Physics Notes for Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance Class 12 - FREE PDF Download



FAQs on Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance Class 12 Physics Chapter 2 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the core topics covered in the summary of Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Class 12 notes?
These revision notes provide a comprehensive summary of key concepts from Chapter 2, including: electrostatic potential and potential difference, potential due to a point charge, dipole, and system of charges, equipotential surfaces, the relationship between field and potential, dielectrics and polarisation, and the principle of capacitors and capacitance, including combinations and energy storage.
2. How can these revision notes help me prepare effectively for the CBSE Class 12 Physics exam (2025-26)?
These notes are designed for quick and effective revision. They help by:
- Summarising all major concepts in one place for easy review.
- Highlighting the most essential formulas you need to memorise.
- Explaining complex topics like polarisation and electrostatic shielding in simple terms.
- Providing a structured flow that helps connect different concepts within the chapter.
3. What are the most important formulas for quick revision from Chapter 2, Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance?
For quick revision, focus on these key formulas:
- Electric Potential: V = W/q
- Potential due to a Point Charge: V = kq/r
- Capacitance: C = Q/V
- Parallel Plate Capacitor: C = ε₀A/d
- Energy Stored in a Capacitor: U = ½ CV²
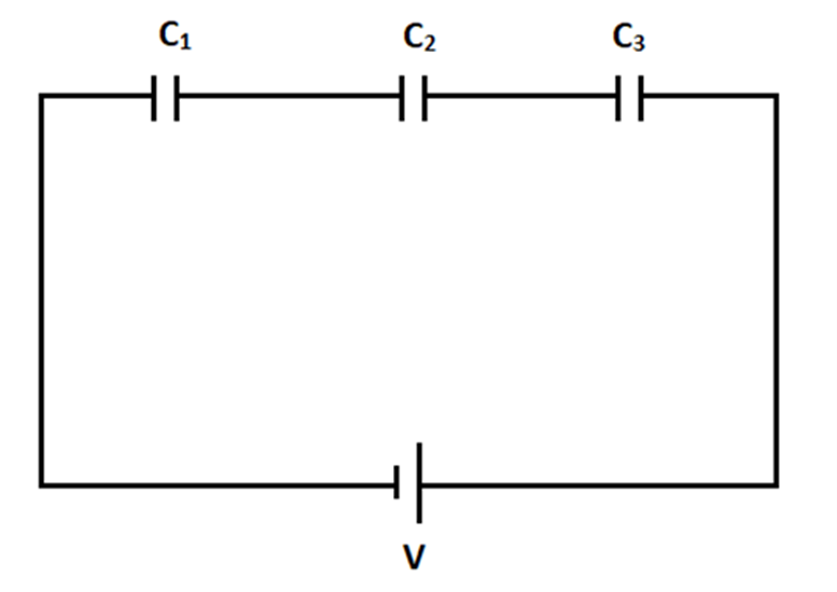
- Capacitors in Series: 1/C_eq = 1/C₁ + 1/C₂ + ...
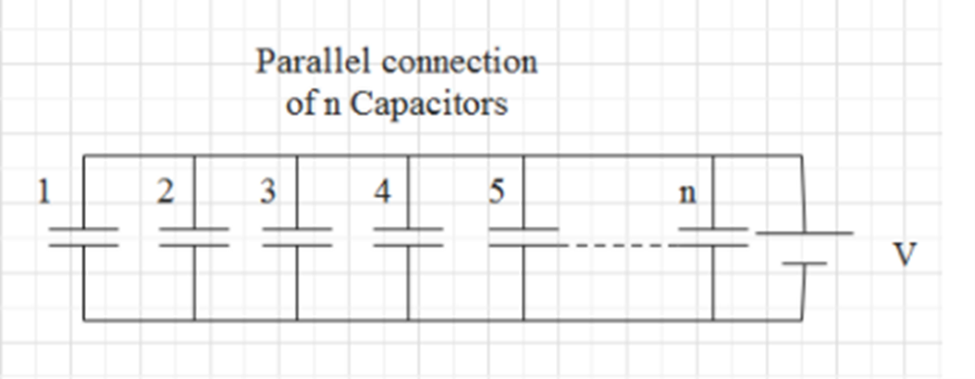
- Capacitors in Parallel: C_eq = C₁ + C₂ + ...
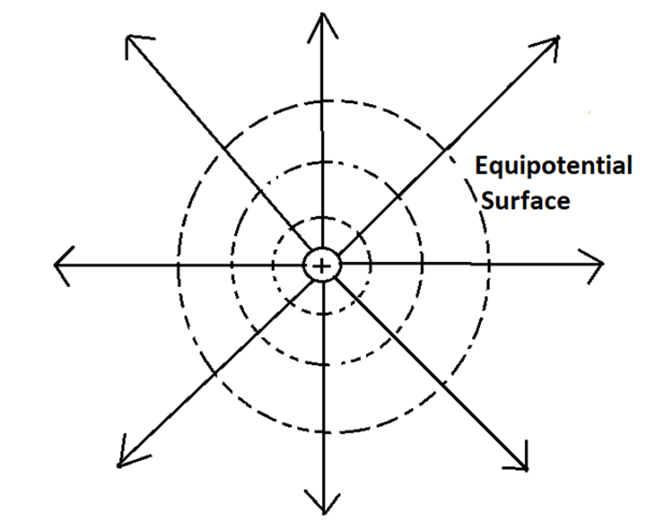
4. How do the concepts of potential and equipotential surfaces in these notes connect to the electric field from the previous chapter?
The connection is fundamental for a complete understanding. The electric field is the negative gradient of the potential (E = -dV/dr), meaning the field points in the direction of the steepest decrease in potential. Consequently, equipotential surfaces, where the potential is constant, are always perpendicular to the electric field lines. Revising this link helps solve a wide range of conceptual problems.
