Science Class 6 Chapter 4 Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Exploring Magnets (2025-26)
1. What are the basic properties of magnets covered in exploring magnets class 6?
Magnets have two poles (north and south), attract magnetic materials like iron and steel, repel like poles, and attract unlike poles. They retain their magnetic properties and can create magnetic fields around them.
2. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 4 help students understand magnetic properties?
NCERT Solutions provide step-by-step explanations for all textbook questions, making magnetic concepts clear through practical examples and simple language.
These solutions break down complex magnetic interactions into simple observations, explain pole behavior through everyday examples, and provide reasoning for each magnetic property with visual descriptions.
3. What methods can students use to make magnets at home?
Students can make magnets by stroking iron objects with a permanent magnet in one direction multiple times, or by using electrical methods under adult supervision. Common materials include iron nails, needles, and paper clips.
4. Where can students access exploring magnets class 6 solutions in PDF format?
Students can download exploring magnets class 6 solutions as Free PDF from Vedantu's website, providing complete access to all chapter solutions offline.
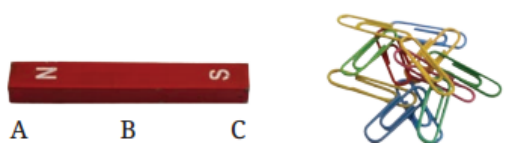
5. Why do some materials get attracted to magnets while others do not?
Materials containing iron, nickel, or cobalt are magnetic and get attracted to magnets. Non-magnetic materials like wood, plastic, and glass do not contain these elements, so magnets cannot attract them.
6. What types of questions are included in exploring magnets class 6 worksheet with answers?
Worksheets typically include multiple choice questions, fill-in-the-blanks, short answer questions about magnetic properties, and practical observation-based problems.
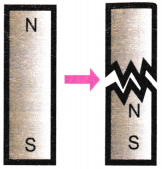
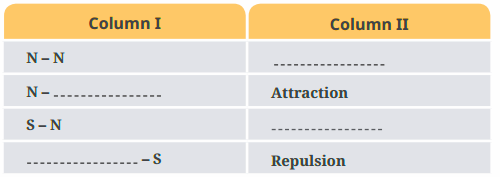
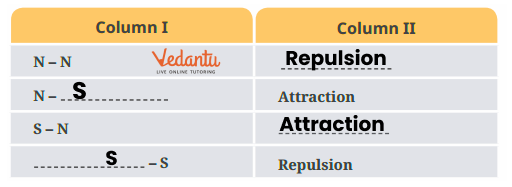
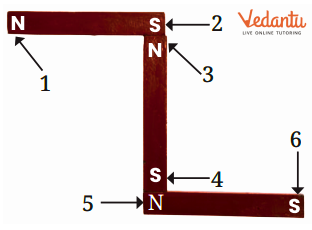
7. How do magnetic poles behave when brought close to each other?
Like poles (north-north or south-south) repel each other and push away, while unlike poles (north-south) attract each other and come together. This behavior is consistent for all magnets regardless of their size or shape.
8. What practical applications of magnets are discussed in the NCERT textbook?
The NCERT textbook covers everyday uses like refrigerator doors, compass needles for navigation, magnetic toys, and separating iron from mixtures.
9. How can students test if an object is magnetic or not?
Students can bring a magnet close to the object without touching it. If the object moves toward the magnet or gets attracted, it is magnetic. If nothing happens, the object is non-magnetic.
10. What safety precautions should students follow while handling magnets during experiments?
Students should keep magnets away from electronic devices, avoid dropping them on hard surfaces, handle with clean hands, and store them properly with keepers.
Following these precautions ensures safe experimentation and maintains magnet effectiveness for repeated use.