
Download Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 NCERT Solutions PDF
Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields introduces the basic principles of electrostatics. This chapter explains electric charges, Coulomb’s law, electric field, electric field lines, and Gauss’s law. Many students find derivations and numerical problems difficult in this chapter. Our NCERT solutions for Physics Class 12 Chapter 1 provide clear and step by step explanations to help you understand every concept with confidence. The Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 NCERT solutions are fully aligned with the latest CBSE Class 12 Physics syllabus for the academic year 2025-26. Each question is solved in a structured format so you can learn the correct method of writing answers in exams. Whether you are revising theory or practising numericals, these solutions make preparation easier and more effective.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentYou can download the NCERT Solutions Physics Class 12 Chapter 1 PDF by clicking on the “Download PDF” button. Study regularly, practise all questions, and strengthen your foundation in electrostatics to score better in your exams.



Master Vedantu's Electric Charges And Fields Class 12 NCERT Solutions For Perfect Exam Preparation
$2\times {{10}^{-7}}C$ and $3\times {{10}^{-7}}C$ placed $30cm$ apart in air?
Ans: We are given the following information:
Repulsive force of magnitude,$F=6\times {{10}^{-3}}N$
Charge on the first sphere, ${{q}_{1}}=2\times {{10}^{-7}}C$
Charge on the second sphere, ${{q}_{2}}=3\times {{10}^{-7}}C$
Distance between the two spheres, $r=30cm=0.3m$
Electrostatic force between the two spheres is given by Coulomb’s law as,
$F=\frac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\frac{{{q}_{1}}{{q}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}$
Where, ${{\varepsilon }_{0}}$is the permittivity of free space and,
$\frac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}=9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}$
Now on substituting the given values, Coulomb’s law becomes,
\[F = \frac{9\times 10^{9}\times 2\times 10^{-7}\times 3\times 10^{-7}}{(0.3)^{2}}\]
Therefore, we found the electrostatic force between the given charged spheres to be $F=6\times {{10}^{-3}}N$. Since the charges are of the same nature, we could say that the force is repulsive.
2. The electrostatic force on a small sphere of charge $0.4\mu C$ due to another small sphere of charge $-0.8\mu C$ in air is 0.2N.
a) What is the distance between the two spheres?
Ans: Electrostatic force on the first sphere is given to be, $F=0.2N$
Charge of the first sphere is, ${{q}_{1}}=0.4\mu C=0.4\times {{10}^{-6}}C$
Charge of the second sphere is, ${{q}_{2}}=-0.8\mu C=-0.8\times {{10}^{-6}}C$
We have the electrostatic force given by Coulomb’s law as,
$F=\frac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\frac{{{q}_{1}}{{q}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow r=\sqrt{\frac{{{q}_{1}}{{q}_{2}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}F}}$
Substituting the given values in the above equation, we get,
$\Rightarrow r=\sqrt{\frac{0.4\times {{10}^{-6}}\times 8\times {{10}^{-6}}\times 9\times {{10}^{9}}}{0.2}}$
$\Rightarrow r=\sqrt{144\times {{10}^{-4}}}$
$\therefore r=0.12m$
Therefore, we found the distance between charged spheres to be $r=0.12m$.
b) What is the force on the second sphere due to the first?
Ans: From Newton’s third law of motion, we know that every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
Thus, we could say that the given two spheres would attract each other with the same force.
So, the force on the second sphere due to the first sphere will be $0.2N$.
3. Check whether the ratio $\frac{k{{e}^{2}}}{G{{m}_{e}}{{m}_{p}}}$is dimensionless. Look up a table of physical constants and hence determine the value of the given ratio. What does the ratio signify?
Ans: We are given the ratio, $\frac{k{{e}^{2}}}{G{{m}_{e}}{{m}_{p}}}$.
Here, G is the gravitational constant which has its unit $N{{m}^{2}}k{{g}^{-2}}$;
${{m}_{e}}$and ${{m}_{p}}$ are the masses of electron and proton in $kg$ respectively;
$e$ is the electric charge in $C$;
$k$ is a constant given by $k=\frac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
In the expression for k, ${{\varepsilon }_{0}}$ is the permittivity of free space which has its unit $N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}$.
Now, we could find the dimension of the given ratio by considering their units as follows:
$\frac{k{{e}^{2}}}{G{{m}_{e}}{{m}_{p}}}=\frac{\left[ N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}} \right]{{\left[ C \right]}^{2}}}{\left[ N{{m}^{2}}k{{g}^{-2}} \right]\left[ kg \right]\left[ kg \right]}={{M}^{0}}{{L}^{0}}{{T}^{0}}$
Clearly, it is understood that the given ratio is dimensionless.
Now, we know the values for the given physical quantities as,
$e=1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}C$
$G=6.67\times {{10}^{-11}}N{{m}^{2}}k{{g}^{-2}}$
${{m}_{e}}=9.1\times {{10}^{-31}}kg$
${{m}_{p}}=1.66\times {{10}^{-27}}kg$
Substituting these values into the required ratio, we get,
$\frac{k{{e}^{2}}}{G{{m}_{e}}{{m}_{p}}}=\frac{9\times {{10}^{9}}\times {{\left( 1.6\times {{10}^{-19}} \right)}^{2}}}{6.67\times {{10}^{-11}}\times 9.1\times {{10}^{-3}}\times 1.67\times {{10}^{-22}}}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{k{{e}^{2}}}{G{{m}_{e}}{{m}_{p}}}\approx 2.3\times {{10}^{39}}$
We could infer that the given ratio is the ratio of electrical force to the gravitational force between a proton and an electron when the distance between them is kept constant.
4.
a) Explain the meaning of the statements ‘electric charge of a body is quantized’.
Ans: The given statement ‘Electric charge of a body is quantized’ means that only the integral number $(1,2,3,...,n)$ of electrons can be transferred from one body to another.
That is, charges cannot be transferred from one body to another in fraction.
b) Why can one ignore quantization of electric charge when dealing with macroscopic i.e., large scale charges?
