
Zeeman effect explains the splitting of spectral lines in:
(A) Magnetic field
(B) Electric field
(C) Both A and B
(D) None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: To attempt this question, compare the difference between the Zeeman effect and the Stark effect.
Complete step by step solution:
The spinning of an electron around the nucleus generates a magnetic dipole moment, denoted by the symbol “$\mu $”. As the electrons are negatively charged, the generated dipole moment points perpendicular to the area circumscribed by the spinning of the electron.
When an atom is placed in the presence of an external field which points along the z-axis, then the applied magnetic field creates a torque on the magnetic dipole moment created by the spinning of the electrons and will orient the torque along the z-axis.
${{\mu }_{z}}={{\mu }_{B}}\cdot {{m}_{l}}$, where${{\mu }_{B}}=$Bohr’s magneton and ${{m}_{l}}=$magnetic quantum number ($l$)
The orbitals of an atom have the skill to split in the presence of an external magnetic field and the number of the splits depends upon the orbital quantum number $l$.
Therefore, the number of splits $=(2l+1)$.
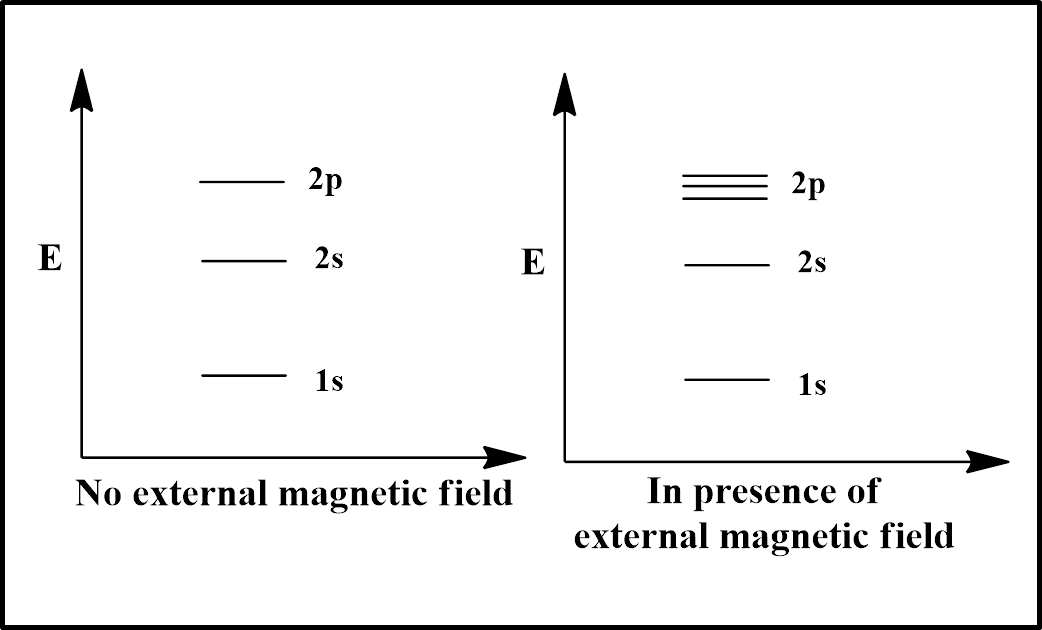
As the spectral splitting depends on magnetic quantum number ‘$l$” and s orbital have $l=0$, so there would be no splitting for s orbital (1s and 2s) as illustrated in the diagram. However, the $l$ value of p orbital is 1, so the 2p orbital will split into 3 splits ($=(2l+1)=(2\times 1+1)=(2+1)=3$).
Hence, the splitting of p orbitals and higher orbitals in an atom in the presence of the external magnetic field is known as the Zeeman effect. This effect is named after Pieter Zeeman (Dutch physicist).
Therefore, the Zeeman effect describes the splitting of spectral lines in presence of the magnetic field.
So, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Analogous to Zeeman effect is the Stark effect, in which spectral lines splitting occurs in the presence of an external electric field. So, answer (B) would have been right in the case of the electric field.
Complete step by step solution:
The spinning of an electron around the nucleus generates a magnetic dipole moment, denoted by the symbol “$\mu $”. As the electrons are negatively charged, the generated dipole moment points perpendicular to the area circumscribed by the spinning of the electron.
When an atom is placed in the presence of an external field which points along the z-axis, then the applied magnetic field creates a torque on the magnetic dipole moment created by the spinning of the electrons and will orient the torque along the z-axis.
${{\mu }_{z}}={{\mu }_{B}}\cdot {{m}_{l}}$, where${{\mu }_{B}}=$Bohr’s magneton and ${{m}_{l}}=$magnetic quantum number ($l$)
The orbitals of an atom have the skill to split in the presence of an external magnetic field and the number of the splits depends upon the orbital quantum number $l$.
Therefore, the number of splits $=(2l+1)$.

As the spectral splitting depends on magnetic quantum number ‘$l$” and s orbital have $l=0$, so there would be no splitting for s orbital (1s and 2s) as illustrated in the diagram. However, the $l$ value of p orbital is 1, so the 2p orbital will split into 3 splits ($=(2l+1)=(2\times 1+1)=(2+1)=3$).
Hence, the splitting of p orbitals and higher orbitals in an atom in the presence of the external magnetic field is known as the Zeeman effect. This effect is named after Pieter Zeeman (Dutch physicist).
Therefore, the Zeeman effect describes the splitting of spectral lines in presence of the magnetic field.
So, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Analogous to Zeeman effect is the Stark effect, in which spectral lines splitting occurs in the presence of an external electric field. So, answer (B) would have been right in the case of the electric field.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




