How Can To Find Nature's Treasures Class 6 Questions And Answers Help In Better Exam Preparation?
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Nature'S Treasures - 2025-26
1. What are the main topics covered in the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Nature's Treasures?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Nature's Treasures cover the identification of natural resources, their classification as renewable and non-renewable, the importance of conserving resources, human impact on nature, traditional conservation methods, and practical application-based questions as per the latest CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
2. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 help students understand the difference between renewable and non-renewable resources?
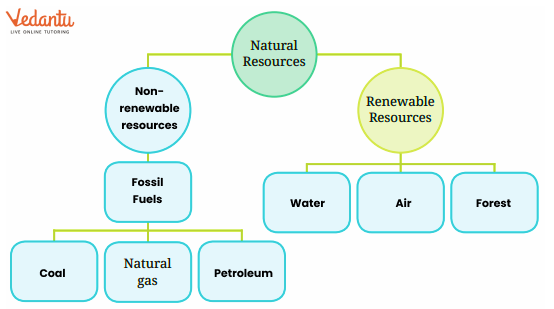
These solutions explain renewable resources (like water and forests, which can be replenished naturally) and non-renewable resources (like coal and petroleum, which are limited and take millions of years to form). Stepwise answers clarify classification with practical examples and CBSE-specific definitions, strengthening student understanding.
3. Which types of questions in Chapter 11 NCERT Solutions require step-by-step reasoning as per the CBSE exam pattern?
Questions that ask students to classify resources, justify statements (True/False), and analyse the impact of human actions (e.g., why petroleum is non-renewable, or why regrowing forests is difficult) are solved using clear, stepwise reasoning, mirroring CBSE's mark-scoring approach.
4. How can practising NCERT Solutions for Chapter 11 Nature's Treasures improve a student's performance in science exams?
Practising these solutions helps students master key concepts, answer formulation, and time management—all of which align with the CBSE 2025–26 marking scheme. The solutions reinforce conceptual understanding, support revision, and build confidence for both objective and subjective questions.
5. Why is it important to classify resources as renewable or non-renewable in the context of Class 6 Science Chapter 11?
Classification helps students understand resource sustainability and environmental impact. It highlights the need for conservation by showing which resources can be replenished (renewable) and which are at risk of depletion (non-renewable), aligning with CBSE's focus on environmental awareness.
6. What are some high-utility CBSE-style questions included in the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 11?
Frequently asked utility questions include:
- Classifying resources with examples
- Explaining consequences of deforestation
- Proposing ways to reduce resource usage in daily life
- Discussing effects of air pollution and possible solutions
- Exploring India's traditional rainwater harvesting methods
7. How do NCERT Solutions for Chapter 11 Nature's Treasures clarify common misconceptions among students?
The solutions address misconceptions such as thinking machines are natural resources, or assuming all natural resources are abundantly available. Clarifications and correct explanations are provided for CBSE-style True/False and fill-in-the-blank questions.
8. In what ways do the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 encourage environmental conservation and responsible resource use?
Solutions integrate CBSE-recommended actions like reducing, reusing, and recycling resources, promoting afforestation, and advocating for water and air conservation. Example-based answers guide students to apply learning in real-life contexts at school and home.
9. What role do the NCERT Solutions play in building a strong science foundation for Class 6 students according to the CBSE syllabus?
By breaking down complex concepts from Chapter 11 into simple, clear steps, these solutions help students develop analytical and critical thinking skills, which are essential for advanced science topics in higher classes.
10. Are the NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 11 sufficient for CBSE exam preparation, or is additional study material recommended?
The NCERT Solutions provide comprehensive, CBSE-aligned answers to all textbook problems, making them highly effective for exam prep. For complete mastery, students should also solve sample papers and revision notes for Class 6 Science as per the 2025–26 syllabus.
11. How do the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 11 handle application-based and higher order thinking questions (HOTS)?
Application-based questions require students to propose environmental plans, justify conservation strategies, and analyse cause-effect relationships (such as the impact of no sunlight on solar panels). Solutions model structured, CBSE-approved HOTS answers.
12. What strategies are suggested in the NCERT Solutions to reduce water and air pollution as per CBSE recommendations?
Key strategies include:
- Using water-saving devices and repairing leaks
- Educating communities about pollution
- Promoting renewable energy and carpooling
- Afforestation and adopting traditional rainwater harvesting methods
13. How are traditional Indian methods of conservation integrated into the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11?
Traditional methods like kunds, johads, zings, and ahar-pyne are explained within solutions to highlight indigenous practices of rainwater harvesting and resource management, as per the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus guidelines.
14. Can using NCERT Solutions for Chapter 11 help students identify key minerals and their uses in daily life?
Yes, the solutions include identification and practical uses of minerals such as granite (construction), gypsum (plaster), and quartz (glass), ensuring students understand real-life applications relevant to both textbook and exam requirements.
15. What is the CBSE-recommended step-by-step approach for solving assertion-reason or justify-type questions in Chapter 11?
The recommended approach is:
- Restate the assertion or statement
- Provide a scientific justification or counter-example
- Support your answer with a CBSE-approved fact or definition
- Conclude with a summary sentence