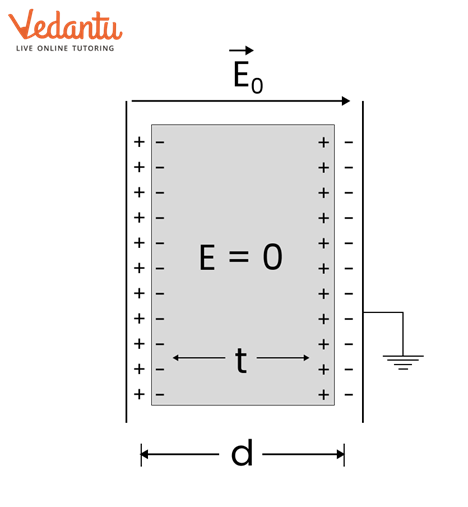
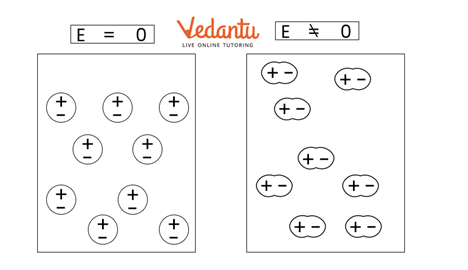
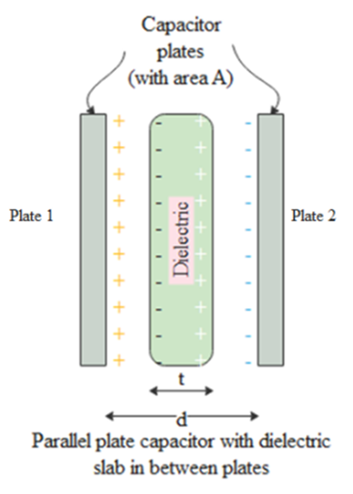
5. Why is it essential to understand dielectrics and polarisation when revising the topic of capacitance?
Understanding dielectrics is crucial because they are used to increase the capacitance of a capacitor. When a dielectric is placed in an external electric field, it gets polarised. This creates an internal electric field that opposes the external one, reducing the net electric field and the potential difference between the plates. Since C = Q/V, a lower potential difference for the same charge results in a higher capacitance.
6. What is the key distinction between the potential energy of a single charge and a dipole in an external field, as explained in these notes?
The key distinction lies in their dependency. The potential energy of a single charge 'q' in an external field depends only on its position (U = qV). However, the potential energy of a dipole depends not just on its position but also on its orientation relative to the electric field. Its formula, U = -pE cosθ, shows that energy is minimum when the dipole is aligned with the field (θ=0°).
7. Do these revision notes cover the important derivations for electrostatic potential and capacitance as per the latest CBSE syllabus?
These notes focus on summarising the final results and core concepts for quick revision. While they explain the logic behind formulas, for detailed, step-by-step derivations like the potential due to a dipole or the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor, you should refer to the NCERT solutions and detailed topic explanations as per the 2025-26 syllabus.
8. When revising combinations of capacitors, what's a helpful way to remember the formulas for series and parallel arrangements?
A simple trick is to remember that capacitor formulas are the opposite of resistor formulas from current electricity. For capacitors in parallel, you simply add their capacitances (C_eq = C₁ + C₂), similar to resistors in series. For capacitors in series, you add their reciprocals (1/C_eq = 1/C₁ + 1/C₂), similar to resistors in parallel.
9. How do these notes explain the practical application of capacitors, such as in energy storage?
The notes explain that a capacitor's primary function is to store electrical energy in the electric field between its plates. This stored energy, given by U = ½ CV², can be released very quickly. This principle is used in devices like camera flashes, power supply filters to smooth out voltage, and timing circuits.
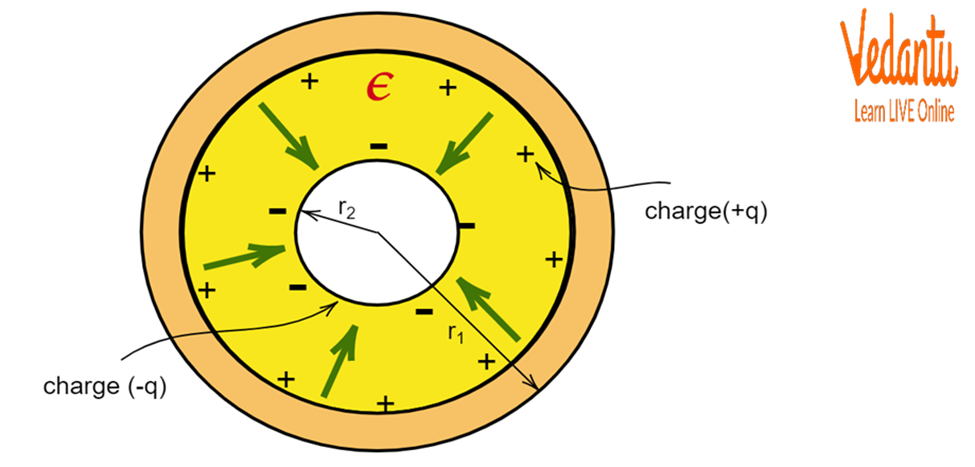
10. What is the concept of electrostatic shielding, and why is it an important revision topic?
Electrostatic shielding is the phenomenon where the electric field inside a hollow conductor is zero, regardless of the external field. This is because free charges on the conductor's surface rearrange themselves to cancel any external field. It's a key revision topic as it explains why sensitive electronic equipment is enclosed in metal cases and is a practical application of the properties of conductors in electrostatics.