Sound Class 8 important questions with answers PDF download
FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 8 Science Sound - 2025-26
1. How can practicing these important questions for Chapter 10, Sound, improve my exam score?
Practicing these questions helps you understand the types of questions that frequently appear in exams. It ensures you cover all key topics from the chapter as per the CBSE syllabus. This improves your confidence, answering speed, and helps you score higher marks by familiarising you with the exam pattern for the 2025-26 session.
2. What kinds of questions are included for Class 8 Science, Chapter 10?
The list includes a variety of question formats to prepare you thoroughly. You will find:
- Very Short Answer (VSA) questions for quick 1-mark concepts.
- Short Answer (SA) questions that require 2-3 mark explanations.
- Long Answer (LA) questions, often worth 5 marks, which may include diagrams.
- Application-based questions to test your practical understanding.
3. Are all topics from the CBSE 2025-26 syllabus for 'Sound' covered?
Yes, these important questions cover all crucial topics from the official NCERT syllabus for the 2025-26 session. This includes how sound is produced and travels, characteristics like amplitude and frequency, the structure of the human ear, audible vs. inaudible sounds, and the effects of noise pollution.
4. How should I use this question bank for the best revision?
First, thoroughly read Chapter 10, 'Sound', from your textbook. After that, attempt to answer these important questions in a separate notebook without looking at the solutions. This will act as a self-test. Finally, check your answers to find areas where you need more practice and to learn the best way to frame your answers for the exam.
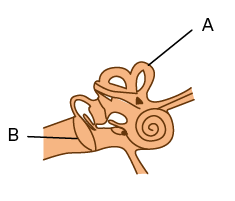
5. Why are diagram-based questions from the 'Sound' chapter so important?
Diagrams, such as the structure of the human ear or the larynx, are a very common type of question from this chapter. They often carry higher marks. Practising them helps you score well by ensuring you can draw and label them accurately and quickly during the exam.
6. Are there any Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) questions included?
Yes, some questions are designed to test your deeper understanding beyond simple definitions. For example, you might be asked to explain *why* a sound from a musical instrument is different from noise, or solve a simple problem involving the frequency and time period of an oscillation. These questions prepare you for the more challenging parts of your exam.
7. What is the usual marks weightage for the 'Sound' chapter in exams?
The 'Sound' chapter is an important part of the syllabus. You can generally expect a mix of questions from this chapter, including 1-mark MCQs or fill-in-the-blanks, 2 or 3-mark questions asking for definitions or short explanations, and occasionally a 5-mark question that requires a detailed explanation with a diagram.