Chemistry Notes for Chapter 5 Thermodynamics Class 11 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26
1. What are the core topics summarised in the Thermodynamics Class 11 notes for quick revision?
The notes for Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry condense key topics such as the laws of thermodynamics (first, second, and third law), enthalpy and internal energy, entropy and spontaneity, key thermodynamic processes (isothermal, adiabatic, isochoric, isobaric), thermodynamic terms (system, surroundings, state functions), Hess's law, and Gibbs free energy and their applications in chemical reactions—all structured for efficient exam preparation as per CBSE 2025–26.
2. How do Class 11 Thermodynamics revision notes help in last-minute exam preparation?
Revision notes provide concise summaries of essential concepts, formula lists, and stepwise breakdowns of important principles, which saves time and aids quick recall. These notes are designed to reinforce core definitions, highlight key differences between processes, and focus attention on the most exam-relevant areas, making them highly valuable for fast-track revision before the test.
3. What is the most efficient strategy to revise Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 using summary notes?
An effective strategy is to
- First skim through the summaries of each subtopic
- Review all key formulae and their derivations
- Practice drawing and labelling diagrams for different thermodynamic processes
- Create personal concept maps linking laws, definitions, and applications
- Regularly self-test with previous exam questions to reinforce understanding
4. How do Thermodynamics notes clarify the differences between isothermal, adiabatic, isobaric, and isochoric processes?
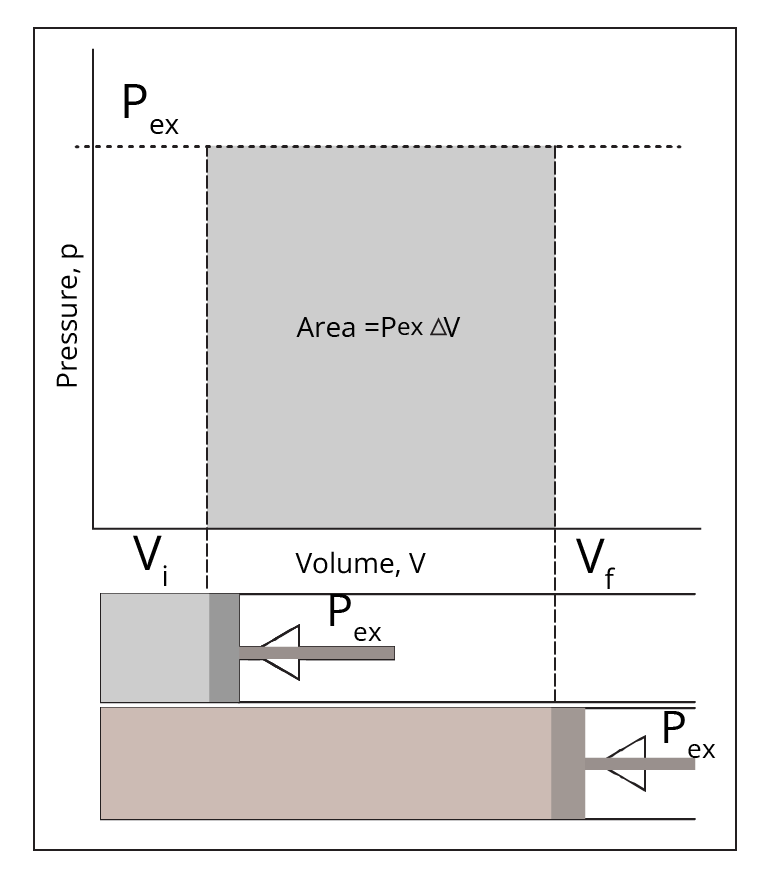
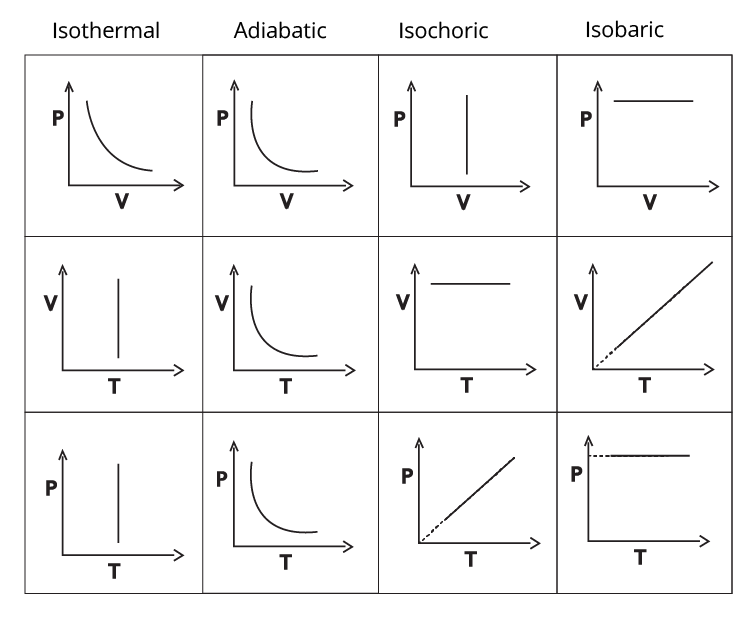
The notes present clear explanations and comparison tables that distinguish each process based on temperature, pressure, volume, and heat transfer conditions. For example, in an isothermal process temperature remains constant; in an adiabatic process, no heat exchange occurs; isobaric means constant pressure, and isochoric means constant volume. Highlighted equations and PV diagrams further reinforce the differences for quick reference.
5. Why is it important to understand entropy and Gibbs free energy for mastering Thermodynamics in Class 11?
