




What Are the Main Sources of Energy? Classification & Real-Life Examples
Sources of energy are very important and we perform different day-to-day tasks with the help of energy. Can you imagine your life without sources of energy? It will be very difficult to survive and life will end. But from where is this energy obtained? Are these sources man-made or natural? Have you ever heard about the alternative sources of energy that are used other than the traditional sources of energy? Let’s discuss these.
People started looking for other energy sources in the late 1900s so they could heat their homes, light their homes, and power their vehicles. People worried that sources like coal, oil, and nuclear power were depleting. Waterpower, wind power, and solar power are examples of alternative energy sources. These and other non-depletable energy sources are referred to as green or renewable.
What are Alternative Sources of Energy?
Alternative sources of energy can be defined as the use of sources of energy other than the traditional fossil fuels (such as oil, coal, and natural gas), which are shorter in supply and which are considered harmful to the environment. It includes all renewable and nuclear energy sources.
The most commonly used alternative sources of energy include the following:
Wind Energy
Solar Energy
Geothermal Energy
Bioenergy
Hydroelectric Energy
Hydrogen Energy
Nuclear Energy
Tidal Energy
The above-listed sources of energy are explained below:
Uses of Alternative Sources of Energy
1. Wind Energy
In this source of energy, the wind is used for producing electricity by making use of the kinetic energy created by air in motion.

Wind Energy
2. Solar Energy
In this source of energy, the radiation from the Sun is used which is capable of producing heat, causing chemical reactions, and generating electricity.

Solar Energy
3. Geothermal Energy
It is a source of energy that is taken from the Earth’s core. It comes from the heat which is generated during the original formation of the planet.

