An Overview of Important Questions Class 12 Maths Chapter 12



FAQs on Important Questions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 12 Linear Programming - 2025-26
1. What types of questions are typically asked in CBSE Class 12 Linear Programming important question sets?
Class 12 Linear Programming important questions generally include graphical method problems, formulation of linear programming problems (LPPs) from real-life scenarios, questions about feasible regions and optimal solutions, as well as minimum/maximum value determination of linear objective functions subject to given constraints. These frequently appear as 5 to 6 mark long answer questions on board exams, as per CBSE 2025–26 pattern.
2. How do you identify and avoid mistakes while formulating a linear programming problem for Class 12 board exams?
To avoid mistakes in LPP formulation for Class 12 boards, students should:
- Correctly define decision variables with clear units.
- Translate real-world constraints into mathematical inequalities consistently.
- Ensure the objective function directly expresses the goal (minimize/maximize) in terms of the variables.
- Include non-negativity constraints (e.g., x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0).
- Double-check that all worded conditions are accounted for mathematically.
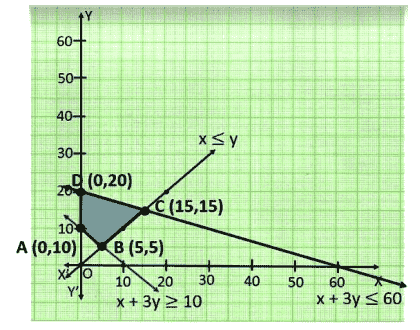
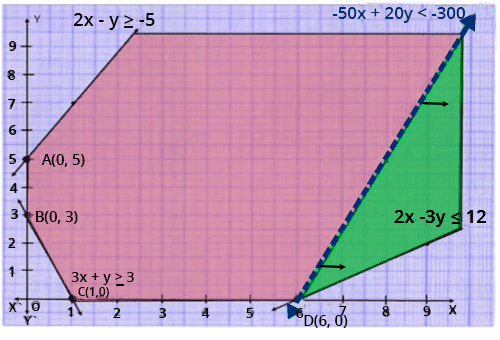
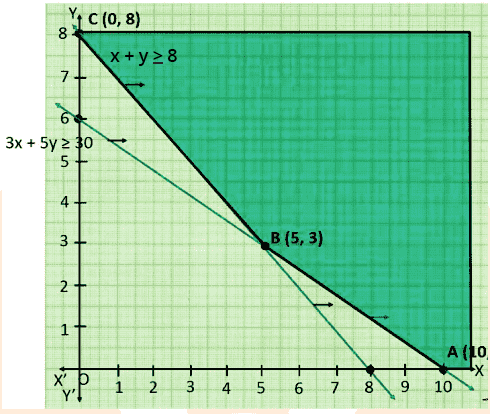
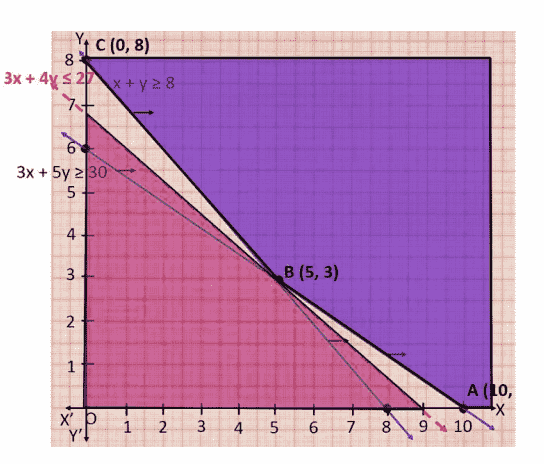
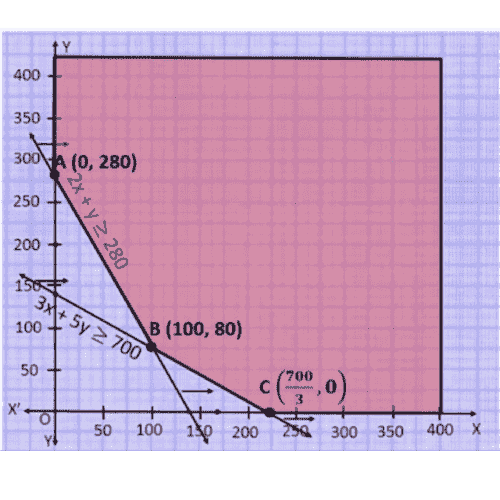
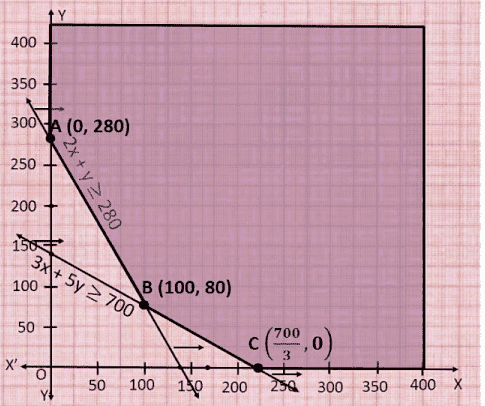
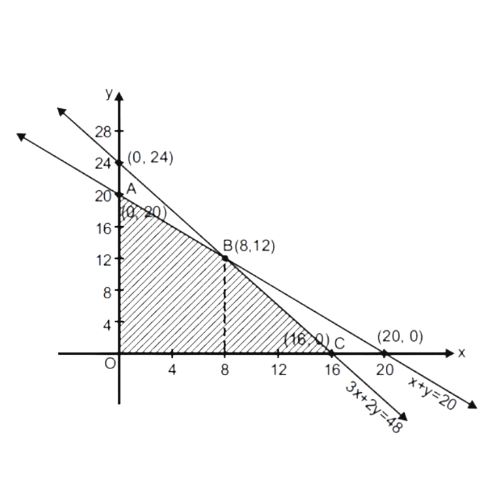
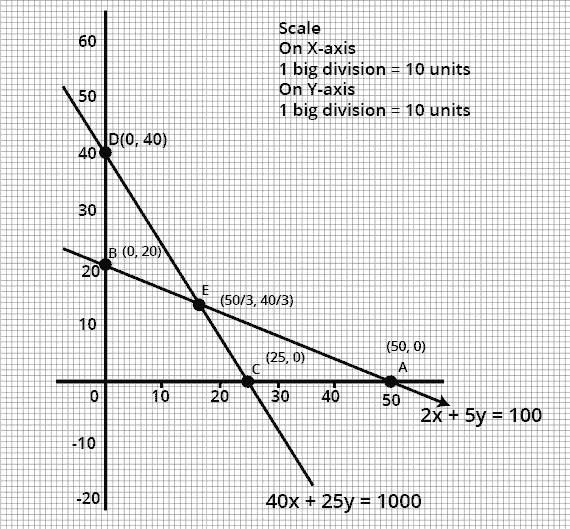
3. What is a feasible region in a linear programming question, and how do you determine its boundedness?
A feasible region is the area in the coordinate plane where all constraints (including inequalities and non-negativity) overlap. To determine boundedness:
- If the feasible region is enclosed on all sides by the constraint lines and axes, it is bounded.
- If the region extends infinitely in any direction, it is unbounded.
- Bounded regions always yield both maximum and minimum values, while unbounded regions may not always yield both.
4. Why are linear programming important questions considered high-weightage in CBSE Class 12 Maths?
Linear programming is given high weightage (typically 5–6 marks) in CBSE Class 12 Maths because it tests both analytical and application skills. The topic requires converting real-life problems into mathematical models, constructing and solving graphical representations, and interpreting results—skills critical for higher studies and various competitive exams.
5. How should students approach long answer linear programming questions to maximize their board marks?
To score well in long-answer LPP questions:
- Begin with a clear, labeled definition of variables.
- Accurately formulate all constraints and the objective function.
- Draw the graph with all constraints, marking feasible region and corner points neatly.
- Calculate the objective function at each vertex of the feasible region.
- Conclude explicitly with maximum/minimum value and its coordinates.
