FAQs on Photosynthesis explained for students
1. What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the biological process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Key points include:
- Occurs mainly in the chloroplasts of plant cells
- Uses chlorophyll to absorb light energy
- Main equation: 6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
- Essential for providing food and oxygen to life on Earth
2. What are the steps of photosynthesis?
The process of photosynthesis involves two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions).
Steps include:
- Light-dependent reactions: Occur in the thylakoid membranes; convert light energy into chemical energy (ATP, NADPH), and release oxygen.
- Calvin cycle: Takes place in the stroma of chloroplasts; uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO₂ into glucose.
3. Where does photosynthesis occur in a plant cell?
Photosynthesis occurs primarily in the chloroplasts of plant leaf cells.
Important details:
- Chloroplasts contain the green pigment chlorophyll
- Mainly found in the mesophyll cells of leaves
- Site for both light-dependent and light-independent reactions
4. What is the importance of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is crucial for sustaining life as it provides energy and oxygen for all living organisms.
Main points:
- Produces glucose, the primary source of energy for living beings
- Releases oxygen (O₂) essential for respiration
- Maintains atmospheric CO₂ and O₂ balance
5. What are the raw materials for photosynthesis?
The raw materials required for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide (CO₂), water (H₂O), and sunlight.
Details include:
- CO₂ from the atmosphere
- H₂O from the soil through roots
- Light energy from the sun
- Chlorophyll acts as the catalyst
6. Write the chemical equation for photosynthesis.
The balanced chemical equation for photosynthesis is:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
- Carbon dioxide plus water produces glucose and oxygen
- Occurs in the presence of chlorophyll and sunlight
7. What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Several factors influence the rate of photosynthesis in plants.
Main factors:
- Light intensity: More light increases the rate to a certain point
- Carbon dioxide concentration: Higher CO₂ increases the rate up to saturation
- Temperature: Optimum temperature enhances enzyme activity
- Water availability
- Chlorophyll content in the leaves
8. What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll is the green pigment that absorbs sunlight and enables photosynthesis to take place.
Functions include:
- Captures light energy for chemical reactions
- Transfers energy to convert CO₂ and H₂O into glucose
- Gives green colour to plant leaves
9. What is the end product of photosynthesis?
The main end products of photosynthesis are glucose (a simple sugar) and oxygen gas (O₂).
Details:
- Glucose is used for energy and growth
- Oxygen is released into the air and used for respiration by living organisms
10. Why do leaves appear green?
Leaves appear green due to the presence of chlorophyll, which absorbs all wavelengths of visible light except green, which is reflected.
Points to note:
- Chlorophyll absorbs red and blue light efficiently
- Reflects green light, making leaves look green
11. What is the difference between photosynthesis and respiration?
Photosynthesis and respiration are opposite processes in plants and animals.
Main differences:
- Photosynthesis: Occurs in plants, uses CO₂ and H₂O to produce glucose and O₂ with the help of sunlight
- Respiration: Occurs in all living cells, uses glucose and O₂ to release energy, CO₂ and H₂O
12. Name the two stages of photosynthesis.
The two stages of photosynthesis are:
- Light-dependent reactions (occur in thylakoid membranes, produce ATP, NADPH, and O₂)
- Light-independent reactions/Calvin cycle (occur in stroma, use ATP and NADPH to form glucose)