Grasping entropy and Gibbs free energy is essential because they determine the direction and feasibility of chemical and physical processes. Entropy measures disorder, and only processes that increase total entropy tend to occur spontaneously. Gibbs free energy directly predicts spontaneity: if ΔG is negative, the process is spontaneous. These concepts are foundational for exam application and future studies in chemistry and physical sciences.
6. What common misconceptions about the first law of thermodynamics are addressed in the Class 11 revision notes?
The notes clarify that the first law (energy conservation) does NOT explain process spontaneity or direction; it only tracks energy changes as heat and work. Many students wrongly assume that if energy is conserved, any process can occur, but the second law and entropy
7. How do concept maps and diagrams in the revision notes improve retention of thermodynamics principles?
Concept maps visually connect related terms—such as system–surroundings, state/path functions, and various processes—making abstract content easier to understand. Diagrams like P–V graphs help students see relationships at a glance, enhancing memory, aiding faster revision, and boosting confidence for exams as per the CBSE 2025–26 curriculum.
8. In what ways do the Thermodynamics Class 11 notes address the application of Hess’s law and enthalpy changes?
Notes succinctly outline how Hess’s law is used to calculate enthalpy changes for reactions occurring in multiple steps. They provide formula-driven explanations and solved examples for finding enthalpy of formation, combustion, and bond dissociation, demonstrating step-by-step calculation methods relevant for board exams.
9. What are the most frequently revisited terms and their definitions included in the Thermodynamics revision notes?
The notes regularly reinforce precise definitions for core terms such as
- System and surroundings
- Open, closed, isolated systems
- State and path functions
- Enthalpy (ΔH) and internal energy (U)
- Work (W), Heat (Q), Entropy (S)
- Spontaneous vs. non-spontaneous processes
10. How can students use Thermodynamics revision notes to prepare for application-based and higher-order thinking questions?
By focusing on conceptual linkages, example-driven explanations, and 'why/how' reasoning in the notes, students can build confidence to tackle application and HOTS questions. Summaries guide students to relate laws and definitions with real-world scenarios and multi-step calculations—key to securing marks in the evolving CBSE exam pattern.