




Key Applications and Advantages of Using a Microscope
The microscope is an instrument which is used to observe tiny objects. They are often used in laboratories. A convex lens is used in a simple microscope to manipulate how light enters an eye. Many types of microscopes are there which are used for different purposes. The invention of the microscope dates back to the 16th century and was founded by Zacharias Janssen, a Dutch eyeglass maker.
Now you must be curious about the various types of microscope and their uses, so let’s read about it in this article.
Microscope
Types of Microscope in Detail
Various types of microscopes are there to use in laboratories. All microscopes have different uses and applications as well as importance. We will learn about the uses of the microscope below. There are majorly five types of microscopes that are mentioned below along with microscope images.
Simple microscope
Compound microscope
Electron microscope
Stereo microscope
Scanning probe microscope
Simple Microscope
A simple microscope is made of a single lens. It has a short focal length and a double convex lens. It produces a big image of tiny objects and creates a visual representation. It is used for very basic purposes rather than big investigations.
The various parts of a simple microscope are an eyepiece, body, specimen stage, objective lens, aperture diaphragm, nosepiece and base.

Simple Microscope
Uses of the Simple Microscope
The uses of the simple microscope are as follows:
It is used for examining archaeological materials such as stamps, engravings, etc.
It is used to observe tiny creatures like algae, fungi, and different biological samples.
Jewellers use it to examine the piece of gem or jewellery.
It is used by skin doctors to inspect skin allergies.
It is often used in nutrition research as well.
Compound Microscope
A compound microscope has a flat mirror on one side and a concave mirror surface on the other side. Many lenses are used in a compound microscope. It is used to examine real-world objects that are too small for the naked eye to see. It is mostly used for extensive investigative purposes.
The various parts of a compound microscope are a base, arm, stage, clips, diaphragm, nosepiece, coarse adjustment knob, and fine adjustment knob.
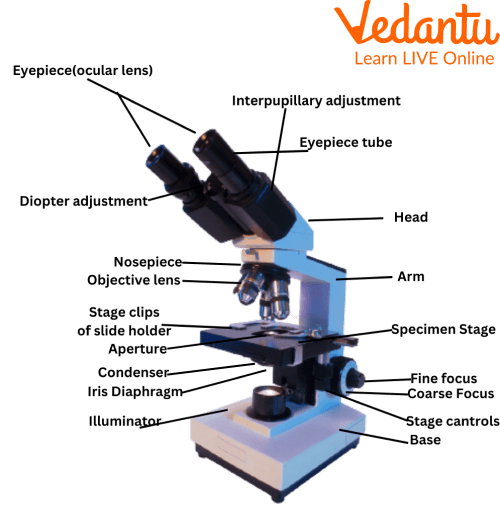
Compound Microscope
Uses of the Compound Microscope
The uses of the compound microscope are as follows:
It is mostly used to examine bacteria and viruses.
It is used to examine the minerals and metals in a blood sample.
It is also used in the investigation of a crime in a forensic lab.
It is used to observe the plant cells and different bacterias that live on these cells.
It is also found in schools for academic purposes.
Electron Microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses electrons rather than light to observe an object. In an electron microscope, electromagnets function as a lens and the whole of its system works in a vacuum.
The resolution of an electron microscope is very high and therefore it produces a high-resolution image of an object on a fluorescent screen. It is used in detailed investigations. Also, there are two types of electron microscopes: Transmission electron microscope (TEM) and Scanning electron microscope (SEM).
The various components of an electron microscope are sources of light, electromagnetic fields, image viewing and recording system.
Electron Microscope Uses
The uses of an electron microscope are as follows:
It is used for high-resolution imaging, inspection, and computer chip manufacturing.
It is used to inspect the tiny features of various diseases like tumours.
It is used in the study of rocks and minerals.
It is also used in the investigation of jewellery and gemstones.
Stereo Microscope
A stereo microscope produces a three-dimensional view of an object/specimen. It has separate objective lenses and eyepieces for each eye. Stereo microscopes have lower magnification, but longer working distances.
The various parts of a stereo microscope are: optical parts: eyepiece lenses, optional eyepiece, eyepiece tube, diopter adjustment knob, and objective lenses. Other vital parts are the focus, working stage, stage clips, and transmitted illumination.
Uses of Stereo Microscope
The uses of the stereo microscope are as follows:
It is used for observing crystals.
It is used when working with circuits and watches.
It is also used in microsurgery.
It is mostly used in examining specimens like animals and plants.
