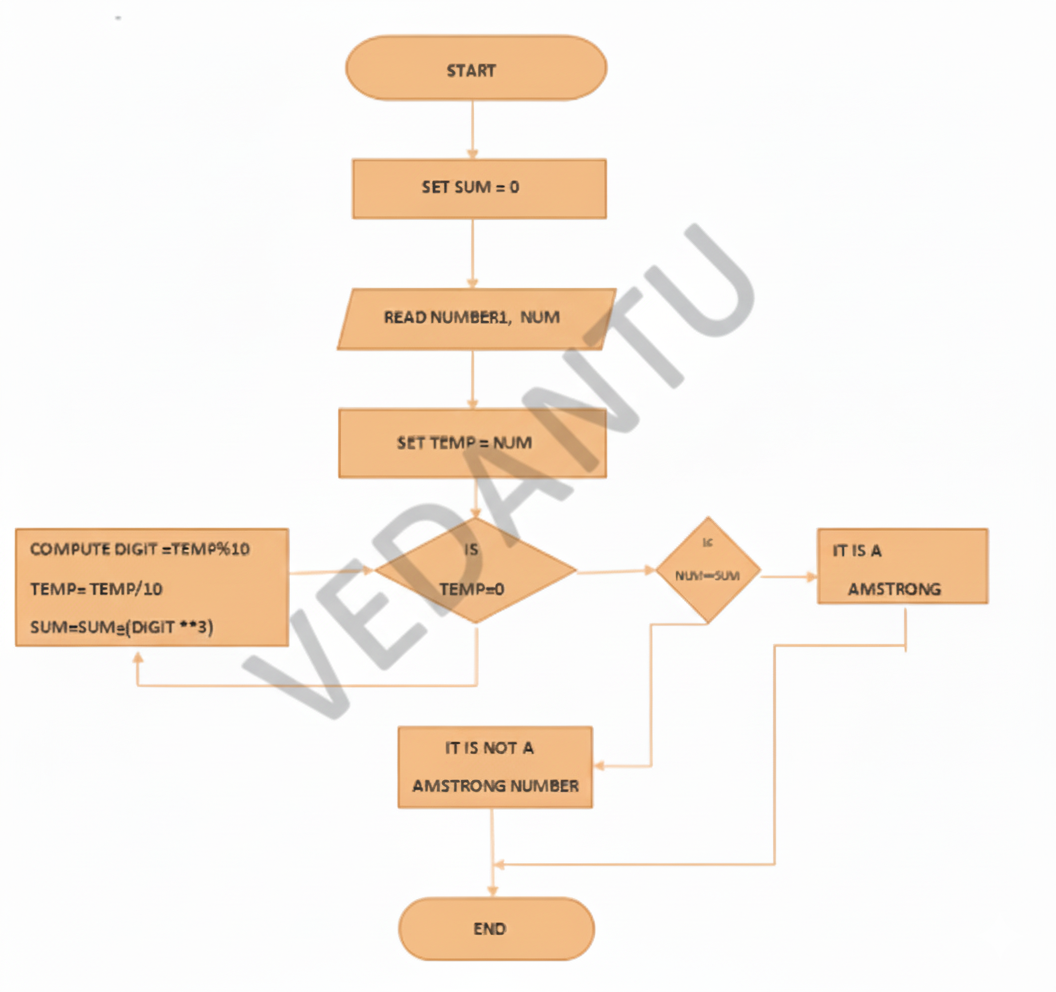
Step-by-Step Answers for Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 4 Exercises
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 4 Introduction To Problem Solving - 2025-26
1. What are NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 4 Introduction To Problem Solving?
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 4 Introduction To Problem Solving provide stepwise, exam-oriented answers for all textbook exercises. These cover:
- Detailed solutions for intext, back exercises, and exemplar questions
- Key definitions and problem-solving concepts
- Marking scheme–compliant structuring, including use of diagrams
- Sample answers tailored for CBSE 2025–26 exams
2. How should I write answers to score full marks in Computer Science Chapter 4?
To score full marks in Computer Science Chapter 4 Introduction To Problem Solving, follow these strategies:
- Use stepwise answers (each step gets marks)
- Include key definitions and diagrams as per the question
- Follow CBSE answer structure: introduction, explanation, conclusion
- Highlight keywords and important steps
- Be neat and concise, avoiding unnecessary information
3. Are diagrams and definitions necessary in answers for this chapter?
Yes, diagrams and definitions are essential for certain questions in Computer Science Chapter 4. Including them:
- Earns easy marks as per marking scheme
- Shows conceptual clarity
- Follows textbook and CBSE guidelines
- Should be neat, labeled, and relevant to the answer
4. Which are the most important topics from Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 4 Introduction To Problem Solving?
Key topics to focus on for exams from NCERT Computer Science Chapter 4 are:
- Problem-solving steps and approaches
- Algorithms and flowcharts
- Characteristics of a good solution
- Difference between algorithm and flowchart
- Real-life problem-solving examples
- Key definitions and diagram labeling
5. How can I download NCERT Solutions for Computer Science Chapter 4 PDF?
You can easily download the free PDF of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 4 Introduction To Problem Solving by:
- Clicking the "Download PDF" button on top of the solutions page
- Accessing platform-provided links for offline study
- Verifying that the PDF includes all exercises, diagrams, and exam tips
6. How do I structure long answers for Computer Science Chapter 4 to match CBSE marking?
To structure long answers for maximum CBSE marks in Computer Science Chapter 4:
- Start with a clear introduction of concepts
- Organize content in logical paragraphs or bullet points
- Include necessary definitions and labeled diagrams
- Use headings for different sections (e.g., Steps, Examples)
- End with a concise conclusion or summary
7. Are NCERT Solutions sufficient for Class 11 Computer Science exams?
NCERT Solutions are sufficient for Class 11 Computer Science board exams as they:
- Cover all NCERT textbook exercises and sample questions
- Align with the latest CBSE syllabus (2025–26)
- Provide stepwise, exam-pattern answers
- Help reinforce basic and advanced concepts
For higher scores, consider solving NCERT Exemplars and important MCQs as well.
8. What common mistakes should I avoid while solving Computer Science Chapter 4 problems?
To avoid losing marks in Computer Science Chapter 4 Introduction To Problem Solving, do not:
- Skip definitions or diagrams where required
- Miss steps in answers
- Use vague explanations or non-standard symbols
- Ignore the CBSE marking scheme and keywords
- Write too briefly or unclearly
9. How can I revise Computer Science Chapter 4 quickly before exams?
For quick revision of NCERT Computer Science Chapter 4 Introduction To Problem Solving:
- Review key definitions and important diagrams
- Practice marking-scheme based stepwise solutions
- Use flash notes and summary tables
- Attempt important questions and previous year's papers
- Follow a 1-day, 3-day, or 7-day revision planner for best results
10. Do examiners award partial marks even if the final answer is incorrect in Computer Science Chapter 4?
Yes, CBSE examiners often award partial marks in Computer Science Chapter 4 if:
- Correct steps or logic are shown, even if the final answer is wrong
- Key definitions, diagrams, or process steps are attempted correctly
- Relevant keywords are used in the explanation
Tip: Always attempt all steps clearly to maximize partial scoring.