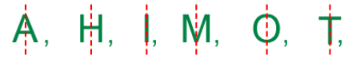Symmetry - Exercise-wise Questions and Answers For Class 6 Maths - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Maths Chapter 13 Symmetry - 2025-26
1. Where can I find reliable, step-by-step NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 13, Symmetry, for the 2025-26 session?
You can find accurate and easy-to-understand NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 13, designed by subject experts at Vedantu. These solutions strictly follow the CBSE 2025-26 syllabus and provide a detailed, step-by-step methodology for solving every question in the NCERT textbook. They are available for free online and can also be downloaded as a PDF for offline study.
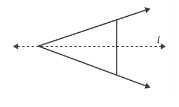
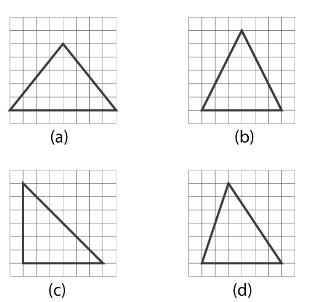
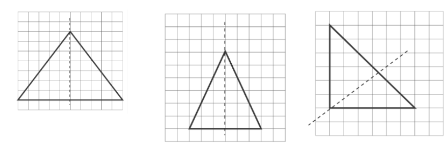
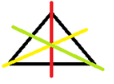
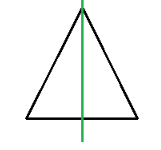
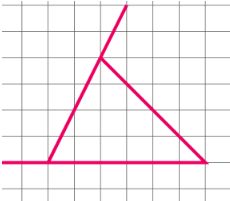
2. What is the correct method to find the line of symmetry in an isosceles triangle as per NCERT Class 6 Maths Chapter 13?
An isosceles triangle has only one line of symmetry. The correct method to find it is to draw a line segment from the vertex that is between the two equal sides to the midpoint of the opposite (unequal) side. This line, which is also the altitude, will divide the triangle into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other.
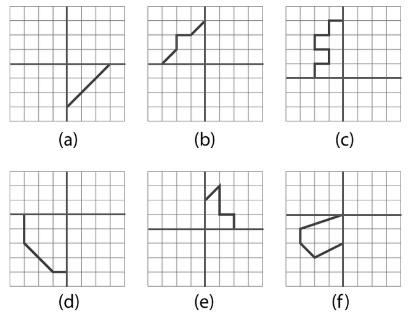
3. How do you solve questions from Exercise 13.2 that require completing a figure with a given line of symmetry?
To solve these problems, follow this step-by-step process:
Treat the given line of symmetry as a mirror line.
Imagine placing a mirror on this line. The reflection of the given half of the figure is the part you need to draw.
For each point or vertex on the given drawing, mark a corresponding point on the other side of the line, ensuring it is at the same perpendicular distance from the line of symmetry.
Connect these new points to complete the symmetrical shape.
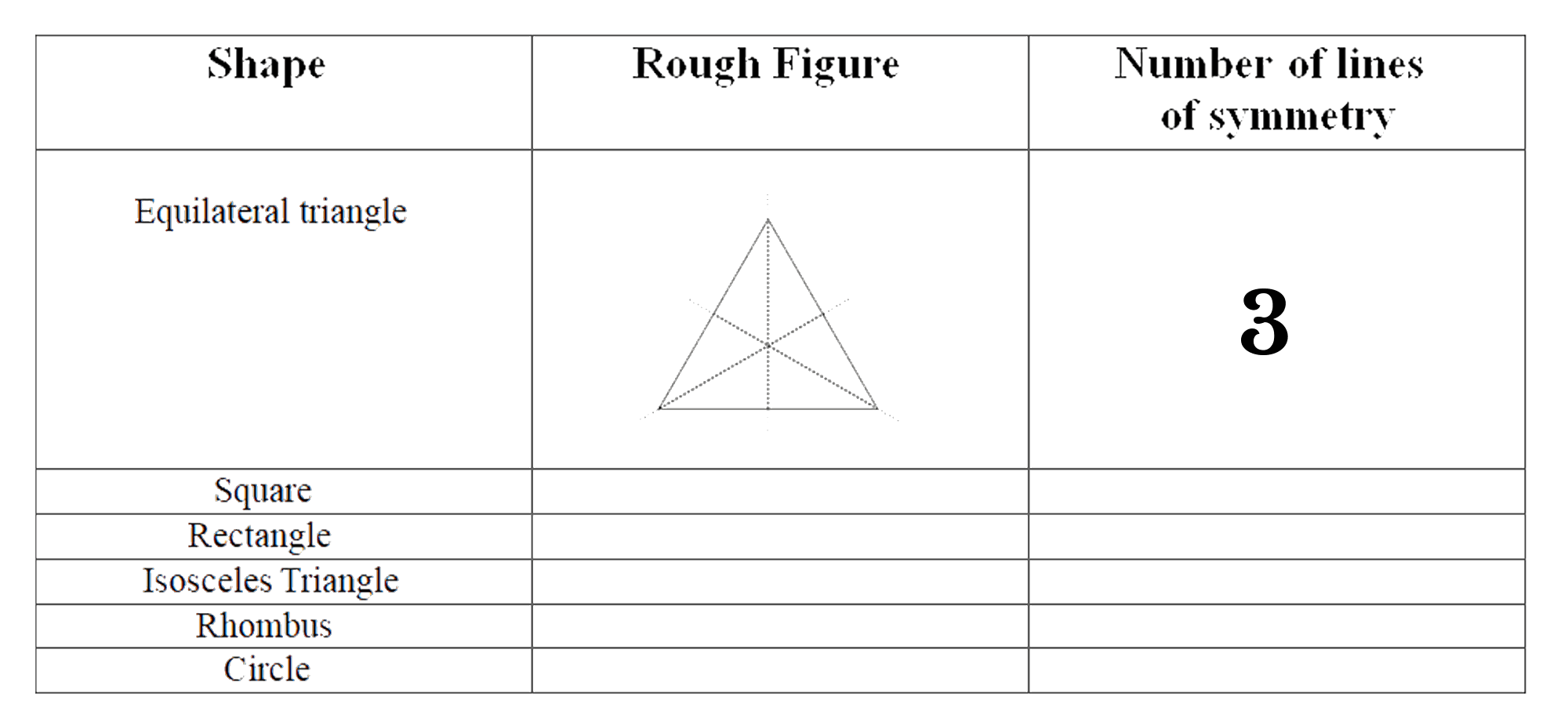
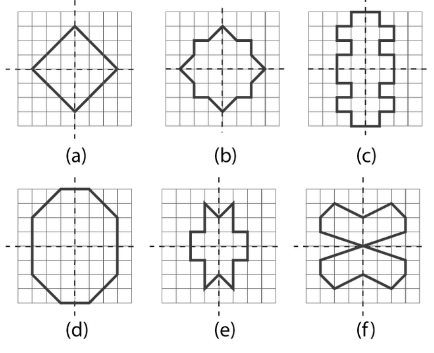
4. Why does a rectangle have only two lines of symmetry while a square has four? What's the key difference in solving for them?
The key difference lies in their properties. A rectangle has equal opposite sides, so it is symmetrical only along the lines joining the midpoints of its opposite sides (one horizontal, one vertical). Its diagonals are not lines of symmetry. A square has four equal sides and equal angles, making it symmetrical along the lines joining the midpoints of opposite sides AND along its two diagonals. Therefore, a square has four lines of symmetry. The solving approach differs because for a square, you must check its diagonals as well.
