An Overview of Ncert Solutions Class 5 Evs Chapter 5
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 5 EVS Chapter 5 Seeds And Seeds (2025-26)
1. Where can I find reliable, step-by-step NCERT Solutions for all questions in Class 5 Science Chapter 5, 'Seeds and Seeds'?
You can find comprehensive and accurate NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Science Chapter 5, 'Seeds and Seeds,' updated for the 2025-26 academic year. These solutions provide step-by-step answers to every question in the textbook, ensuring you understand the correct methodology as per the CBSE pattern.
2. How do the NCERT Solutions explain the experiment for seed sprouting using three bowls?
The NCERT Solutions explain the experiment by detailing the conditions in each of the three bowls to find the correct answer:
- Bowl 1: Seeds with only water (no air).
- Bowl 2: Seeds in a damp cloth (both air and water).
- Bowl 3: Seeds with only air (no water).
The solutions clarify that seeds only sprout in Bowl 2, demonstrating that both air and water are essential for germination.
3. What are the different ways seeds are spread, according to the solutions for Chapter 5?
The NCERT solutions for 'Seeds and Seeds' explain that seeds are spread or dispersed in several ways to find new places to grow. The primary methods covered are:
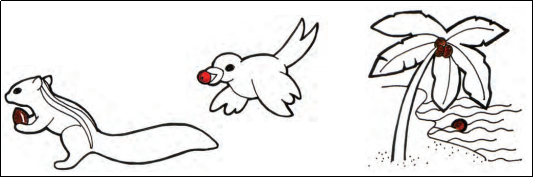
- By Wind: Light seeds, like those of dandelions, are carried by the wind.
- By Water: Seeds like coconuts can float and travel long distances via water.
- By Animals: Seeds get stuck to fur or are eaten and later excreted by animals and birds.
- By Bursting: Pods like peas and soybeans dry and burst open, flinging the seeds away.
4. What are the essential conditions for a seed to germinate, as explained in the NCERT textbook solutions?
The solutions for Class 5 EVS Chapter 5 clearly state that for a seed to germinate or sprout, it needs three essential things from its environment:
- Sufficient water
- Adequate air (oxygen)
- A suitable temperature (warmth)
Without all three conditions, a seed will not be able to grow into a new plant.
5. Why is it important to follow the step-by-step method provided in the NCERT solutions for the seed germination activity?
Following the step-by-step method is crucial for understanding the scientific process and arriving at the correct conclusion for your exams. The method ensures that only one condition (like the presence of air or water) is changed at a time, which is the correct way to conduct a fair test. This helps to prove definitively that both air and water are necessary for germination, a key concept in this chapter.
6. The NCERT solutions explain what happens if a seed gets only water but no air. What would be the observation if the seed got air but no water at all?
According to the principles in the NCERT solutions, a seed that gets plenty of air but remains completely dry will not sprout. It would remain dormant. The initial step of germination is the absorption of water, which activates the embryo inside and softens the seed coat. Without water, this critical process cannot begin, regardless of how much air is available.
7. How do the solutions for Chapter 5 help explain the difference between a seed and a spice like cumin (jeera)?
The NCERT solutions guide students to understand this through observation. While both come from plants, a seed's primary biological purpose is to grow into a new plant (e.g., a bean or mustard seed). A spice like cumin is technically the dried fruit or seed of a plant, but in a culinary context, it's primarily used for flavour. The solutions help clarify that many items we use as spices, like cumin and mustard, are also biologically seeds that can grow under the right conditions.
8. The chapter discusses seeds that fly and seeds that came from other countries. How do the NCERT Solutions connect these two different ideas?
The NCERT solutions connect these concepts through the central theme of seed dispersal. 'Flying seeds' are an example of natural dispersal by wind. Seeds arriving from other countries, like tomatoes or chillies brought by traders, are an example of dispersal by humans. Both concepts, as explained in the solutions, illustrate the different ways seeds travel far from their parent plant to grow in new places, ensuring the spread of the plant species.