6. What are common conceptual traps students should avoid in linear programming important questions?
Common traps include:
- Not including non-negativity constraints (e.g., x, y ≥ 0).
- Mistaking ‘at least’ and ‘at most’ for incorrect inequality directions.
- Omitting a constraint condition mentioned in the problem.
- Selecting a maximum/minimum value from outside the feasible region.
- Failing to check for unbounded regions as required by the question.
7. How is the optimal solution interpreted in real-life context in CBSE Linear Programming important questions?
After calculating the optimal solution (either maximum or minimum value), students must interpret it in terms of the original scenario (e.g., number of products to produce, minimum cost or maximum profit to achieve) and mention clearly which values the variables represent in context. This step is crucial for full marks in board exams.
8. In CBSE Class 12, can a linear programming problem have multiple optimal solutions? How should such answers be presented?
Yes, if the objective function has the same value at more than one vertex (usually along an edge of the feasible region), then multiple optimal solutions exist. Indicate all the values of variables that yield this optimum and represent the segment (if applicable). Clearly state: 'All points lying on the line segment between (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are optimal solutions.'
9. What are the expected trends for linear programming 5-mark questions in Class 12 CBSE exams (2025–26)?
For 2025–26, trends indicate emphasis on:
- New application contexts for LPP (transportation, diet, manufacturing, etc.)
- Questions combining 3 or more constraints, including word problems.
- Focus on correct graph plotting, intersection point calculation, and detailed interpretation.
- Occasional HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills) questions requiring explanation of unbounded solution cases.
10. Why is it necessary to check intersections and corner points while solving linear programming important questions?
Corner points are critical because, for bounded feasible regions, the optimal solution of the objective function always occurs at a vertex or along an edge. Calculating values at all intersections ensures the maximum or minimum found is truly optimal as per CBSE board marking scheme.
11. How does linear programming help in decision-making, as applied in important Class 12 board questions?
Linear programming provides a structured mathematical approach for making decisions that maximize or minimize a given objective (profit, cost, output) under specified constraints. In board questions, this demonstrates a student’s ability to apply math to solve practical, real-world issues involving resource allocation.
12. What happens if the feasible region is unbounded in a linear programming problem in Class 12?
If the feasible region is unbounded, the calculated optimum value (minimum or maximum) may not actually be the true minimum/maximum. In such cases, students must check further by analyzing whether the objective function can go lower/higher beyond the feasible region, as specifically required by CBSE examiners.