Biology Class 12 Chapter 12 Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem - 2025-26
1. How do Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 help in board exam preparation?
These solutions are designed to align perfectly with the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus and marking scheme. They provide a clear, step-by-step methodology for solving every question in the textbook exercise, which helps you understand the expected answer format and include all necessary keywords and diagrams to secure full marks.
2. What is the correct method to answer questions about the components of an ecosystem from the NCERT exercise?
Start by defining an ecosystem. Then, use a structured format to explain its two main components as per the NCERT guidelines:
- Abiotic Components: List non-living factors such as light, temperature, water, and soil.
- Biotic Components: Detail the living organisms by their trophic levels—Producers (autotrophs), Consumers (heterotrophs), and Decomposers (saprotrophs).
3. How should I draw and explain ecological pyramids for questions in Chapter 12 to score well?
To correctly present an ecological pyramid answer:
- First, draw a neat, labelled diagram representing the specific pyramid (e.g., Pyramid of Numbers or Biomass).
- Clearly label each trophic level, from producers at the base to top carnivores at the apex.
- State whether the pyramid is upright or inverted and briefly explain why, using examples from the NCERT textbook, such as a grassland ecosystem for an upright pyramid or a single tree ecosystem for an inverted one.
4. What is the best way to structure an answer for "distinguish between" questions, like comparing the grazing and detritus food chains?
For distinction questions, a tabular format is the most effective method as shown in NCERT Solutions. Create two columns, one for each concept (e.g., Grazing Food Chain and Detritus Food Chain). List the differences point-by-point based on key criteria such as:
- The starting point or primary energy source.
- The organisms involved at the first trophic level.
- The relative size and speed of energy flow.
5. How do the NCERT Solutions explain the complex process of decomposition step-by-step?
The solutions break down decomposition into five distinct, sequential steps to make it easy to remember and explain:
- Fragmentation: The breakdown of detritus into smaller particles by detritivores.
- Leaching: The process where water-soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon.
- Catabolism: The enzymatic degradation of detritus into simpler inorganic substances.
- Humification: The formation of a dark-coloured, amorphous substance called humus.
- Mineralisation: The final release of inorganic nutrients from the humus.
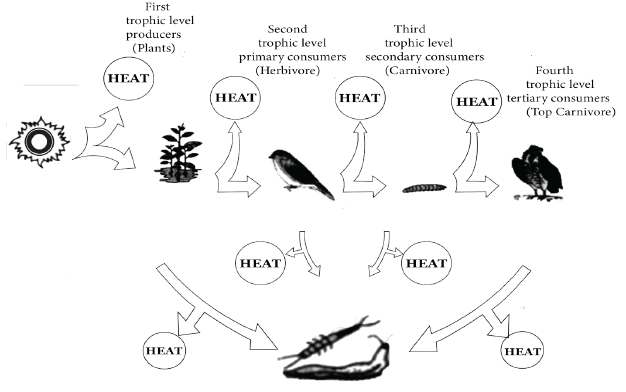
6. Why is the flow of energy in an ecosystem always unidirectional, as explained in the NCERT Solutions?
The NCERT Solutions explain that energy flow is unidirectional because it follows the laws of thermodynamics. Energy enters the ecosystem from the sun and is captured by producers. At each successive trophic level, a significant amount of energy (about 90%) is lost as heat during metabolic activities. This lost energy cannot be reused by organisms at a lower trophic level, so it flows in one direction only and does not cycle back.
7. How can I use the NCERT Solutions to master the concept of the "ten percent law" of energy transfer?
The solutions demonstrate the ten percent law by explaining that only about 10% of the energy from one trophic level is transferred and stored as biomass in the next. They advise using simple examples, like a food chain from a producer to a tertiary consumer, to show the drastic reduction in available energy at each step. This explanation helps clarify why food chains are typically limited to 4-5 trophic levels.
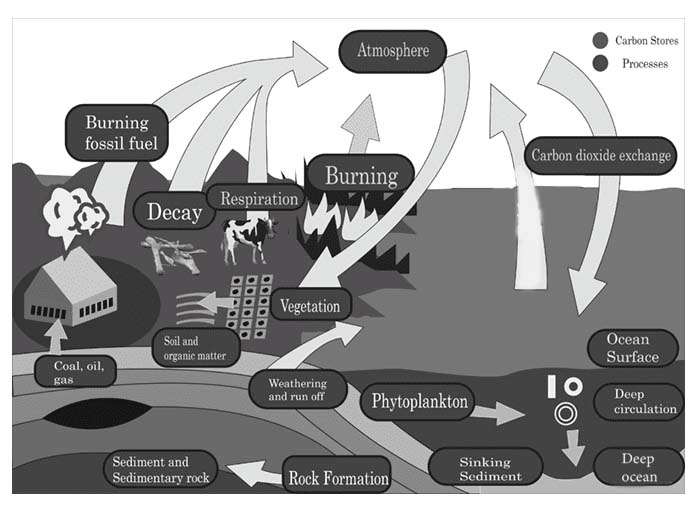
8. What is the recommended approach for answering application-based questions on nutrient cycles like the carbon cycle?
According to the CBSE pattern, you should first define the nutrient cycle. Then, systematically outline the key processes involved, such as photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and combustion for the carbon cycle. It is highly recommended to support your explanation with a simple, labelled diagram showing the reservoirs (e.g., atmosphere, oceans) and the flow of the nutrient between biotic and abiotic components.
9. What are common mistakes to avoid when solving problems from the Ecosystem chapter using NCERT Solutions?
A common mistake is simply memorising the solutions without understanding the underlying concepts. For example, students often confuse the inverted pyramid of biomass (seen in aquatic ecosystems) with the pyramid of numbers. Another frequent error is neglecting to draw labelled diagrams where required, such as for ecological pyramids or nutrient cycles, which can result in losing marks. Always focus on understanding the 'why' behind each step in the solution.
10. How do NCERT Solutions help in tackling Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) questions related to this chapter?
NCERT Solutions provide a strong foundational understanding of core concepts like productivity, decomposition, and energy flow. For HOTS questions, which often require applying these concepts to new scenarios (e.g., "What would happen to an ecosystem if all decomposers were removed?"), the solutions equip you with the correct terminology and logical framework. By mastering the standard answers, you can better analyse, synthesise, and formulate responses for complex, application-based problems.