Ans: On a macroscopic scale or large-scale, the number of charges is as large as the magnitude of an electric charge.
So, quantization is considered insignificant at a macroscopic scale for an electric charge and electric charges are considered continuous.
5. When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth, charges appear on both. A similar phenomenon is observed with many other pairs of bodies. Explain how this observation is consistent with the law of conservation of charge.
Ans: Rubbing two objects would produce charges that are equal in magnitude and opposite in nature on the two bodies.
This happens due to the reason that charges are created in pairs. This phenomenon is called charging by friction.
The net charge of the system however remains zero as the opposite charges equal in magnitude annihilate each other.
So, rubbing a glass rod with a silk cloth creates opposite charges of equal magnitude on both of them and this observation is found to be consistent with the law of conservation of charge.
6. Four point charges ${{q}_{A}}=2\mu C$, ${{q}_{B}}=-5\mu C$, ${{q}_{C}}=2\mu C$and ${{q}_{D}}=-5\mu C$ are located at the corners of a square ABCD with side 10cm. What is the force on the $1\mu C$ charge placed at the centre of this square?
Ans: Consider the square of side length $10cm$ given below with four charges at its corners and let O be its centre.
From the figure we find the diagonals to be,
$AC=BD=10\sqrt{2}cm$
$\Rightarrow AO=OC=DO=OB=5\sqrt{2}cm$
Now the repulsive force at O due to charge at A,
${{F}_{AO}}=k\frac{{{q}_{A}}{{q}_{O}}}{O{{A}^{2}}}=k\frac{\left( +2\mu C \right)\left( 1\mu C \right)}{{{\left( 5\sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}}$…………………………………………… (1)
And the repulsive force at O due to charge at D,
${{F}_{DO}}=k\frac{{{q}_{D}}{{q}_{O}}}{O{{D}^{2}}}=k\frac{\left( +2\mu C \right)\left( 1\mu C \right)}{{{\left( 5\sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}}$………………………………………….. (2)
And the attractive force at O due to charge at B,
${{F}_{BO}}=k\frac{{{q}_{B}}{{q}_{O}}}{O{{B}^{2}}}=k\frac{\left( -5\mu C \right)\left( 1\mu C \right)}{{{\left( 5\sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}}$……………………………………………. (3)
And the attractive force at O due to charge at C,
${{F}_{CO}}=k\frac{{{q}_{C}}{{q}_{O}}}{O{{C}^{2}}}=k\frac{\left( -5\mu C \right)\left( 1\mu C \right)}{{{\left( 5\sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}}$……………………………………………… (4)
We find that (1) and (2) are of same magnitude but they act in the opposite direction and hence they cancel out each other.
Similarly, (3) and (4) are of the same magnitude but in the opposite direction and hence they cancel out each other too.
Hence, the net force on charge at centre O is found to be zero.
7.
a) An electrostatic field line is a continuous curve. That is, a field line cannot have sudden breaks. Why not?
Ans: An electrostatic field line is a continuous curve as the charge experiences a continuous force on being placed in an electric field.
As the charge doesn’t jump from one point to the other, field lines will not have sudden breaks.
b) Explain why two field lines never cross each other at any point?
Ans: If two field lines are seen to cross each other at a point, it would imply that the electric field intensity has two different directions at that point, as two different tangents (representing the direction of electric field intensity at that point) can be drawn at the point of intersection.
This is however impossible and thus, two field lines never cross each other.
8. Two point charges ${{q}_{A}}=3\mu C$and ${{q}_{B}}=-3\mu C$are located 20cm apart in vacuum.
a) What is the electric field at the midpoint O of the line AB joining the two charges?
Ans: The situation could be represented in the following figure. Let O be the midpoint of line AB.
We are given:
\[AB=20cm\]
\[AO=OB=10cm\]
Take E to be the electric field at point O, then,
The electric field at point O due to charge $+3\mu C$would be,
${{E}_{1}}=\frac{3\times {{10}^{-6}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{\left( AO \right)}^{2}}}=\frac{3\times {{10}^{-6}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{\left( 10\times {{10}^{-2}} \right)}^{2}}}N{{C}^{-1}}$along OB
The electric field at point O due to charge $-3\mu C$would be,
${{E}_{2}}=\left| \frac{3\times {{10}^{-6}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{\left( OB \right)}^{2}}} \right|=\frac{3\times {{10}^{-6}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{\left( 10\times {{10}^{-2}} \right)}^{2}}}N{{C}^{-1}}$along OB
The net electric field,
$\Rightarrow E={{E}_{1}}+{{E}_{2}}$
$\Rightarrow E=2\times \frac{9\times {{10}^{9}}\times 3\times {{10}^{-6}}}{{{\left( 10\times {{10}^{-2}} \right)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow E=5.4\times {{10}^{6}}N{{C}^{-1}}$
Therefore, the electric field at mid-point O is $E=5.4\times {{10}^{6}}N{{C}^{-1}}$ along OB.
b) If a negative test charge of magnitude $1.5\times {{10}^{-19}}C$ is placed at this point, what is the force experienced by the test charge?
Ans: We have a test charge of magnitude $1.5\times {{10}^{-9}}C$ placed at mid-point O and we found the electric field at this point to be $E=5.4\times {{10}^{6}}N{{C}^{-1}}$.
So, the force experienced by the test charge would be F,
$\Rightarrow F=qE$
$\Rightarrow F=1.5\times {{10}^{-9}}\times 5.4\times {{10}^{6}}$
$\Rightarrow F=8.1\times {{10}^{-3}}N$
This force will be directed along OA since like charges repel and unlike charges attract.
9. A system has two charges ${{q}_{A}}=2.5\times {{10}^{-7}}C$and ${{q}_{B}}=-2.5\times {{10}^{-7}}C$located at points $A:\left( 0,0,-15cm \right)$ and $B:\left( 0,0,+15cm \right)$ respectively. What are the total charge and electric dipole moment of the system?
