Step-by-Step Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles: FREE PDF Download
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles - 2025-26



FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles - 2025-26
1. What topics are covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles NCERT Solutions?
Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles NCERT Solutions cover topics such as properties of tangents, theorems related to radii and tangents, and angle properties in circles.
2. What kind of circle theorems are explained in Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles NCERT Solutions?
Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles NCERT Solutions explain theorems related to tangents to a circle, equal tangents from an external point, and the angle between radius and tangent.
3. Are the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles easy to understand?
Yes, the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles are written in a clear and student-friendly manner to help learners understand circle concepts easily.
4. Where can I get NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles question answers?
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles question answers are available on Vedantu with step-by-step explanations for all textbook problems.
5. Do the Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles NCERT Solutions include all questions from the textbook?
Yes, the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles include answers to every exercise question from the NCERT textbook.
6. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles help with exam preparation?
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles help students learn the correct methods required to solve circle-based questions commonly asked in exams.
7. Why should students practise Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles NCERT Solutions?
Practising Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles NCERT Solutions strengthens understanding of geometric concepts and improves accuracy in problem-solving.
8. Are the Class 10 Maths Circles NCERT question answers useful for competitive exams?
Yes, the Class 10 Maths Circles NCERT question answers help build strong geometry fundamentals that are useful for competitive and entrance exams as well.
9. How should students revise Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles using NCERT Solutions?
Students should first attempt questions from Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles and then compare their solutions with the NCERT Solutions to identify mistakes.
10. Can I download the Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles NCERT Solutions PDF?
