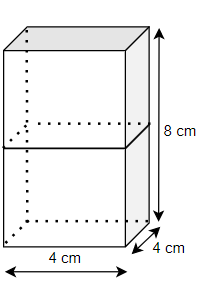
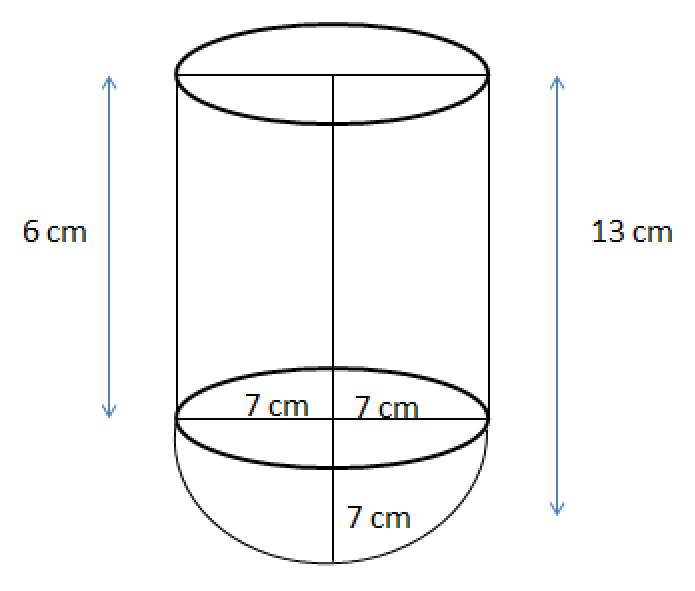
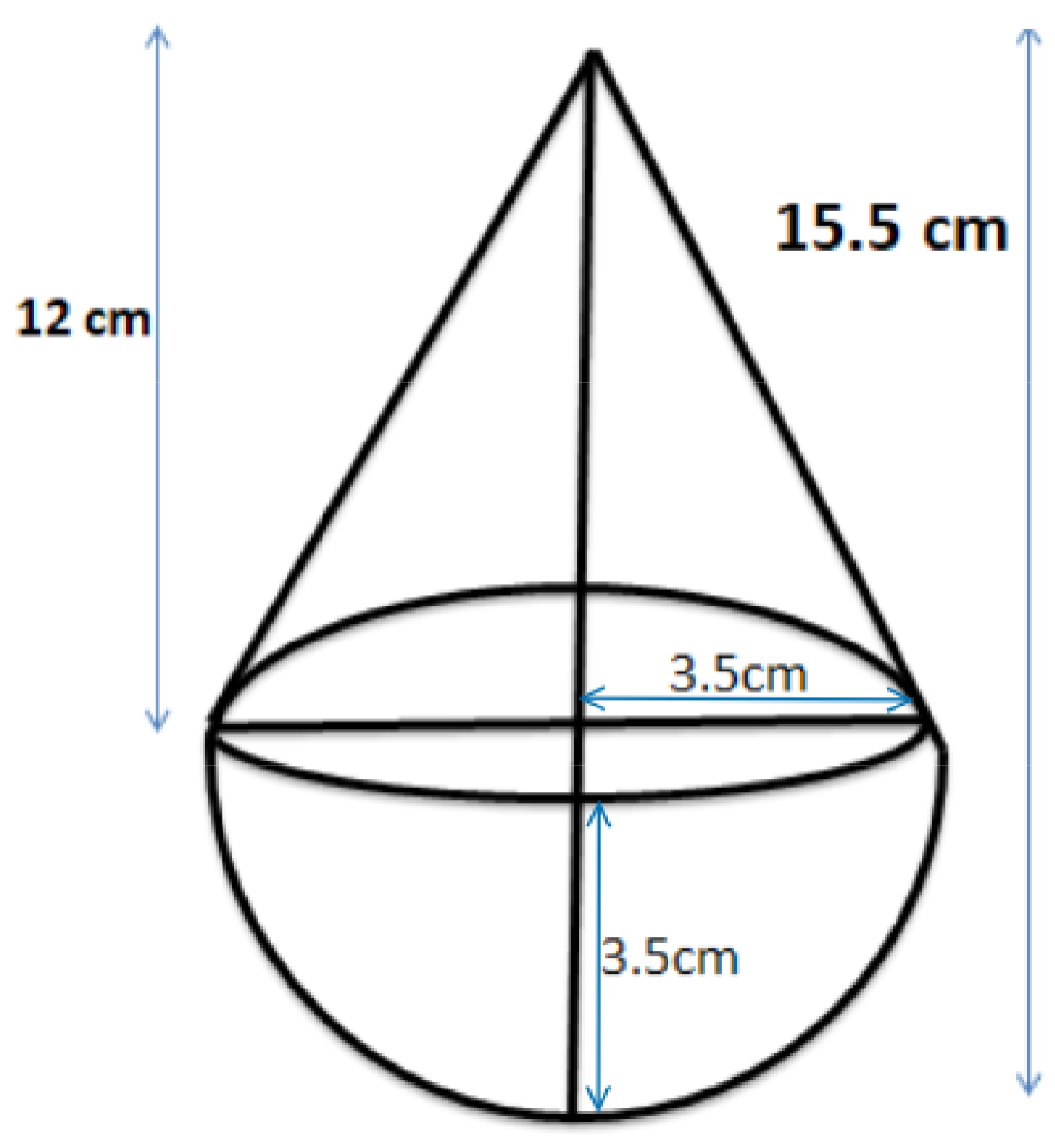
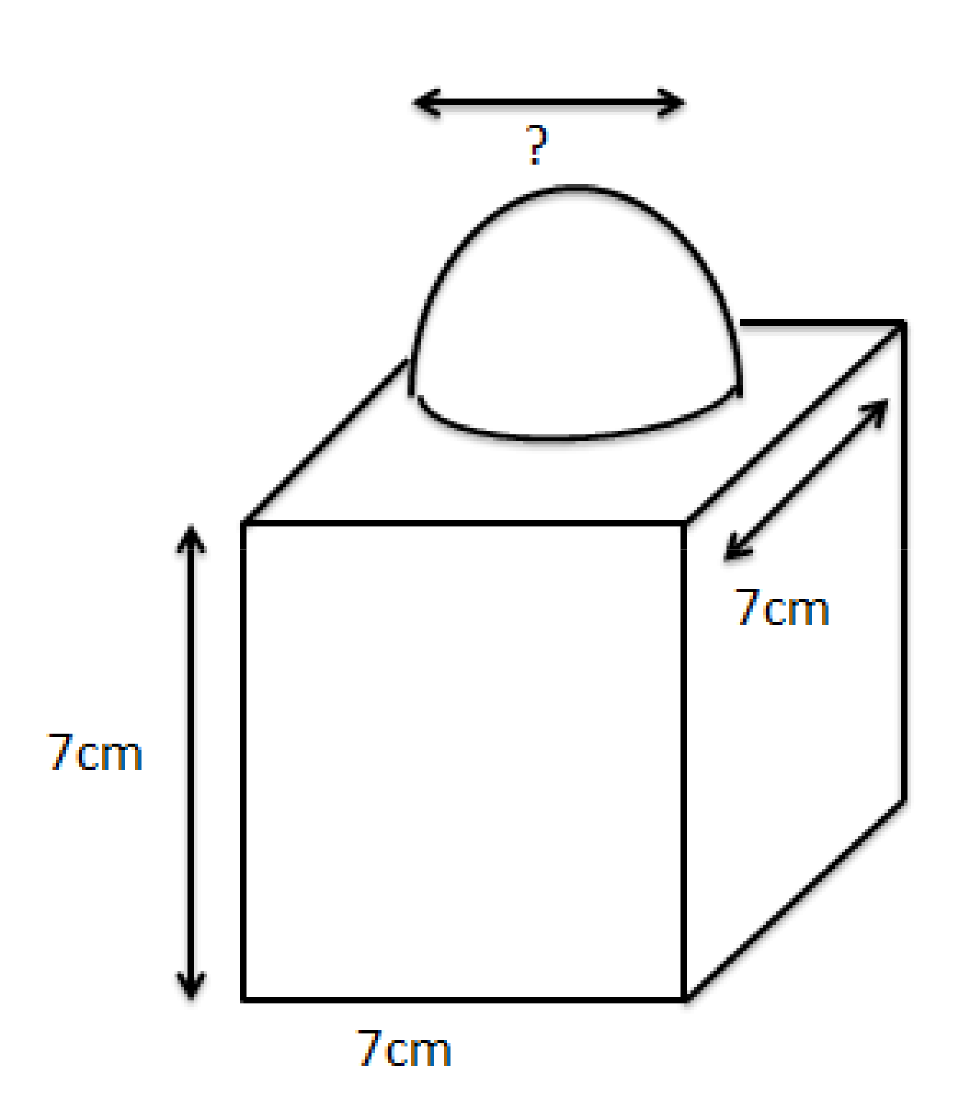
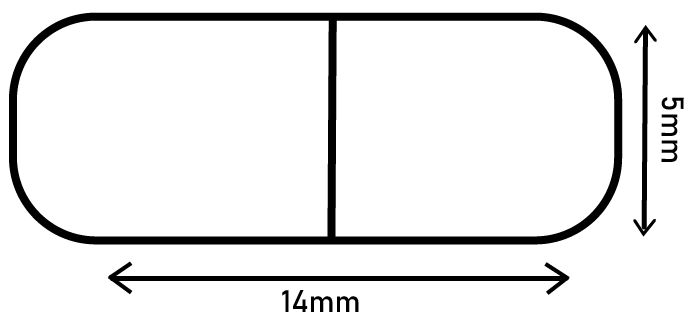
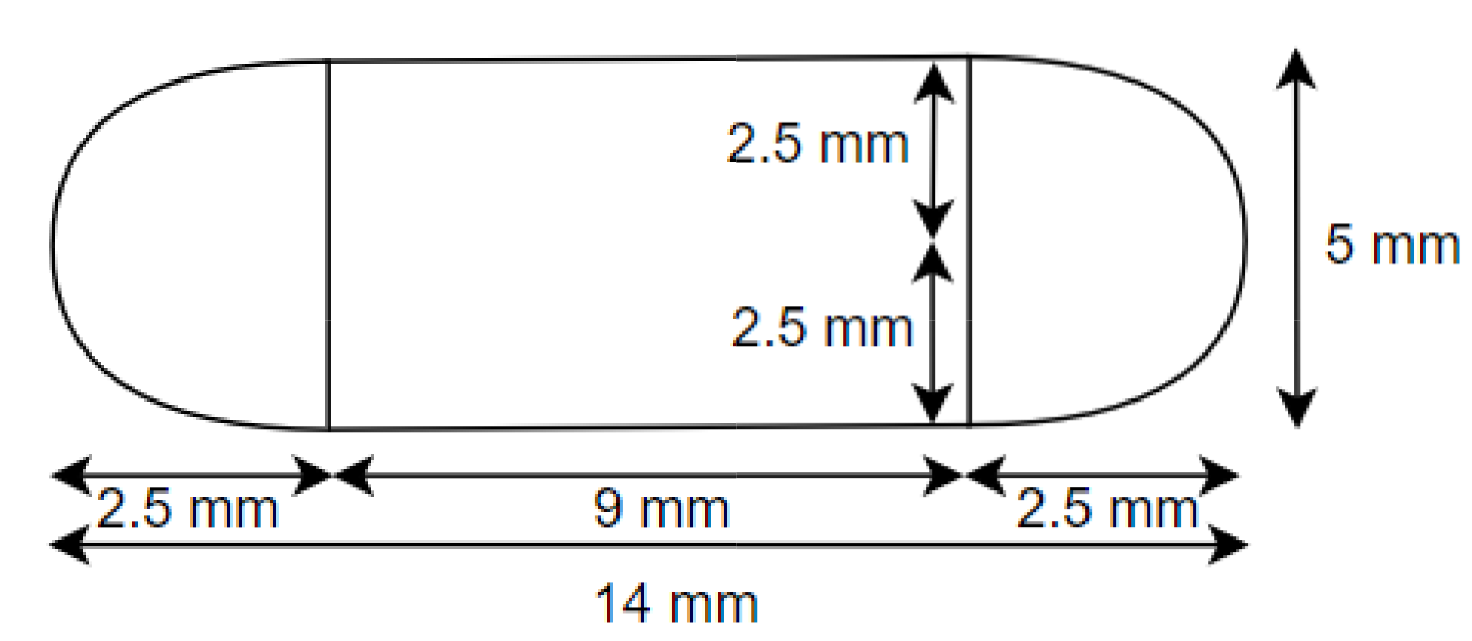
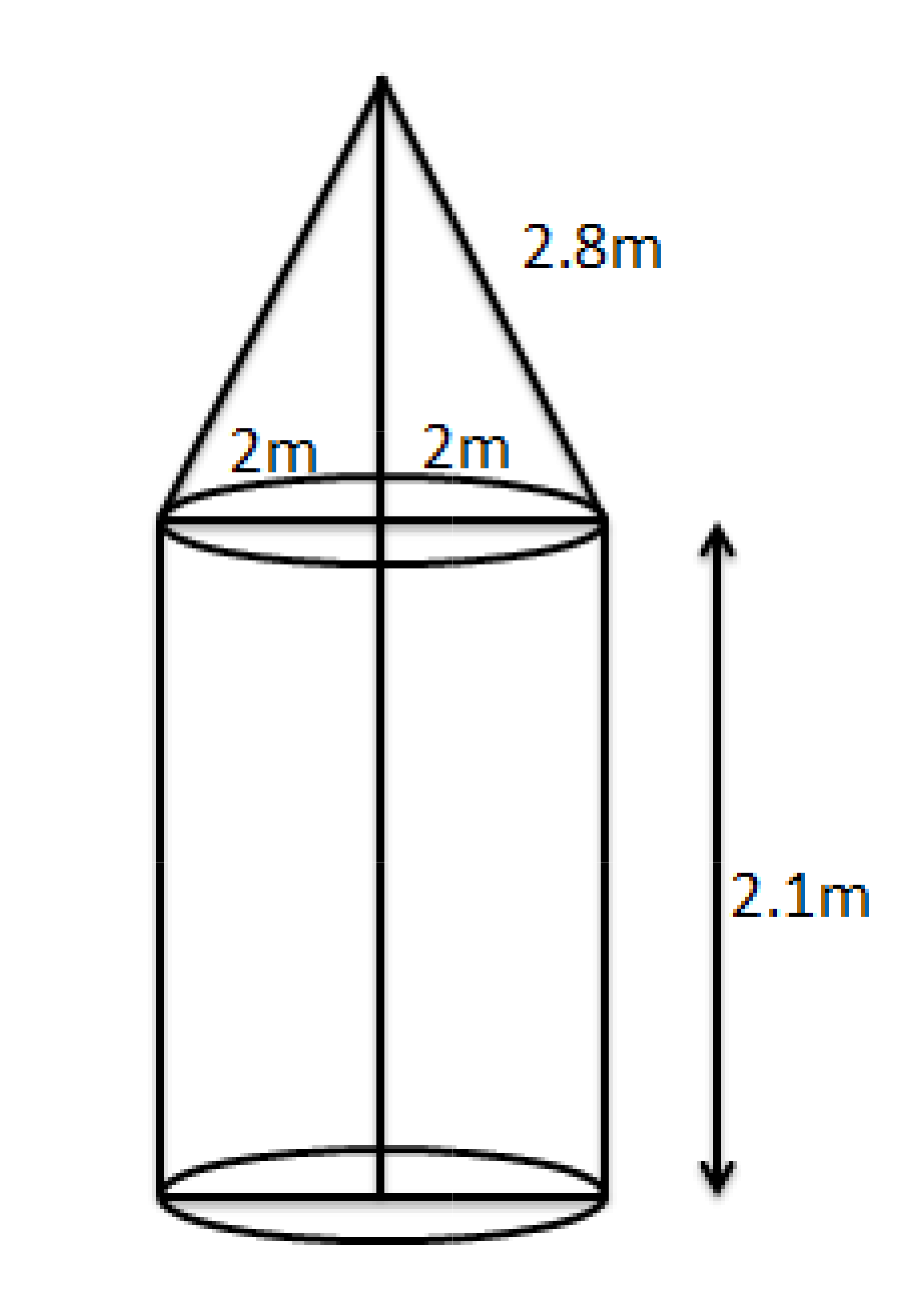
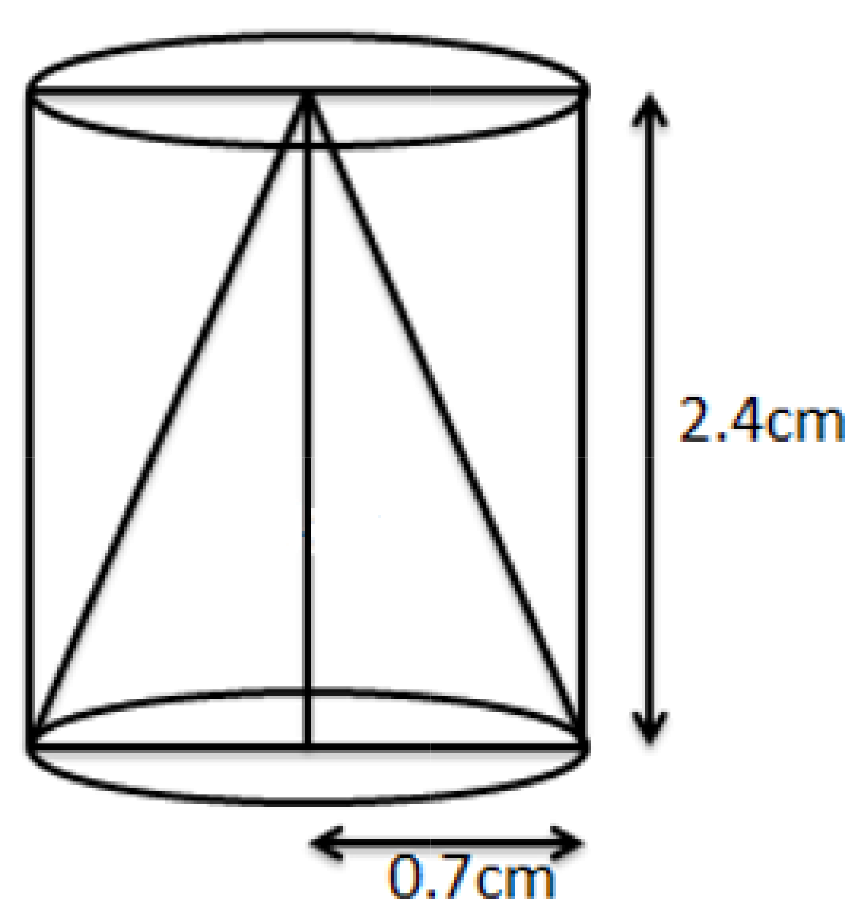
Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.1 Solutions for Surface Areas and Volumes: FREE PDF
Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.1 Surface Areas and Volumes NCERT Solutions
FAQs on Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.1 Surface Areas and Volumes NCERT Solutions
1. What does NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes Exercise 12.1 focus on?
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.1 focus on stepwise problem-solving for calculating the surface areas and volumes of fundamental 3D shapes such as cubes, cuboids, cylinders, cones, spheres, and hemispheres, in line with the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus. These solutions emphasize applying formulas, visualizing composite solids, and strengthening conceptual understanding for CBSE board exam readiness.
2. How should students approach combined solid figures in Surface Areas and Volumes as per NCERT Solutions?
To solve problems involving composite solids in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12, students should:
- Identify each individual component (cube, cuboid, hemisphere, etc.).
- Calculate surface area and volume for each component separately using the correct formulas.
- Add or subtract the relevant areas or volumes according to how the solids are joined or cut.
- Carefully note which surfaces are exposed or hidden in the final composite object as per the question.
3. What are the key formulas covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes NCERT Solutions?
Key formulas provided in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 include:
- Surface Area (SA) and Volume (V) of basic solids: Cube, Cuboid, Sphere, Cylinder, Cone, Hemisphere.