Ans: The figure given below represents the system mentioned in the question:
The charge at point A, ${{q}_{A}}=2.5\times {{10}^{-7}}C$
The charge at point B, ${{q}_{B}}=-2.5\times {{10}^{-7}}C$
Then, the net charge would be, $q={{q}_{A}}+{{q}_{B}}=2.5\times {{10}^{-7}}C-2.5\times {{10}^{-7}}C=0$
The distance between two charges at A and B would be,
\[d=15+15=30cm\]
$d=0.3m$
The electric dipole moment of the system could be given by,
$P=\mathop{q}_{A}\times d=\mathop{q}_{B}\times d$
$\Rightarrow P=2.5\times {{10}^{-7}}\times 0.3$
$\therefore P=7.5\times {{10}^{-8}}Cm$ along the \[+z\]axis.
Therefore, the electric dipole moment of the system is found to be $7.5\times {{10}^{-8}}Cm$ and it is directed along the positive \[z\]-axis.
10. An electric dipole with dipole moment $4\times {{10}^{-9}}Cm$ is aligned at $30{}^\circ $ with direction of a uniform electric field of magnitude $5\times {{10}^{4}}N{{C}^{-1}}$. Calculate the magnitude of the torque acting on the dipole.
Ans: We are given the following:
Electric dipole moment, $\overrightarrow{p}=4\times {{10}^{-9}}Cm$
Angle made by $\overrightarrow{p}$ with uniform electric field, $\theta =30{}^\circ $
Electric field, $\overrightarrow{E}=5\times {{10}^{4}}N{{C}^{-1}}$
Torque acting on the dipole is given by
$\tau =pE\sin \theta $
Substituting the given values we get,
$\Rightarrow \tau =4\times {{10}^{-9}}\times 5\times {{10}^{4}}\times \sin 30{}^\circ $
$\Rightarrow \tau =20\times {{10}^{-5}}\times \frac{1}{2}$
$\therefore \tau ={{10}^{-4}}Nm$
Thus, the magnitude of the torque acting on the dipole is found to be ${{10}^{-4}}Nm$.
11. A polythene piece rubbed with wool is found to have a negative charge of $3\times {{10}^{-7}}C$
a) Estimate the number of electrons transferred (from which to which?)
Ans: When polythene is rubbed against wool, a certain number of electrons get transferred from wool to polythene.
As a result of which wool becomes positively charged on losing electrons and polythene becomes negatively charged on gaining them.
We are given:
Charge on the polythene piece, $q=-3\times {{10}^{-7}}C$
Charge of an electron, $e=-1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}C$
Let n be the number of electrons transferred from wool to polythene, then, from the property of quantization we have,
$q=ne$
$\Rightarrow n=\frac{q}{e}$
Now, on substituting the given values, we get,
$\Rightarrow n=\frac{-3\times {{10}^{-7}}}{-1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}}$
$\therefore n=1.87\times {{10}^{12}}$
Therefore, the number of electrons transferred from wool to polythene would be$1.87\times {{10}^{12}}$.
b) Is there a transfer of mass from wool to polythene?
Ans: Yes, during the transfer of electrons from wool to polythene, along with charge, mass is transferred too.
Let $m$ be the mass being transferred in the given case and ${{m}_{e}}$ be the mass of the electron, then,
$m={{m}_{e}}\times n$
$\Rightarrow m=9.1\times {{10}^{-31}}\times 1.85\times {{10}^{12}}$
$\therefore m=1.706\times {{10}^{-18}}kg$
Thus, we found that a negligible amount of mass does get transferred from wool to polythene.
12.
a) Two insulated charged copper spheres $A$ and $B$ have their centres separated by a distance of $50cm$. What is the mutual force of electrostatic repulsion if the charge on each is $6.5\times {{10}^{-7}}C$? The radii of A and B are negligible compared to the distance of separation.
Ans: We are given:
Charges on spheres $A$ and $B$ are equal,
${{q}_{A}}={{q}_{B}}=6.5\times {{10}^{-7}}C$
Distance between the centres of the spheres is given as,
$r=50cm=0.5m$
It is known that the force of repulsion between the two spheres would be given by Coulomb’s law as,
$F=\frac{{{q}_{A}}{{q}_{B}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{r}^{2}}}$
Where, ${{\varepsilon }_{o}}$ is the permittivity of the free space
Substituting the known values into the above expression, we get,
$F=\frac{9\times {{10}^{9}}\times {{(6.5\times {{10}^{-7}})}^{2}}}{{{(0.5)}^{2}}}=1.52\times {{10}^{-2}}N$
Thus, the mutual force of electrostatic repulsion between the two spheres is found to be$F=1.52\times {{10}^{-2}}N$.
b) What is the force of repulsion if each sphere is charged double the above amount, and the distance between them is halved?
Ans: It is told that the charges on both the spheres are doubled and the distance between the centres of the spheres is halved. That is,
${{q}_{A}}'={{q}_{B}}'=2\times 6.5\times {{10}^{-7}}=13\times {{10}^{-7}}C$
$r'=\frac{1}{2}(0.5)=0.25m$
Now, we could substitute these values in Coulomb’s law to get,
$F'=\frac{{{q}_{A}}'{{q}_{B}}'}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r{{'}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow F=\frac{9\times {{10}^{9}}\times {{(13\times {{10}^{-7}})}^{2}}}{{{(0.25)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow F=0.243N$
The new mutual force of electrostatic repulsion between the two spheres is found to be $0.243N$.
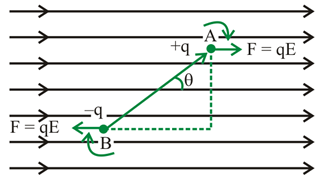
13. Figure below shows tracks taken by three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field. Give the signs of the three charges and also mention which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio?
Ans: From the known properties of charges, we know that the unlike charges attract and like charges repel each other.
So, the particles 1 and 2 that move towards the positively charged plate while repelling away from the negatively charged plate would be negatively charged and the particle 3 that moves towards the negatively charged plate while repelling away from the positively charged plate would be positively charged.
Now, we know that the charge to mass ratio (which is generally known as emf) is directly proportional to the displacement or the amount of deflection for a given velocity.