Scanning Probe Microscope
A scanning probe microscope is a type of microscope in which the examination of specimens is done at the nanoscale level. This type of microscope helps to study the specimen’s properties, reaction time, and also its behaviour when stimulated.
Uses of Scanning Probe Microscope
The uses of scanning probe microscope are as follows:
It is used to study the magnetic properties of any object.
Information can be transferred to the specimens by using this microscope.
It is used for studying the electrical properties of an object.
It is also used for the examination of nanoscale measurements of friction, wear, adhesion, and lubrication.
How to Use a Microscope?
The uses of the microscope are as follows:
Place your prepared slide on stage with care (flat one down under the lens).
Aim the glass or light such that it is illuminating the stage's hole.
Start by using the lens with the least power so you can see more of the slide.
As soon as the image seems clear, look through the eyepiece and adjust the focusing knob.
Until you acquire a clear image, try using alternative (higher-powered) objective lenses.
Summary
A microscope is used to magnify small objects/specimens. An image of an object or a sample can be examined or observed in detail with a lens. As we read, various microscopes serve different purposes. Some are used to see the shape of a cell and its nucleus, some are used for the investigation of a crime, some are used for inspecting diseases or allergies while others are used for even high-resolution imaging or nanoscale measurements. We studied the uses of the microscope and also looked at the microscope images in this article. We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Visit our website to learn more of such articles.
FAQs on Uses of Microscope Explained for Students
1. What are the main types of microscopes and what are they used for?
Microscopes are broadly classified into three main types based on their working principle and magnification power:
- Simple Microscope: This is the most basic type, using a single convex lens to magnify an object. It is used for simple tasks like reading small print or examining the parts of a flower.
- Compound Microscope: This type uses two or more lenses (an eyepiece and objective lenses) to provide much higher magnification. It is commonly used in school laboratories to observe cells, bacteria, and other microorganisms.
- Electron Microscope: This is the most powerful type, using a beam of electrons instead of light to view an object. It offers extremely high magnification and is used in advanced research to study viruses, molecules, and the detailed structure of cells.
2. What is the difference between a simple microscope and a compound microscope?
The primary difference between a simple and a compound microscope lies in their lens system and magnification capability. A simple microscope, like a magnifying glass, uses only one lens for magnification. In contrast, a compound microscope uses a system of at least two lenses (an objective lens near the object and an eyepiece lens near the eye) to achieve significantly higher levels of magnification and resolution.
3. In which fields are microscopes most commonly used?
Microscopes are essential tools in many fields. In biology and medicine, they are used to study cells, tissues, and microorganisms, helping to diagnose diseases. Forensic science uses them to analyse evidence like hair and fibres from crime scenes. Geologists use microscopes to examine the composition of rocks and minerals, while jewellers use them to inspect the quality of gemstones.
4. How does a basic light microscope work to make things look bigger?
A basic light microscope magnifies an object by passing light through it. First, a light source, often reflected by a mirror, illuminates the specimen placed on the stage. The light then passes through the specimen and into the objective lens, which creates a magnified primary image. This image is then further magnified by the eyepiece lens before the light reaches your eye, making the tiny object appear much larger.
5. Why was the invention of the microscope so important for science?
The invention of the microscope was a revolutionary moment in science because it allowed humans to see a world that was previously invisible. This led to the discovery of microorganisms, such as bacteria and protozoa. This discovery was the foundation of the germ theory of disease, which transformed medicine and public health by helping us understand how diseases spread and how they can be prevented and treated.
6. What are the basic parts of a compound microscope that a student should know?
For a student using a compound microscope, the key parts to know are:
- Eyepiece: The lens you look through at the top.
- Objective Lenses: The set of lenses on a rotating turret, closest to the specimen, which provide different levels of magnification.
- Stage: The flat platform where you place the slide with the specimen.
- Diaphragm: Controls the amount of light that passes through the specimen.
- Focus Knobs: The coarse and fine adjustment knobs that move the stage or objective lens up and down to bring the image into focus.
7. Can you see a virus with a regular school microscope? Why or why not?
No, you cannot see a virus with a regular school light microscope. The reason is a matter of magnification and resolution limits. Light microscopes can magnify objects up to about 1000-1500 times, which is enough to see larger structures like bacteria and plant cells. However, viruses are extremely small, often hundreds of times smaller than bacteria. To see them, scientists must use a much more powerful electron microscope, which uses electrons instead of light to create a highly magnified image.









