CBSE Important Questions for Class 8 Science Microorganisms: Friend and Foe - 2025-26
FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 8 Science Microorganisms: Friend and Foe - 2025-26
1. What are the five major groups of microorganisms as per the Class 8 syllabus? Name one important example for each group.
For the CBSE 2025-26 exams, it's important to know the five major groups of microorganisms. These are:
- Bacteria: Single-celled organisms, e.g., Lactobacillus (used in making curd).
- Fungi: Mostly multicellular, non-green organisms, e.g., Yeast (used in baking).
- Protozoa: Unicellular organisms, e.g., Amoeba.
- Algae: Simple, plant-like organisms, e.g., Chlamydomonas.
- Viruses: Microscopic infectious agents that replicate only inside living cells, e.g., Influenza virus.
2. Explain how microorganisms are considered "friends" in the food industry. Provide at least three examples that are frequently asked in exams.
Microorganisms play a crucial role in the production of various food items, making them our 'friends'. This is an important topic for 3-mark questions. Key examples include:
- Curd Making: The bacterium Lactobacillus promotes the formation of curd from milk.
- Baking Industry: Yeast is a fungus used in baking bread, cakes, and pastries. It reproduces rapidly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration, which makes the dough rise.
- Fermentation: Yeast is also used for the large-scale commercial production of alcohol, wine, and vinegar (acetic acid) through the process of fermentation.
3. What are antibiotics, and what is one crucial precaution that must be taken while using them?
Antibiotics are medicines produced by certain microorganisms (like fungi and bacteria) to kill or stop the growth of other disease-causing microorganisms. An example is Penicillin. A crucial precaution, often highlighted in HOTS questions, is that antibiotics should be taken only on the advice of a qualified doctor and the prescribed course must be completed. Taking them unnecessarily can kill beneficial bacteria in the body and may make the drug ineffective in the future due to the development of antibiotic resistance.
4. How do vaccines work to protect us from diseases? Explain the principle of vaccination.
Vaccination is a highly important concept for preventing diseases. A vaccine contains dead or weakened microbes of a particular disease. When introduced into a healthy body, the body's immune system is stimulated to produce antibodies to fight and destroy these invaders. These antibodies remain in the body, providing immunity. If the actual disease-causing microbes enter the body later, the existing antibodies can fight them off quickly, preventing the disease. This is the principle of immunisation.
5. List any five common methods of food preservation. Explain the scientific principle behind using 'sugar' and 'pasteurisation' as preservatives.
This is a potential 5-mark question. Five common methods of food preservation are:
- Chemical Method (using preservatives like sodium benzoate)
- Preservation by Common Salt
- Preservation by Sugar
- Preservation by Oil and Vinegar
- Heat and Cold Treatments (Pasteurisation and Refrigeration)
The principles for two of these methods are:
- Preservation by Sugar: Sugar reduces the moisture content in food items like jams and jellies. This lack of moisture inhibits the growth of bacteria and other microbes that spoil food.
- Pasteurisation: This method involves heating milk to about 70°C for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilling and storing it. This process kills most of the harmful bacteria without significantly affecting the milk's nutritional value.
6. Why are viruses considered to be on the borderline between living and non-living things? How does this unique characteristic make them a foe?
Viruses are considered unique because they exhibit characteristics of both living and non-living entities. Outside a host organism, they behave like non-living particles and can be crystallised. However, once they enter the cells of a living host (like a plant, animal, or bacterium), they use the host's cellular machinery to reproduce and multiply, which is a key characteristic of living organisms. This dual nature makes them formidable foes because they cannot be treated with antibiotics (which target bacterial cell processes), making viral infections like the common cold or flu difficult to cure.
7. A farmer notices the leaves of his wheat crop are turning yellow with rust-coloured spots. Identify the type of microorganism likely causing this and explain how such plant diseases are transmitted.
The described condition is likely 'rust of wheat,' which is a plant disease caused by a type of fungus. Understanding the transmission of plant diseases is important for application-based questions. Such diseases are primarily transmitted through:
- Air: Fungal spores are lightweight and can be easily carried by wind over long distances.
- Water: Rain or irrigation water can splash spores from infected plants to healthy ones.
- Seeds: Infected seeds can carry the pathogen and spread the disease to a new crop.
- Insects: Some insects can act as carriers, transferring pathogens from one plant to another.