Since the deflection of particle 3 is found to be maximum among the three, it would have the highest charge to mass ratio.
14. Consider a uniform electric field $E=3\times {{10}^{3}}\hat{i}N/C$.
a) Find the flux of this field through a square of side $10cm$whose plane is parallel to the y-z plane.
Ans: We are given:
Electric field intensity, $\overrightarrow{E}=3\times {{10}^{3}}\hat{i}N/C$
Magnitude of electric field intensity, $\left| \overrightarrow{E} \right|=3\times {{10}^{3}}N/C$
Side of the square, $a=10cm=0.1m$
Area of the square, $A={{a}^{2}}=0.01{{m}^{2}}$
Since the plane of the square is parallel to the y-z plane, the normal to its plane would be directed in the x direction. So, angle between normal to the plane and the electric field would be, $\theta =0{}^\circ $
We know that the flux through a surface is given by the relation,
$\phi =\left| E \right|\left| A \right|\cos \theta $
Substituting the given values, we get,
$\Rightarrow \phi =3\times {{10}^{3}}\times 0.01\times \cos 0{}^\circ $
$\therefore \phi =30N{{m}^{2}}/C$
Thus, we found the net flux through the given surface to be $\phi =30N{{m}^{2}}/C$.
b) What would be the flux through the same square if the normal to its plane makes $60{}^\circ $ angle with the x-axis?
Ans: When the plane makes an angle of $60{}^\circ $ with the x-axis, the flux through the given surface would be,
$\phi =\left| E \right|\left| A \right|\cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow \phi =3\times {{10}^{3}}\times 0.01\times \cos 60{}^\circ $
$\Rightarrow \phi =30\times \frac{1}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \phi =15N{{m}^{2}}/C$
So, we found the flux in this case to be, $\phi =15N{{m}^{2}}/C$.
15. What is the net flux of the uniform electric field of exercise $1.15$ through a cube of side $20cm$ oriented so that its faces are parallel to the coordinate planes?
Ans: We are given that all the faces of the cube are parallel to the coordinate planes.
Clearly, the number of field lines entering the cube is equal to the number of field lines entering out of the cube. As a result, the net flux through the cube would be zero.
16. Careful measurement of the electric field at the surface of a black box indicates that the net outward flux through the surface of the box is $8.0\times {{10}^{3}}N{{m}^{2}}/C$.
a) What is the net charge inside the box?
Ans: We are given that:
Net outward flux through surface of the box,
$\phi =8.0\times {{10}^{3}}N{{m}^{2}}/C$
For a body containing of net charge $q$, flux could be given by,
$\phi =\frac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
Where, ${{\varepsilon }_{0}}=8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}{{N}^{-1}}{{C}^{2}}{{m}^{-2}}=$ Permittivity of free space
Therefore, the charge $q$ is given by
$q=\phi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}$
$\Rightarrow q=8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}\times 8.0\times {{10}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow q=7.08\times {{10}^{-8}}$
$\Rightarrow q=0.07\mu C$
Therefore, the net charge inside the box is found to be $0.07\mu C$.
b) If the net outward flux through the surface of the box were zero, could you conclude that there were no charges inside the box? Why or why not?
Ans: No, the net flux entering out through a body depends on the net charge contained within the body according to Gauss’s law.
So, if the net flux is given to be zero, then it can be inferred that the net charge inside the body is zero.
However, the net charge of the body being zero only implies that the body has equal amount of positive and negative charges and thus, we cannot conclude that there were no charges inside the box.
17. A point charge $+10\mu C$ is a distance $5cm$ directly above the centre of a square of side $10cm$, as shown in Figure below. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through the square? (Hint: Think of the square as one face of a cube with edge $10cm$)
Ans: Consider the square as one face of a cube of edge length $10cm$ with a charge $q$ at its centre, according to Gauss's theorem for a cube, total electric flux is through all its six faces.
${{\phi }_{total}}=\frac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
The electric flux through one face of the cube could be now given by, \[\phi =\frac{{{\phi }_{total}}}{6}\].
$\phi =\frac{1}{6}\frac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
${{\varepsilon }_{0}}=8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}{{N}^{-1}}{{C}^{2}}{{m}^{-2}}=$ Permittivity of free space
The net charge enclosed would be, $q=10\mu C=10\times {{10}^{-6}}C$
Substituting the values given in the question, we get,
$\phi =\frac{1}{6}\times \frac{10\times {{10}^{-6}}}{8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}}$
$\therefore \phi =1.88\times {{10}^{5}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}}$
Therefore, electric flux through the square is found to be $1.88\times {{10}^{5}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}}$.
18. A point charge of $2.0\mu C$ is kept at the centre of a cubic Gaussian surface of edge length $9cm$. What is the net electric flux through this surface?
Ans: Let us consider one of the faces of the cubical Gaussian surface considered (square).
Since a cube has six such square faces in total, we could say that the flux through one surface would be one-sixth the total flux through the gaussian surface considered.
The net flux through the cubical Gaussian surface by Gauss’s law could be given by,
${{\phi }_{total}}=\frac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
So, the electric flux through one face of the cube would be, \[\phi =\frac{{{\phi }_{total}}}{6}\]
$\Rightarrow \phi =\frac{1}{6}\frac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$……………………………….. (1)
But we have,
${{\varepsilon }_{0}}=8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}{{N}^{-1}}{{C}^{2}}{{m}^{-2}}=$ Permittivity of free space
Charge enclosed, $q=10\mu C=10\times {{10}^{-6}}C$
Substituting the given values in (1) we get,
$\phi =\frac{1}{6}\times \frac{10\times {{10}^{-6}}}{8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}}$
$\Rightarrow \phi =1.88\times {{10}^{5}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}}$
Therefore, electric flux through the square surface is $1.88\times {{10}^{5}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}}$.
19. A point charge causes an electric flux of $-1.0\times {{10}^{3}}N{{m}^{2}}/C$ to pass through a spherical Gaussian surface of $10cm$ radius centred on the charge.
a) If the radius of the Gaussian surface were doubled, how much flux could pass through the surface?