Geothermal Energy
4. Bioenergy
In this source of energy electricity and gas are generated from the organic matter known as biomass. Bioenergy is one of the resources available to help meet the demand for energy, it includes electricity, heat and transportation fuel.
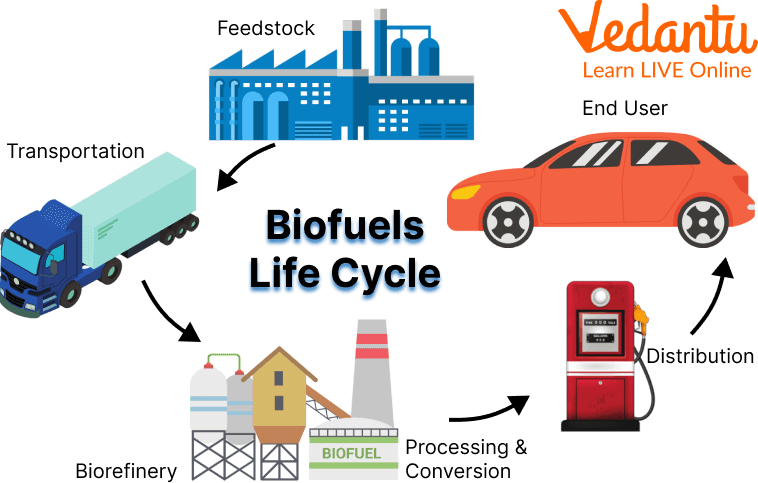
Bioenergy
5. Hydroelectric Energy
It is a source of energy that is obtained by falling water from high potential to low potential as potential is defined to flow down from a certain height. It is a form of energy that harnesses the power of water in motion—such as water flowing over a waterfall—to generate electricity.
Importance of Alternative Sources of Energy
The importance of alternative sources of energy are discussed below:
Protects the Environment: Alternative sources of energy help to protect the environment and give it the opportunity to regenerate.
Helps in Providing Sustainable Fuel Systems: The alternative sources of energy can help in creating a sustainable fuel system and can help in sustaining the ecological balance of a region.
Helps in Reducing the Dependence on Imported Fuels: Another use of alternate sources of energy is that it helps to reduce the dependence on imported fuels.
Helps in Enhancing Income: It helps in enhancing the income of the country by creating additional employment opportunities for the population of the country.
Useful in Conserving Fossil Fuels: When we make use of alternate sources of energy it helps us in conserving fossil fuels.
Useful in Slowing and Reversing Climate Change: Because the alternate sources of energy have a much lower carbon content it helps to slow down and reverse climate change.
Useful in Economic Growth: Producing more utility-scale energy systems can help in creating more economic growth.
Summary
Thus it can conclude that the alternate sources of energy are the future energy sources that will help in sustaining the environment as well as help in minimising the dependency on conventional energy sources. These sources of energy need to be explored more and more.
FAQs on Sources of Energy: Definition, Types & Benefits
1. What are alternative sources of energy?
Alternative sources of energy, also known as non-conventional energy sources, are energy sources intended to replace traditional fossil fuels like coal, petroleum, and natural gas. They are sought after because they are generally more environmentally friendly and often renewable. Key examples include solar energy, wind energy, hydropower, geothermal energy, and biomass.
2. Why is it important to develop alternative sources of energy?
It is critically important to develop alternative sources of energy for two main reasons. Firstly, conventional sources like fossil fuels are finite and are being depleted at a rapid rate. Secondly, the burning of fossil fuels releases harmful greenhouse gases, leading to air pollution, acid rain, and global climate change. Shifting to cleaner, alternative sources helps ensure a sustainable energy supply for the future while protecting our environment.
3. What are the main types of alternative energy sources as per the syllabus?
There are several main types of alternative energy sources, each harnessing a different natural process. The most common types explained in the CBSE syllabus for the 2025-26 session include:
- Solar Energy: Energy derived from the sun's radiation, used in devices like solar cookers and solar cells.
- Wind Energy: Energy generated by harnessing the power of wind through turbines.
- Hydropower: Energy created from the force of moving water, such as in large dams.
- Geothermal Energy: Heat energy from the Earth's molten core, accessed through hot springs or steam vents.
- Biomass Energy: Energy produced from organic matter like agricultural waste, wood, or animal dung in biogas plants.
- Ocean Energy: This includes tidal energy from the rise and fall of tides and wave energy from ocean surface waves.
4. How does a solar panel work to generate electricity?
A solar panel generates electricity through a process called the photovoltaic effect. Each panel contains many solar cells, typically made of silicon. When sunlight (photons) strikes the silicon cell, it transfers energy to electrons, knocking them loose. These free electrons are directed to flow in one direction, creating a direct current (DC). An inverter then converts this DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is the type of electricity used to power our homes and appliances.
5. What is the difference between renewable and alternative energy sources?
The terms are often used interchangeably, but there's a key distinction. Renewable energy refers to sources that replenish naturally over a short period, such as solar, wind, and hydropower. Alternative energy is a broader term for any source that is an alternative to fossil fuels. While most alternative sources are renewable, some, like nuclear energy, are considered alternative because they don't produce greenhouse gases during operation, but they rely on a non-renewable fuel (uranium).
6. How do alternative energy sources benefit the environment?
Alternative energy sources significantly benefit the environment by reducing our reliance on fossil fuels. Their primary advantage is the low or zero emission of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, which helps combat global warming and climate change. They also reduce air pollutants that cause smog and acid rain, leading to cleaner air and better public health. By using resources that are naturally replenished, they promote long-term environmental sustainability.
7. Which alternative energy source is considered the 'best' to use?
There is no single "best" alternative energy source, as the ideal choice depends heavily on several factors. For example, solar energy is most effective in sunny regions, while wind energy is best suited for areas with consistent, strong winds. Hydropower requires large rivers and significant infrastructure. The "best" source is determined by a region's geographical location, climate, available resources, and economic feasibility. Often, a combination of different sources provides the most reliable and sustainable energy solution.
8. What are the main disadvantages or challenges of using alternative energy?
While highly beneficial, alternative energy sources have several challenges. A major disadvantage is intermittency; solar power is only generated during the day, and wind power requires wind. This creates a need for expensive energy storage solutions like batteries. Other challenges include:
- High initial cost: Building solar farms, wind turbines, or dams requires a large upfront investment.
- Geographical limitations: Not all locations are suitable for every type of alternative energy.
- Land and environmental impact: Large solar farms or wind turbine installations can require vast areas of land and may impact local ecosystems.









