Stepwise Answers and Key Concepts for Societal Impact Class 11
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 11 Societal Impact - 2025-26
1. What are NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 11 Societal Impact?
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 11 Societal Impact provide stepwise answers to all intext and back exercise questions, following the CBSE marking scheme. These include:
- Detailed stepwise solutions for each exercise question
- Key definitions, diagrams, and important points for revision
- Exam-oriented presentation to help score full marks
- Practice with MCQ, short, and long answer formats
2. How can I write stepwise NCERT answers to score full marks in Chapter 11 Societal Impact?
To score full marks in Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 11 Societal Impact answers, follow these steps:
- Start with a clear introduction or definition using textbook terms
- Break the answer into points or steps, adding bullets or numbering
- Include diagram or example where required, labelled neatly
- End the answer with a short conclusion or summary
- Highlight key words and phrases as per CBSE style
3. Which questions are frequently asked from Societal Impact Class 11 in school exams?
Commonly asked questions from Societal Impact Class 11 in school exams include:
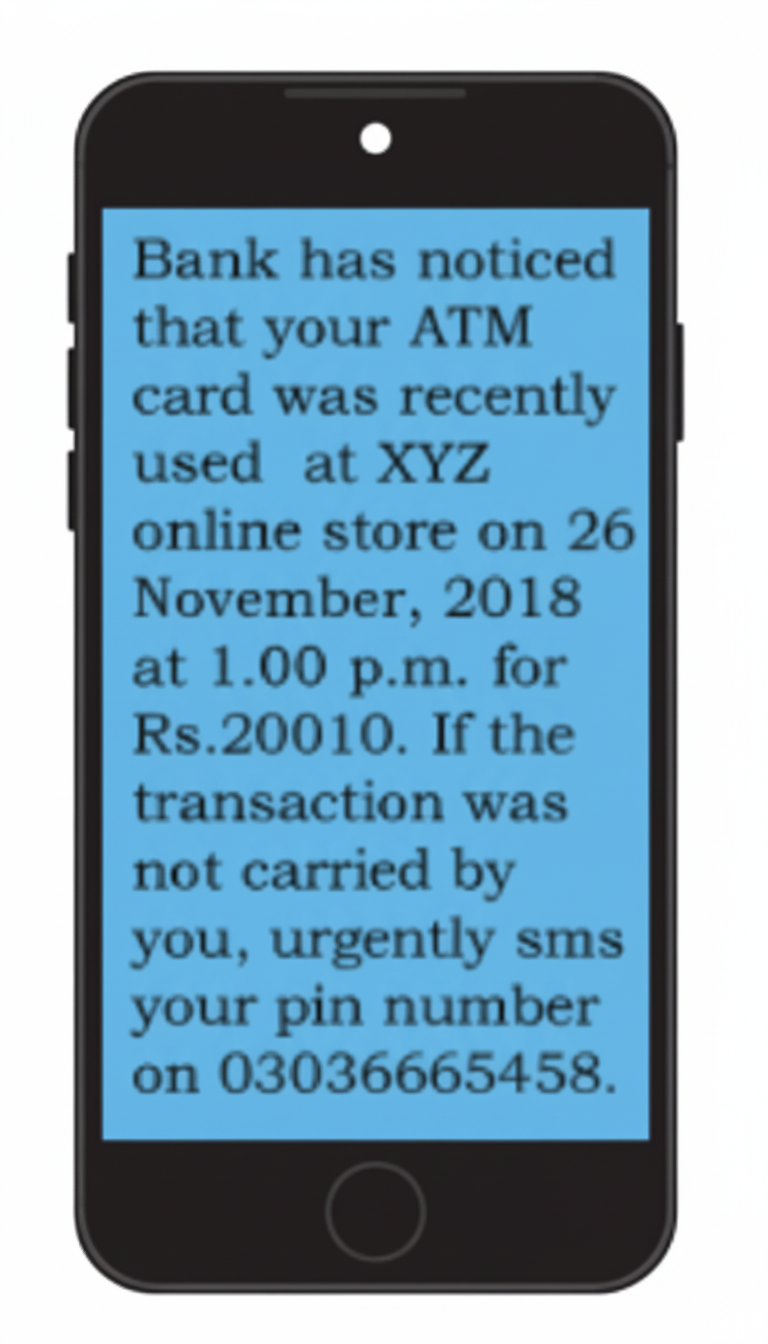
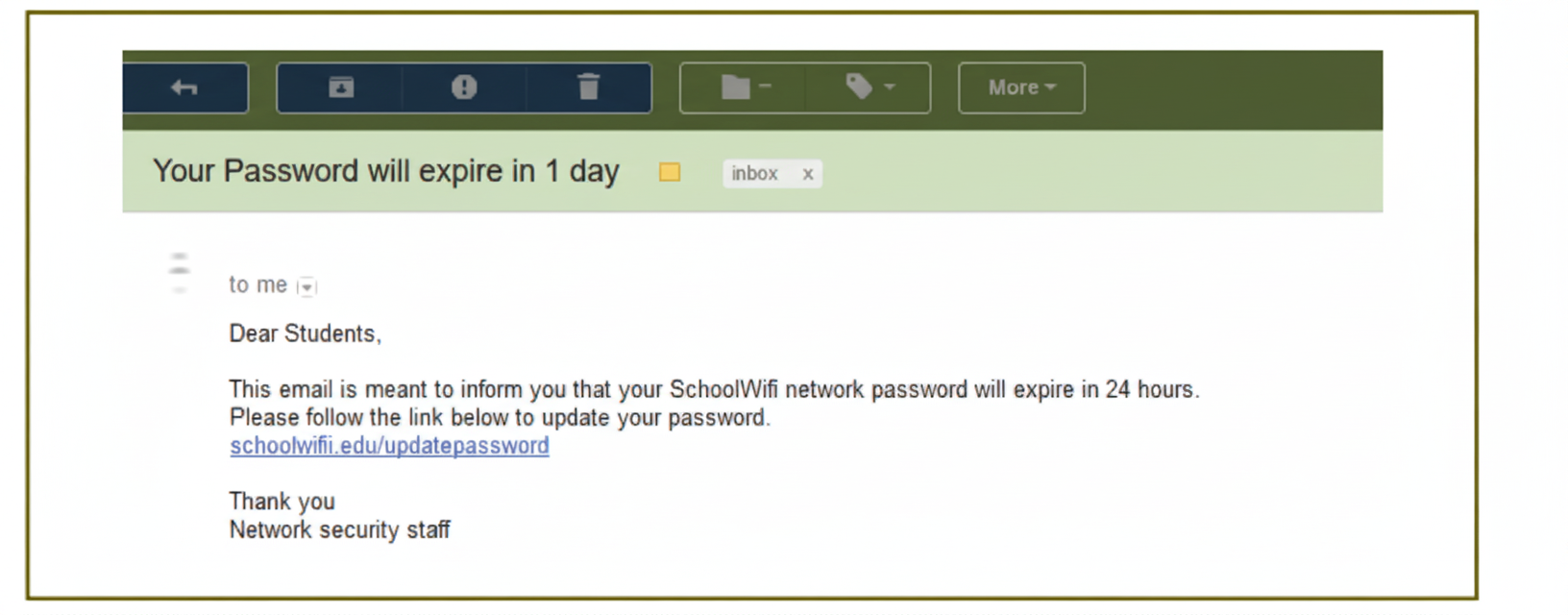
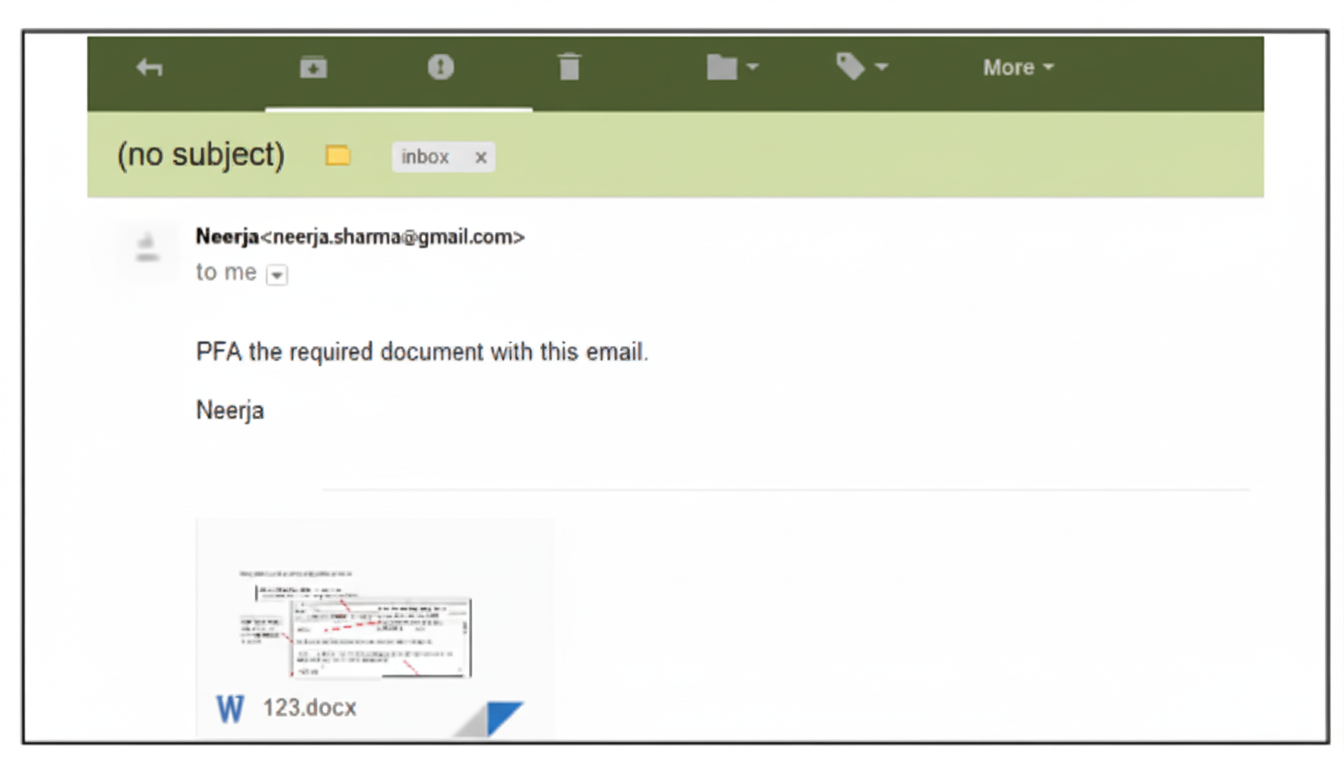
- Definitions like e-waste, digital footprint, cyber safety
- Short notes on IT Act, privacy, plagiarism, copyright
- Difference between open source and proprietary software
- List advantages and disadvantages of IT in society
- Case-based, scenario Qs on cyberbullying and netiquettes