Ans: We are given:
Electric flux due to the given point charge, $\phi =-1.0\times {{10}^{3}}N{{m}^{2}}/C$
Radius of the Gaussian surface enclosing the point charge,$r=10.0cm$
Electric flux piercing out through a surface depends on the net charge enclosed by the surface according to Gauss’s law and is independent of the dimensions of the arbitrary surface assumed to enclose this charge.
Hence, if the radius of the Gaussian surface is doubled, then the flux passing through the surface remains the same i.e., $-{{10}^{3}}N{{m}^{2}}/C$.
b) What is the magnitude of the point charge?
Ans: Electric flux could be given by the relation,
${{\phi }_{total}}=\frac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
Where,$q=$ net charge enclosed by the spherical surface
${{\varepsilon }_{0}}=8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}{{N}^{-1}}{{C}^{2}}{{m}^{-2}}=$ Permittivity of free space
$\Rightarrow q=\phi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}$
Substituting the given values,
$\Rightarrow q=-1.0\times {{10}^{3}}\times 8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}=-8.854\times {{10}^{-9}}C$
$\Rightarrow q=-8.854nC$
Thus, the value of the point charge is found to be $-8.854nC$.
20. A conducting sphere of radius $10cm$ has an unknown charge. If the electric field at a point $20cm$ from the centre of the sphere of magnitude $1.5\times {{10}^{3}}N/C$ is directed radially inward, what is the net charge on the sphere?
Ans: We have the relation for electric field intensity $E$ at a distance \[\left( d \right)\] from the centre of a sphere containing net charge $q$ is given by,
$E=\frac{q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{d}^{2}}}$ ……………………………………………… (1)
Where,
Net charge, $q=1.5\times {{10}^{3}}N/C$
Distance from the centre, $d=20cm=0.2m$
${{\varepsilon }_{0}}=8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}{{N}^{-1}}{{C}^{2}}{{m}^{-2}}=$ Permittivity of free space
$\frac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}=9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}$
From (1), the unknown charge would be,
$q=E\left( 4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}} \right){{d}^{2}}$
Substituting the given values we get,
$\Rightarrow q=\frac{1.5\times {{10}^{3}}\times {{\left( 0.2 \right)}^{2}}}{9\times {{10}^{9}}}=6.67\times {{10}^{-9}}C$
$\Rightarrow q=6.67nC$
Therefore, the net charge on the sphere is found to be$6.67nC$.
21. A uniformly charged conducting sphere of $2.4m$ diameter has a surface charge density of $80.0\mu C/{{m}^{2}}$.
a) Find the charge on the sphere.
Ans: Given that,
Diameter of the sphere, $d=2.4m$.
Radius of the sphere, $r=1.2m$.
Surface charge density,
\[\sigma =80.0\mu C/{{m}^{2}}=80\times {{10}^{-6}}C/{{m}^{2}}\]
Total charge on the surface of the sphere,
$Q=\text{Charge density }\times \text{ Surface area}$
$\Rightarrow \text{Q}=\sigma \times \text{4}\pi {{\text{r}}^{2}}=80\times {{10}^{-6}}\times 4\times 3.14\times {{\left( 1.2 \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow Q=1.447\times {{10}^{-3}}C$
Therefore, the charge on the sphere is found to be $1.447\times {{10}^{-3}}C$.
b) What is the total electric flux leaving the surface of the sphere?
Ans: Total electric flux $\left( {{\phi }_{total}} \right)$ leaving out the surface containing net charge $Q$ is given by Gauss’s law as,
${{\phi }_{total}}=\frac{Q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$…………………………………………………. (1)
Where, permittivity of free space,
${{\varepsilon }_{0}}=8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}{{N}^{-1}}{{C}^{2}}{{m}^{-2}}$
We found the charge on the sphere to be,
$Q=1.447\times {{10}^{-3}}C$
Substituting these in (1), we get,
${{\phi }_{total}}=\frac{1.447\times {{10}^{-3}}}{8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\phi }_{total}}=1.63\times {{10}^{-8}}N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}}$
Therefore, the total electric flux leaving the surface of the sphere is found to be $1.63\times {{10}^{-8}}N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}}$.
22. An infinite line charge produces a field of magnitude $9\times {{10}^{4}}N/C$ at a distance of $2cm$. Calculate the linear charge density.
Ans: Electric field produced by the given infinite line charge at a distance $d$having linear charge density$\lambda $ could be given by the relation,
$E=\frac{\lambda }{2\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}d}$
$\Rightarrow \lambda =2\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}Ed$…………………………………….. (1)
We are given:
$d=2cm=0.02m$
$E=9\times {{10}^{4}}N/C$
Permittivity of free space,
${{\varepsilon }_{0}}=8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}{{N}^{-1}}{{C}^{2}}{{m}^{-2}}$
Substituting these values in (1) we get,
$\Rightarrow \lambda =2\pi \left( 8.854\times {{10}^{-12}} \right)\left( 9\times {{10}^{4}} \right)\left( 0.02 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \lambda =10\times {{10}^{-8}}C/m$
Therefore, we found the linear charge density to be $10\times {{10}^{-8}}C/m$.
23. Two large, thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On their inner faces, the plates have surface charge densities of opposite signs and of magnitude $17.0\times {{10}^{-22}}C{{m}^{-2}}$. What is $E$ in the outer region of the first plate? What is $E$ in the outer region of the second plate? What is E between the plates?
Ans: The given nature of metal plates is represented in the figure below:
Here, A and B are two parallel plates kept close to each other. The outer region of plate A is denoted as $I$, outer region of plate B is denoted as $III$, and the region between the plates, A and B, is denoted as $II$.
It is given that:
Charge density of plate A, $\sigma =17.0\times {{10}^{-22}}C/{{m}^{2}}$
Charge density of plate B, $\sigma =-17.0\times {{10}^{-22}}C/{{m}^{2}}$
In the regions $I$and$III$, electric field E is zero. This is because the charge is not enclosed within the respective plates.