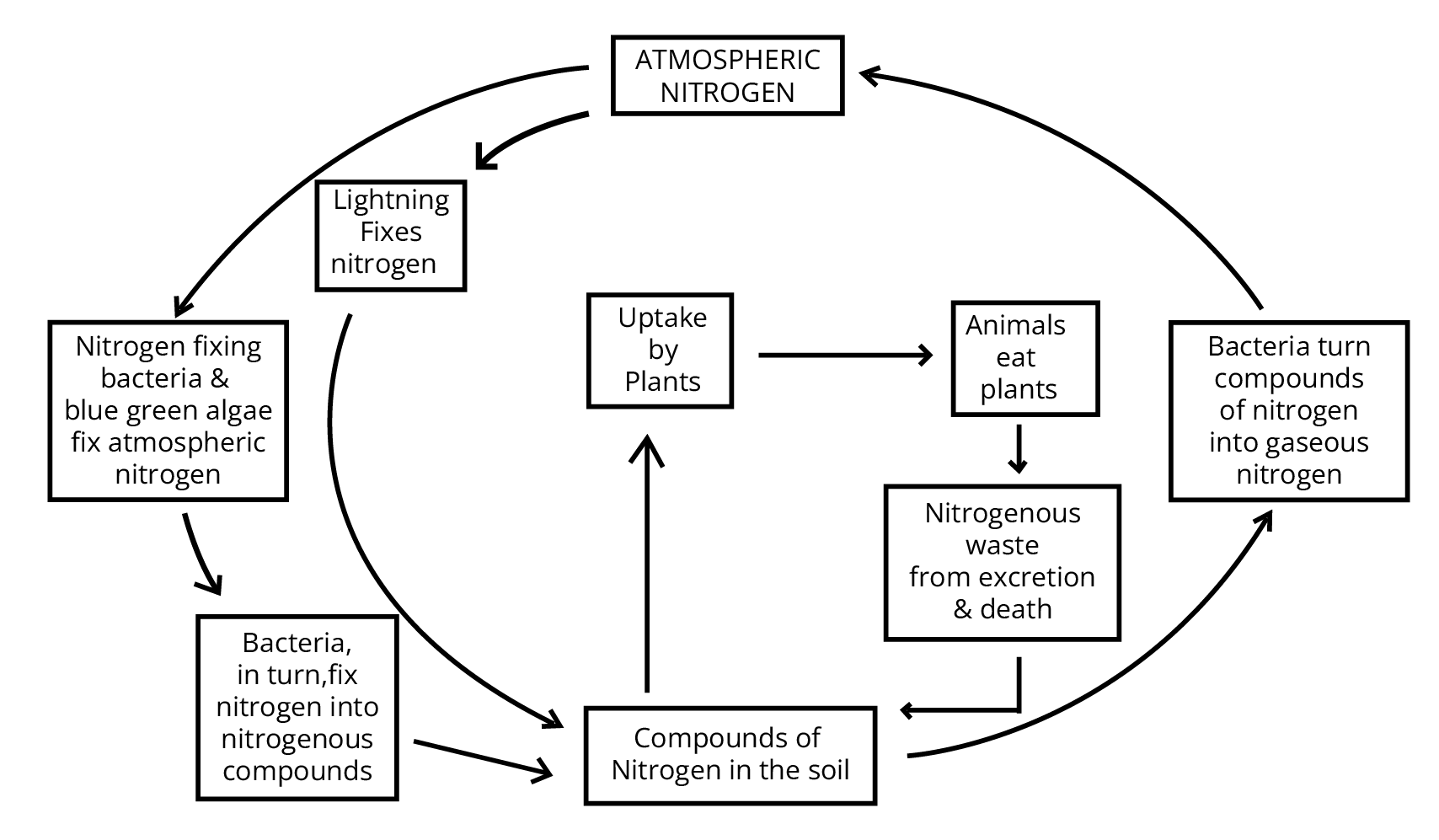
8. Explain the role of microorganisms in the Nitrogen Cycle. Why is this cycle essential for an ecosystem?
Microorganisms are central to the Nitrogen Cycle. Certain bacteria like Rhizobium (in the root nodules of leguminous plants) and blue-green algae present in the soil can fix atmospheric nitrogen, converting it into usable compounds like nitrates. When plants and animals die, other bacteria and fungi in the soil act as decomposers, converting the nitrogenous wastes back into nitrogen compounds to be used again by plants. Some bacteria (e.g., Pseudomonas) perform denitrification, releasing nitrogen gas back into the atmosphere. This cycle is essential because nitrogen is a vital component of proteins, nucleic acids, and vitamins, and this cycle ensures a continuous supply of it for all living organisms.
9. While making dough, your mother adds yeast and keeps it in a warm place. Why does the dough rise? What would happen if she forgot to add sugar?
This is an excellent HOTS question based on a real-world application. The dough rises because the yeast, a type of fungus, undergoes a process called anaerobic respiration (or fermentation). During this process, the yeast breaks down the sugar present in the flour to produce energy, releasing carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas and alcohol. The bubbles of CO₂ gas get trapped in the dough, causing it to increase in volume, or 'rise'. If sugar was not added, the fermentation process would be very slow or might not happen effectively, as yeast needs sugar as its food source to respire rapidly and produce enough CO₂ to make the dough rise.