4. Are diagrams or definitions mandatory in NCERT answers for this chapter?
Including definitions and diagrams as per question requirement in Societal Impact Class 11 answers is recommended:
- Definitions must be precise for key terms and usually fetch direct marks
- Diagrams, flowcharts, or tables can enhance clarity and earn extra marks (especially for lists/processes)
- Follow marking scheme by reading all parts of the question carefully
5. How should I structure long answers in Computer Science Chapter 11 for better marks?
For long answers in Computer Science Chapter 11, use this structure:
- Start with a clear introduction/definition
- Divide your answer into headings and sub-points
- Use numbered or bulleted lists for clarity
- Incorporate relevant examples, diagrams, or real-life cases
- Write a conclusion/summary linking back to main themes
6. Where can I download the NCERT Solutions Computer Science Chapter 11 Societal Impact PDF?
You can download NCERT Solutions Computer Science Chapter 11 Societal Impact PDF for free from most trusted educational websites. Look for:
- Free PDF download buttons on chapter solution pages
- Available with stepwise, exam-aligned answers
- Also includes revision notes and MCQ practice
7. Are NCERT solutions enough for scoring well in Class 11 Computer Science exams?
NCERT solutions are essential and sufficient for strong exam performance in Class 11 Computer Science:
- Covers all concepts as per the CBSE syllabus
- Provides exam-style answers and examples
- Helps understand marking pattern and step distribution
- Use alongside exemplar Qs and sample papers for extra practice
8. What are key topics covered in NCERT Solutions Computer Science Chapter 11 Societal Impact?