Now, the electric field $E$ in the region $II$ is given by
$E=\frac{|\sigma |}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
Where,
Permittivity of free space ${{\varepsilon }_{0}}=8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}{{N}^{-1}}{{C}^{2}}{{m}^{-2}}$
Clearly,
$E=\frac{17.0\times {{10}^{-22}}}{8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}}$
$\Rightarrow E=1.92\times {{10}^{-10}}N/C$
Thus, the electric field between the plates is $1.92\times {{10}^{-10}}N/C$.
List of Important Formulas in Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges And Fields
While preparing a chapter, it is important for students to memorize the formula of a particular topic. This will help them to boost their score. Some important formulas are listed below.
Coulomb’s Law
The electric force between the two-point charges are directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
F = K$\frac{q_{1}q_{2}}{r2}$
Here,
F represents the electric force.
K represents Coulomb’s constant.
$q_{1}q_{2}$ represents the two charges.
$\lambda$ represents the distance between two charges.
Electric field intensity
Electric field intensity is the vector quantity.
E $\frac{F}{q_{1}}$
Here,
F is the force experienced by the test charge.
$q_1$ is the test charge.
Electric Flux
dФ = E.da
dФ = E.da cos𝛉
Ф = ഽ E.da
Chapter Summary of Electric Charges & Fields NCERT Solutions
From simple experiments on frictional electricity, one can infer that there are two types of charges in nature; and that like charges repel and unlike charges attract. By convention, the charge on a glass rod rubbed with silk is positive; that on a plastic rod rubbed with fur is then negative.
Charge is not only a scalar (or invariant) under rotation; it is also invariant for frames of reference in relative motion. This is not always true for every scalar. For Example-, kinetic energy is a scalar under rotation, but is not invariant for frames of reference in relative motion.
Conductors allow movement of electric charge through them, insulators do not. In metals, the mobile charges are electrons; in electrolytes both positive and negative ions are mobile.
Coulomb’s Law: The mutual electrostatic force between two point charges q1 and q2 is proportional to the product q1q2 and inversely proportional to the square of the distance r21 separating them.
$F_{21}=\text{force}\;q_{2} \;\text{du to}\;q_{1}\;=\frac{k(q_{1}q_{2})}{r^2_{21}}\;r_{21}$
Where $r_{21}$ is a unit vector in the direction from q1 to q2 and $k=\frac{1}{4\pi \varepsilon _{0}}$ is the constant of proportionality.
In SI units, the unit of charge is coulomb. The experimental value of the constant $\varepsilon _{0}$ is
$\varepsilon _{0}=8.854\times 10^{-12}C^{2}N^{-}M^{-2}$
The approximate value of k is- 9\times $10^{9}Nm^2C^{-2}$
Superposition Principle: The principle is based on the property that the forces with which two charges attract or repel each other are not affected by the presence of a third (or more) additional charge(s). For an assembly of charges Q1, Q2, Q3..., the force on any charge, say Q1, is the vector sum of the force on Q1 due to Q2, the force on Q1 due to Q3, and so on. For each pair, the force is given by Coulomb's law for two charges stated earlier.
An electric field line is a curve drawn in such a way that the tangent at each point on the curve gives the direction of the electric field at that point. The relative closeness of field lines indicates the relative strength of electric field at different points; they crowd near each other in regions of strong electric field and are far apart where the electric field is weak. In regions of constant electric field, the field lines are uniformly spaced parallel straight lines.
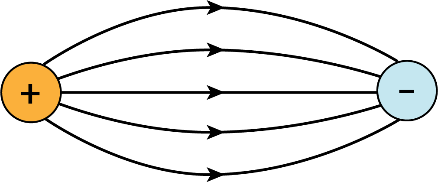
Some of the important properties of field lines are: (i) Field lines are continuous curves without any breaks. (ii) Two field lines cannot cross each other. (iii) Electrostatic field lines start at positive charges and end at negative charges (iv) They cannot form closed loops.
Electric flux is the measure of the field lines crossing a surface. It is scalar quantity, with SI unit $\frac{N}{C}$-m2 or V-m. “The number of field lines passing through perpendicular unit area will be proportional to the magnitude of Electric Field there”
Gauss’s law: The flux of electric field through any closed surface S is $1/\varepsilon _0$ times the total charge enclosed by S. The law is especially useful in determining electric field E, when the source distribution has simple symmetry.