Yes, students can download the Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles NCERT Solutions PDF from Vedantu for offline study and quick revision.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video





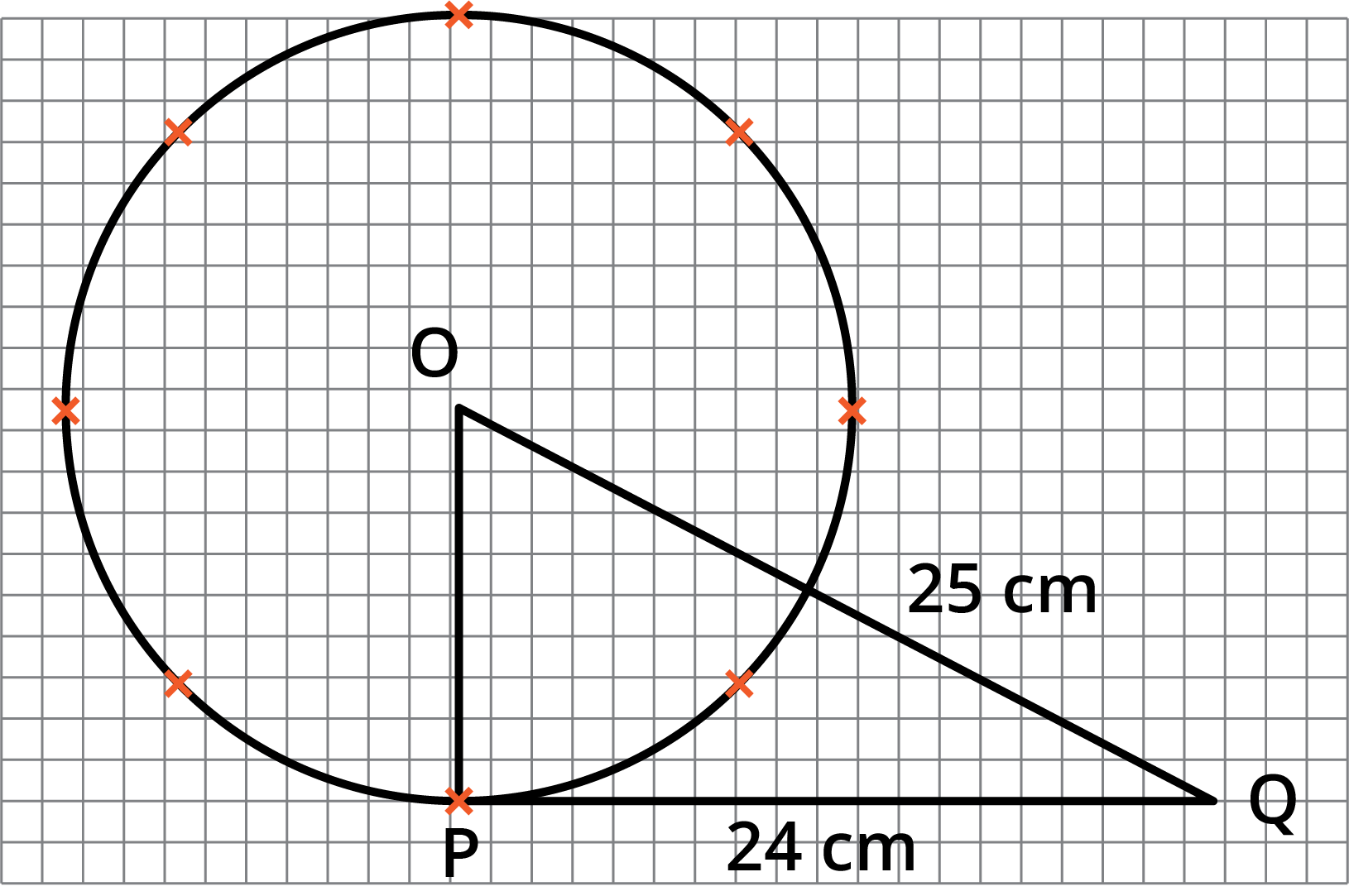
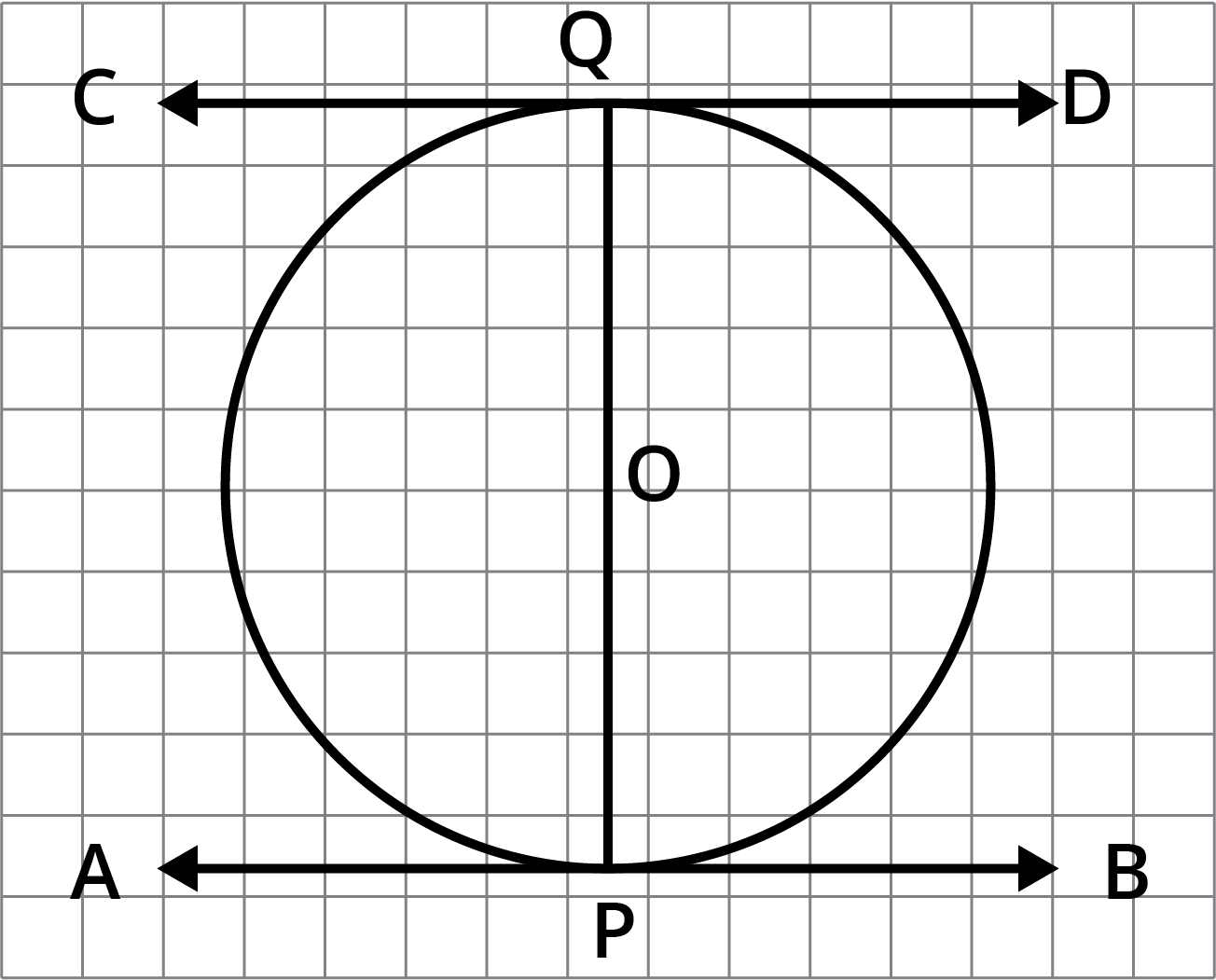

![The length of a tangent from a point \[A\] at distance \[5\ \text{cm}\] from the centre of the circle is \[4\ \text{cm}\].](https://www.vedantu.com/seo/content-images/eb745167-72ab-43c5-afd0-b50d06bbb585.png)
![Two concentric circles are of radii \[5\ \text{cm}\] and \[3\ \text{cm}\]](https://www.vedantu.com/seo/content-images/4ae23b52-8e21-42f2-9dbd-61c1e56c4022.png)
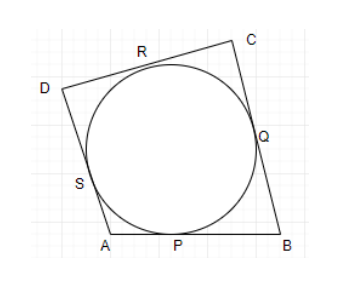
![\[XY\] and \[X'Y'\] are two parallel tangents to a circle with centre \[O\] and another tangent \[AB\] with point of contact \[C\] intersecting \[XY\] at \[A\] and \[X'Y'\] at \[B\]](https://www.vedantu.com/seo/content-images/d7c1ab06-ceb6-4ab7-bc2c-70e44f7d3ca9.png)
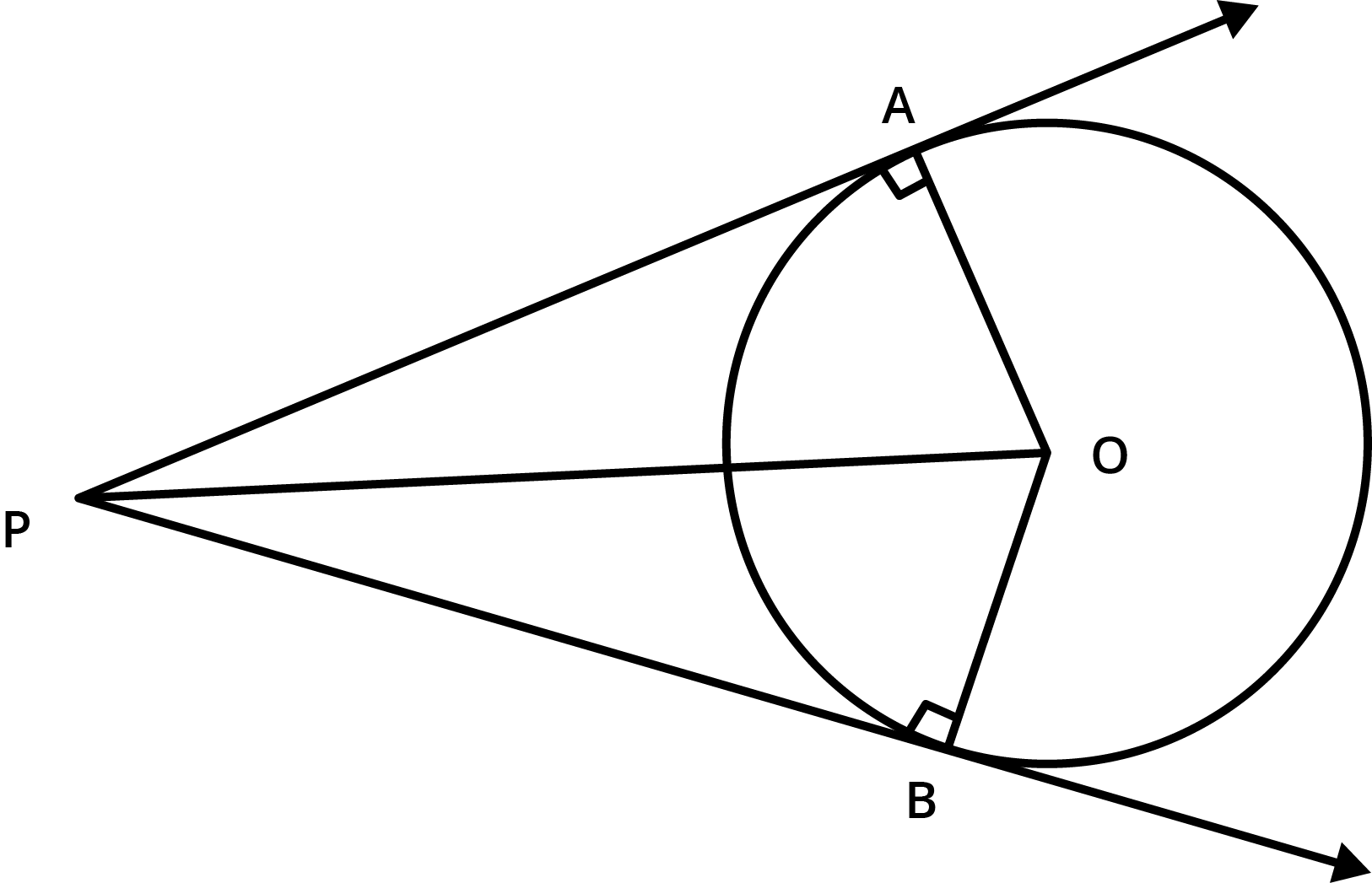
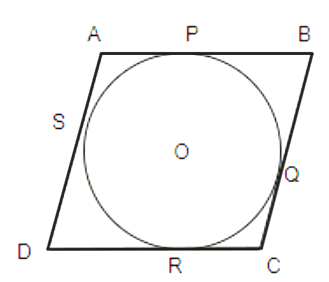
![A triangle \[ABC\] is drawn to circumscribe a circle of radius \[4\ \text{cm}\] such that the Segments \[BD\] and \[DC\] into which \[BC\] is divided by the point of contact \[D\] are of lengths \[8\ \text{cm}\] and \[6\ \text{cm}\] respectively](https://www.vedantu.com/seo/content-images/5ad089ce-f737-4b35-a21d-6c10294c57f1.png)