- Curved Surface Area (CSA), Total Surface Area (TSA) for each solid figure.
- Volume conversions for composite and transformed solids.
- Frustum of a cone surface area and volume formulas.
4. How many questions are in Exercise 12.1 of Class 10 Maths Chapter 12, and what types do they cover?
Exercise 12.1 of Class 10 Maths NCERT Chapter 12 contains nine questions (seven long and two short answer types). These cover direct application of surface area and volume formulas, as well as complex scenarios involving composite solids and real-life applications such as containers, vessels, toys, and practical geometrical arrangements.
5. What is a frustum of a cone as defined in the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12?
A frustum of a cone is the part of a cone that remains after cutting through it with a plane parallel to its base and removing the smaller, top portion. The resulting solid has two parallel circular faces—one larger (base) and one smaller (top)—with the same axis as the original cone.
6. Why is understanding the practical application of surface area and volume important for Class 10 students?
Understanding surface area and volume is crucial because these concepts have direct real-world uses, such as:
- Calculating material requirements (e.g., amount of canvas, tin, or paint needed to cover objects).
- Solving problems related to packaging, construction, and manufacturing.
- Forming a foundation for advanced topics in geometry, calculus, and engineering fields.
7. How do the NCERT Solutions ensure accuracy and CBSE compliance for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12?
Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Chapter 12 are prepared by CBSE subject experts. All solutions strictly follow the latest CBSE guidelines for 2025–26, use standard mathematical notation, and provide in-depth stepwise explanations. This ensures alignment with board expectation and facilitates high exam scores.
8. What is the most common mistake students make when solving surface area of composite solids?
The most frequent error is misidentifying which surfaces are actually exposed after combining or cutting solids. Students sometimes count surfaces twice or omit hidden faces, leading to incorrect answers. Always analyze the final structure carefully and calculate only the visible surface area required by the problem.
9. Can different composite solids have the same volume but different surface areas? Explain using an example.
Yes, two composite solids can have equal volumes but different surface areas. For example, a cube and a tall thin cuboid may both have a volume of 64 cm³, but the surface area will differ depending on edge lengths. Surface area depends on how the exposed faces are arranged; volume depends only on the space occupied.
10. What strategy should you use when a question asks for "area of canvas used" or "outer surface area covered"?
Focus on calculating the Curved Surface Area (CSA) or Total Surface Area (TSA) of the exposed part only. If the base is not required to be covered (e.g., tent or vessel), exclude its area. Always read the question to identify whether you need to include or omit certain faces in your calculation.
11. How is the slant height of a cone calculated in surface area questions in NCERT Solutions?
In Class 10 Maths Chapter 12, the slant height (l) of a cone is found using the formula: l = √(r² + h²), where r is the radius of the base and h is the vertical height. This value is crucial for calculating the curved surface area of conical shapes.
12. What are some real-life applications of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 concepts?
Important applications from this chapter include:
- Designing tanks, vessels, capsules, and tents.
- Planning packaging, shipping boxes, and storage containers.
- Calculating the amount of paint or wrapping needed for curved surfaces.
- Modeling and constructing solid toys and industrial parts with combined shapes.
13. How can Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions help students preparing for the Class 10 board exam in 2025–26?
Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 provide accurate, step-wise answers with explanations following CBSE 2025–26 patterns. This helps students quickly master concept application, avoid common errors, and build exam confidence, ensuring strong foundational understanding and improved performance in school and board exams.
14. What should a student do if they get stuck on a Surface Areas and Volumes problem in NCERT Ex 12.1?
- Break the problem down into smaller parts: Identify each solid separately.
- Write down and label all dimensions given in the question.
- Draw a rough diagram to visualize the object.
- Apply the correct NCERT formula for each step.
- Check if any surfaces are hidden or not included in the calculation.
15. If a solid is transformed from one shape to another (like melting a cylinder to form a sphere), what remains constant and why?
The volume remains constant during such transformations. This is because the material used does not change in quantity; only the shape changes. The surface area often changes, but the total space occupied (volume) stays the same as per the law of conservation of matter in such problems.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video