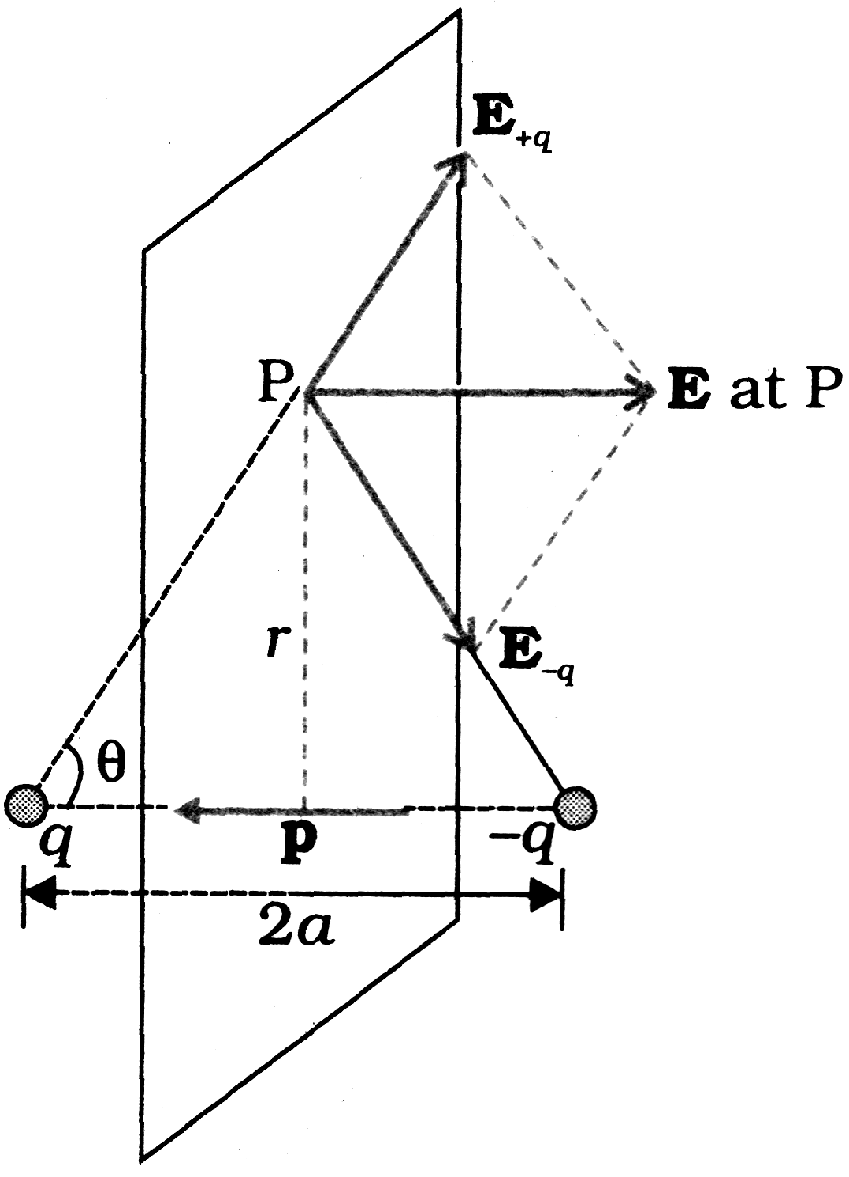
An electric dipole is a pair of equal and opposite charges q and –q separated by some distance 2a. Its dipole moment vector p has magnitude 2qa and is in the direction of the dipole axis from –q to q.
Field of an electric dipole in its equatorial plane (i.e., the plane perpendicular to its axis and passing through its centre) at a distance r from the centre:
$E=\frac{-P}{4\pi \varepsilon _0}\frac{1}{(\alpha^2+r^2)^{3/2}}\cong \frac{-P}{4\pi \varepsilon _0r^3}.\,\text{for}\,r\gg \alpha $
Dipole electric field on the axis at a distance r from the centre:
$E=\frac{2pr}{4\pi\varepsilon_0(r^2-\alpha^2)^3}\cong \frac{2{p}}{4\pi\varepsilon_0{r}^3}\,\,\text{for}\,\,r\gg\alpha$

The 1/r3 dependence of dipole electric fields should be noted in contrast to the 1/r2 dependence of electric field due to a point charge.
In a uniform electric field E, a dipole experiences a torque τ given by: τ = p × E
but experiences no net force.
Electric Field Due to Various Uniform Charge Distribution
(i) At the centre of circular arc 
| $E=\frac{kQ}{R^2}\frac{\text{sin}(\theta/2)}{\theta/2}$ |
(ii) At a point on the axis of ring 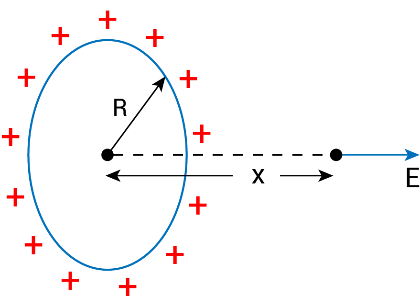
| $E=\frac{kQx}{(R^2+x^2)^{3/2}}$ 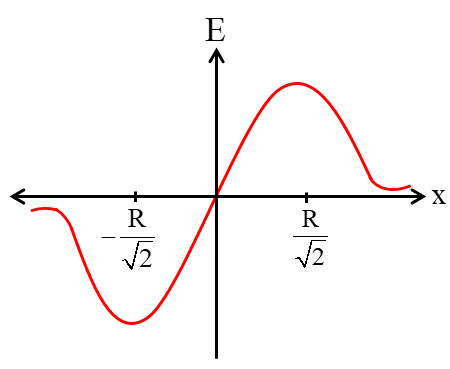
|
(iii) At a point on the axis of disc 
| $E=\frac{2kQ}{R^2}\left [ 1-\frac{x}{(R^2+x^2)^{3/2}} \right ]$ |
(iv) Hollow sphere 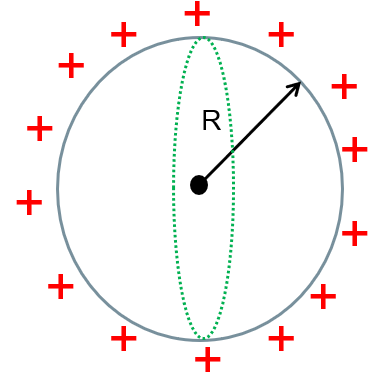
| For x < R: E = 0 For x ≥ R: $E=\frac{kQ}{x^2}$ 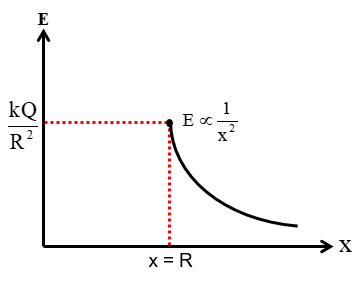
|
(v) Non conducting solid sphere 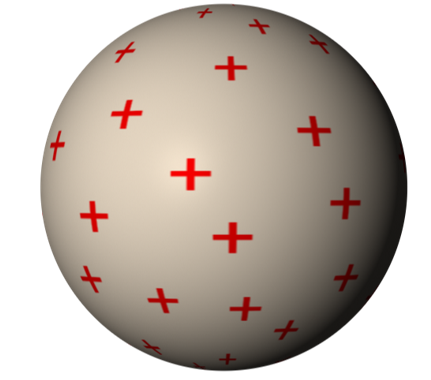
| For x < R: $E=\frac{kQx}{R^3}$ For x ≥ R: $E=\frac{kQ}{x^2}$ 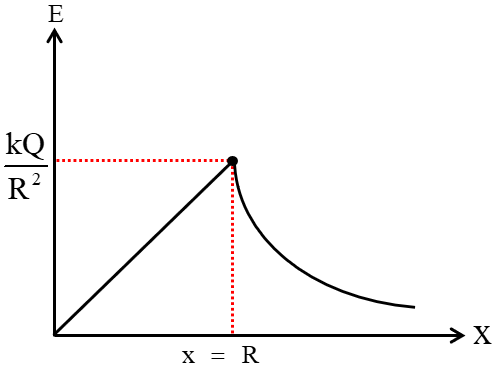
|
(vi) Infinite thin sheet 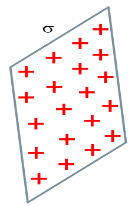
| $E=\frac{\sigma }{2\varepsilon _0}$ |
(vii) Infinite wire 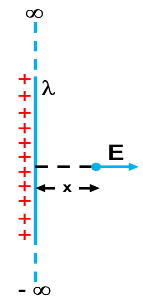
| $E=\frac{2k\lambda}{x}$ |
Overview of Deleted Syllabus for CBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields
Chapter | Dropped Topics |
Electric Charges and Fields | 1.2 Electric Charge (delete only activity with paper strips and making electroscope) |
1.3 Conductors and Insulators (delete only the concept of earthing) | |
1.4 Charging by Induction | |
Exercises 1.13 | |
1.25–1.34 |
Conclusion
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 - Electric Charges And Fields focuses on mastering fundamental concepts like Coulomb's law, electric field, Gauss's law, and electric dipole. It's important to understand these principles and their applications thoroughly. Key topics include electric charge properties, force interactions between multiple charges, electric flux, and the behaviour of electric fields in various configurations. Previous year question papers often include 17 marks (5-6 questions) worth of questions from this chapter, emphasizing its importance in the exam. Focus on practising both exercise and additional questions provided in the NCERT solutions to solidify your understanding and improve exam performance.
Other Study Material for CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 1
Sr.No | Important Links for Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | Class 12 Electric Charges and Fields NCERT Exemplar Solution |
Chapter-Specific NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics
Given below are the chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics. Go through these chapter-wise solutions to be thoroughly familiar with the concepts.
S.No. | NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics Chapter-wise List |
1 | Chapter 2 - Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Solutions |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | |
11 | |
12 | |
13 | Chapter 14 - Semiconductor Electronic: Material, Devices and Simple Circuits Solutions |
Related Links for NCERT Class 12 Physics in Hindi
Discover relevant links for NCERT Class 12 Physics in Hindi, offering comprehensive study materials, solutions, and resources to enhance understanding and aid in exam preparation.
S.No. | Related NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics |
1 | |
2 |
Chapter-Specific NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics
Given below are the chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics. Go through these chapter-wise solutions to be thoroughly familiar with the concepts.
