Vedantu's Diversity In The Living World Class 6 PDF Solutions for Exam Preparation
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 2 Diversity In The Living World (2025-26)
1. What are the key concepts explained in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 2: Diversity in the Living World?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 2 cover grouping of plants and animals, types of roots (taproot and fibrous), leaf venation (reticulate and parallel), classification into herbs, shrubs, and trees, features of dicots and monocots, and adaptation of living organisms. These solutions are designed as per CBSE 2025–26 pattern to help students understand biological diversity and its importance.
2. How does the NCERT Solution explain the difference between taproot and fibrous root systems in Class 6 Science Chapter 2?
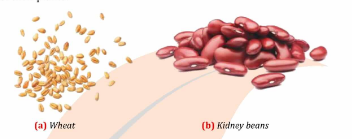
Taproot system: One main thick root grows deep into the soil, with smaller lateral roots (example: mango, radish). Fibrous root system: A cluster of thin roots arises from the base of the stem, spreading in all directions and staying near the surface (example: wheat, grass).
3. Which types of leaf venation are described in Class 6 Science Chapter 2, and how do they relate to plant classification?
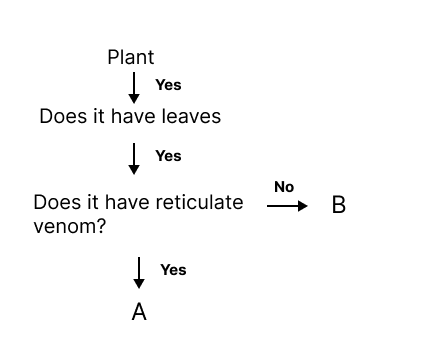
Two main types of leaf venation are explained: Reticulate venation (veins form a network, seen in dicot plants) and Parallel venation (veins run parallel, found in monocot plants). Understanding venation helps group plants and connect them with their root type, as per NCERT solutions Class 6 Science Chapter 2.
4. What are the main features used to group animals according to Class 6 Science Chapter 2 NCERT Solutions?
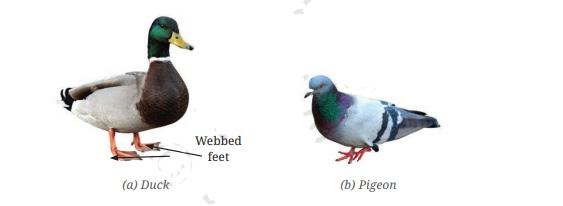
Animals are grouped based on habitat (aquatic, terrestrial, amphibious), mode of movement (flying, swimming, crawling), and body adaptations (webbed feet in ducks, streamlined bodies in fish). Grouping helps understand biodiversity and survival adaptations.
5. How does studying diversity in living organisms benefit students, according to NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 2?
Studying diversity:
- Builds appreciation for the natural world
- Develops observation and grouping skills
- Explains ecological balance and ecosystem roles
- Highlights why biodiversity is essential for stability and survival
6. What adaptations are explained in Chapter 2 to show how animals survive in different habitats?
NCERT Solutions describe adaptations like thick fur in mountain goats for cold climates, webbed feet in ducks for swimming, and streamlined bodies in aquatic animals for faster swimming. These adaptations help animals meet environmental challenges and thrive in their habitats.
7. In what ways do the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 2 clarify differences between herbs, shrubs, and trees?
Herbs: Short, soft stems (e.g., mint). Shrubs: Medium-height, woody stems, bushy, branches arise near ground (e.g., hibiscus). Trees: Tall, hard woody stems, branches higher up (e.g., mango). Understanding these differences is essential for plant classification as taught in the CBSE syllabus.
8. How does Chapter 2 relate root type and leaf venation with seed type for plant grouping?
As per the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 2, dicot plants have taproots and reticulate venation; monocots have fibrous roots and parallel venation. This correlation helps in identifying plants and understanding classification rules in botany.
9. Why is it important to conserve biodiversity, as emphasised in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 2?
Conserving biodiversity ensures:
- Stability of ecosystems
- Availability of food and shelter for all species
- Maintenance of natural cycles
- Protection against disturbances (e.g., climate change, habitat loss)
10. How does Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 2 help with exam preparation?
Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions offer stepwise answers, clarify conceptual doubts, cover all in-text and end-chapter questions, and present solutions according to the latest CBSE 2025–26 guidelines. This helps students in thorough understanding and improves performance in school exams.
11. What is the process adopted in NCERT Solutions to classify animals based on their habitats in Chapter 2?
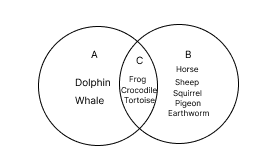
Animals are grouped as aquatic (live in water, e.g., whale, fish), terrestrial (live on land, e.g., cow, lion), and amphibians (live in both, e.g., frog). NCERT Solutions use clear examples and tabular classification for effective learning and exam readiness.
12. What are some high-level questions (FUQs) students should consider from Class 6 Science Chapter 2 for deeper understanding?
- Why is scientific grouping of plants and animals more reliable than grouping by appearance?
- How would the absence of adaptations affect survival in a particular habitat?
- What if an organism possesses both fibrous roots and reticulate venation—how would that challenge the classification system?
- How can deforestation impact both plant and animal diversity, according to this chapter?
13. What real-life examples are used in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 2 to clarify grouping and adaptations?
NCERT Solutions use examples like mountain goat vs. plains goat to explain adaptations, radish vs. wheat for taproot and fibrous root distinction, and duck’s webbed feet versus pigeon’s feet for movement in water versus land. These examples connect textbook concepts to observable real-world phenomena.
14. How does Class 6 Science Chapter 2 NCERT Solutions ensure student mistakes are addressed during revision?
The solutions highlight common errors like confusing root types with leaf venation, misclassifying plants due to ambiguous features, and missing links between adaptation and survival. Explanations stress following the correct classification criteria as per NCERT and CBSE standards.
15. What is the relationship between diversity in the living world and ecosystem stability, according to the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 2?
Diversity in the living world increases an ecosystem’s ability to resist disruptions and recover from changes. High biodiversity ensures that ecological processes (nutrient cycling, pollination, food webs) continue smoothly, maintaining environmental balance as outlined in CBSE Science 2025–26 syllabus.