Major topics in Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 11 Societal Impact include:
- E-waste, privacy, and data protection
- IT Act and Cyber Laws
- Digital society and digital divide
- Cyber safety, security, malware, netiquettes
- Plagiarism, copyright, and open source vs proprietary software
9. How do I revise Societal Impact Class 11 quickly before exams?
To revise Societal Impact Class 11 quickly:
- Read chapter summaries and key notes
- Practice NCERT exercise and MCQ questions
- Memorise definitions, important acts, and case studies
- Revise with free PDF solution downloads
10. How does CBSE evaluate stepwise answers for Class 11 Computer Science Societal Impact?
CBSE awards marks in stepwise fashion for each part of the answer in Class 11 Computer Science Societal Impact:
- Each correct point or step scores partial marks
- Key terms, proper structuring, and presentation fetch full marks
- Diagrams and examples add value where required
- Even with mistakes in one part, correct steps can get marks
11. Do examiners award partial marks for correct steps even if the final answer is wrong?
Yes, CBSE examiners usually award partial marks for each correct step or point, even if the final answer is not fully accurate. Especially in step-marked questions:
- Accurate definitions, examples, or diagram labels receive partial credit
- Only completely irrelevant or missing steps lose marks
12. What are common mistakes to avoid in Societal Impact Class 11 answers?
Common mistakes in Societal Impact Class 11 answers include:
- Missing out on definitions or supporting examples
- Writing unclear or incomplete steps
- Not labelling diagrams or maps properly
- Ignoring CBSE marking keywords
Avoid these by reviewing stepwise NCERT solutions and marking schemes.