S.No | Other CBSE Study Materials for Class 12 Physics |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 |
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges And Fields - 2025-26
1. What are the fundamental properties of electric charges covered in this chapter?
Electric charges have three fundamental properties: quantization (charge exists in discrete multiples of elementary charge e), conservation (total charge in an isolated system remains constant), and additivity (charges can be algebraically added). The chapter also covers charge interactions through Coulomb's law and the concept that like charges repel while opposite charges attract.
2. How do NCERT Solutions for Electric Charges and Fields help students understand complex concepts?
NCERT Solutions provide step-by-step explanations for all in-text questions and exercises, breaking down complex electrostatics problems into manageable steps.
Electric field calculations and Coulomb's law applications require systematic problem-solving approaches that build conceptual clarity.
3. What is Gauss's law and why is it important in electrostatics?
Gauss's law states that the electric flux through any closed surface is proportional to the net electric charge enclosed by that surface. Mathematically, ∮E⃗·dA⃗ = qenc/ε₀. This fundamental law provides an elegant method to calculate electric fields for symmetric charge distributions and establishes the relationship between electric field and charge distribution in electrostatics.
4. Can students access the Electric Charges and Fields question answers in PDF format?
Students can download the Free PDF of NCERT Solutions containing all question answers for Electric Charges and Fields chapter from Vedantu's platform.
PDF format enables offline study, easy printing, and convenient access during exam preparation without internet dependency.
5. How does the electric field concept differ from electric force?
Electric field is the force per unit positive charge at a point in space (E⃗ = F⃗/q), making it an intrinsic property of the region around charges. Electric force is the actual force experienced by a charge when placed in an electric field (F⃗ = qE⃗). The field exists independently of test charges, while force requires the presence of a charge to experience it.
6. Why are NCERT Solutions essential for Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 preparation?
These solutions provide comprehensive coverage of all electrostatics concepts with detailed explanations, making complex topics like electric field calculations and charge distributions accessible to students.
Chapter 1 forms the foundation for advanced electromagnetism topics, requiring solid conceptual understanding and problem-solving skills.
7. What is the principle of superposition in electric fields?
The principle of superposition states that the resultant electric field at any point due to multiple charges equals the vector sum of individual electric fields produced by each charge at that point. Mathematically, E⃗net = E⃗₁ + E⃗₂ + E⃗₃ + ... This principle allows calculation of complex field patterns by considering each charge contribution separately.
8. How do the question answers cover electric field lines and their properties?
The solutions explain electric field lines as imaginary curves whose tangent at any point gives the direction of electric field, with line density representing field strength.
Field lines provide visual representation of electric fields, helping students understand field patterns around different charge configurations.
9. What numerical problems are typically included in this chapter?
The chapter includes Coulomb's law calculations for force between point charges, electric field computations at various distances, potential energy problems for charge systems, and dipole moment calculations. Students also solve problems involving field due to continuous charge distributions, application of Gauss's law for symmetric geometries, and work done in moving charges through electric fields.
10. How does the Free PDF help students prepare for board examinations?
The Free PDF contains complete solutions to all NCERT questions, providing students with authentic reference material aligned with board exam requirements and marking schemes.
Board exams often include direct questions from NCERT exercises, making thorough practice with these solutions crucial for scoring well.


















