Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Summary Notes PDF Download
CBSE Notes Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 - Circles - 2025-26



FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 - Circles - 2025-26
1. What is the definition of a circle according to the Class 10 Maths syllabus?
A circle is defined as the collection of all points in a plane that are at a constant distance from a fixed point, called the centre. The constant distance is known as the radius as per the CBSE Class 10 Circles Revision Notes.
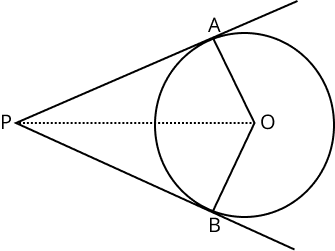
2. What are the key properties of tangents to a circle in Class 10 Circles Revision Notes?
The important properties of tangents in circles covered in Class 10 revision notes include:
- A tangent touches the circle at exactly one point.
- The tangent is always perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact.
- From a point outside the circle, exactly two tangents can be drawn, and their lengths are equal.
3. How does the number of tangents vary with the position of a point relative to the circle?
- No tangents can be drawn from a point inside the circle.
- Exactly one tangent can be drawn from a point on the circle.
- Exactly two tangents of equal length can be drawn from a point outside the circle.
4. What is the main theorem on tangents stated in Class 10 Circles Notes?
The key theorem from Class 10 Circles Revision Notes is: The tangent to a circle at any point is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact. This is fundamental for solving exam questions on circle tangents (CBSE 2025–26).
5. Why are the two tangents drawn from an external point to a circle always equal in length?
The lengths of two tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are always equal because the triangles formed (by joining the points of contact and the centre with the external point) are congruent by the RHS criterion. This property is proved using congruence in the chapter’s theorems and is key for reasoning questions in board exams.
6. Can a chord of a circle be a tangent? Why or why not?
No, a chord of a circle cannot be a tangent. A chord connects two points on the circle and passes through the interior, while a tangent touches the circle at only one point without entering the circle's interior. This conceptual distinction is important for MCQ and short-answer formats.
7. What are common misconceptions students have about tangents in Class 10 Circles?
Frequent misconceptions include:
- Assuming that the lengths of tangents from different external points to the circle are equal (they are only equal when from the same external point)
- Believing that tangents can be drawn from every point in the plane (not possible from interior points)
- Confusing chords and tangents due to their line-like appearance
8. Give the differences between a secant and a tangent as per Class 10 Circles Notes.
- Secant: A line that intersects a circle at exactly two distinct points.
- Tangent: A line that touches a circle at exactly one point.
9. How do you prove that the radius at the point of contact is perpendicular to the tangent?
This is shown by demonstrating that the shortest distance from the centre of a circle to the tangent line is along the radius, and this shortest distance is perpendicular. Any other line from the centre to the tangent is longer than the radius, confirming that the radius and the tangent form a right angle at the point of contact.
10. Why is it important to learn all theorems related to tangents in Class 10 Circles Revision Notes?
These theorems form the backbone of both direct and application-based questions in CBSE board exams. A clear understanding allows students to solve unseen problems, prove properties, and tackle HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills) questions efficiently, as per CBSE 2025–26 requirements.
11. What key terms should be memorized from Class 10 Circles for efficient revision?
The most important terms are: circle, centre, radius, diameter, chord, secant, tangent, point of contact, perpendicular. Knowing these helps students write precise answers during exams.
12. How are revision notes useful for quick exam preparation of Class 10 Chapter 10 Circles?
Revision notes for Class 10 Circles offer:
- Short summaries of concepts
- Key theorems with proofs
- Quick reference of formulas and properties
- Definition highlights for one-mark questions
13. What is the relation between diameter and chord in the context of Class 10 Circles?
The diameter is the longest chord of a circle, passing through the centre. Every diameter is a chord, but not every chord is a diameter. Understanding this is frequently tested in objective-type questions.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video