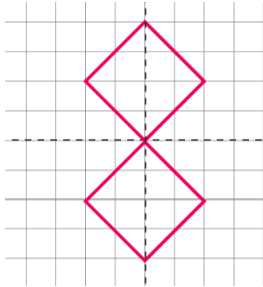
5. How does understanding the 'mirror line' concept in NCERT solutions help solve symmetry problems?
The 'mirror line' is a practical way to understand the line of symmetry. It establishes a fundamental rule: for a figure to be symmetrical, every point on one side must have a corresponding point on the other side at an equal perpendicular distance from the mirror line. This concept simplifies the process of completing shapes and verifying symmetry, as it transforms the abstract idea of symmetry into a concrete method of checking for a perfect reflection.
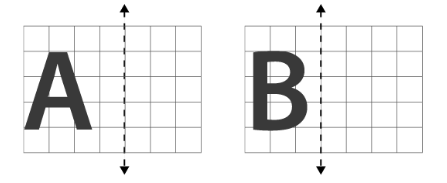
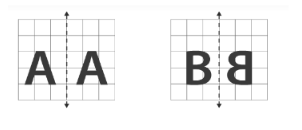
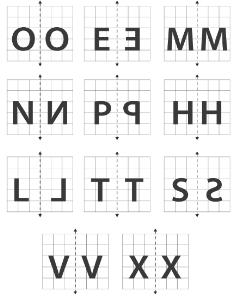
6. What is the correct method to identify lines of symmetry in English alphabet letters like 'H', 'S', and 'A' as per the NCERT textbook?
The method involves visualizing or drawing a line through the letter and checking if it divides the letter into two identical, overlapping halves. Using this method:
The letter 'H' has two lines of symmetry: one horizontal line across the middle and one vertical line down the centre.
The letter 'S' has no lines of symmetry because no single line can divide it into two identical halves that are mirror images.
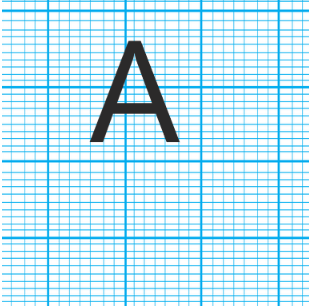
The letter 'A' has one vertical line of symmetry that runs through its apex down to the middle of the base.
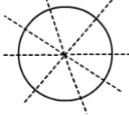
7. Can a circle have infinite lines of symmetry? How do the Class 6 NCERT solutions explain this concept?
Yes, a circle has an infinite number of lines of symmetry. The NCERT solutions explain this by defining a line of symmetry as a line along which a figure can be folded so that the two halves coincide exactly. For a circle, any line that passes through its centre (i.e., any diameter) acts as a line of symmetry. Since you can draw an infinite number of diameters through the centre of a circle, it has infinite lines of symmetry.
8. Why is the paper-folding activity suggested in the NCERT solutions a reliable way to verify symmetry?
The paper-folding method is reliable because it provides a direct, physical test of the definition of symmetry. It demonstrates that:
The fold line represents the potential line of symmetry.
If the two halves of the figure on either side of the fold coincide perfectly (match up exactly without any overlap), the fold line is confirmed as a true line of symmetry.
This activity reinforces the idea that symmetry is based on a perfect reflection or correspondence across a line.