




Top 10 Everyday Uses of Transition Metals You Should Know
Transition metals are one of the groups of elements in the periodic table and make up the largest section of the periodic table located at the centre of the table. It includes columns 3 to column 12. This group is also called the “d-block” of the periodic table. Metals such as copper, nickel, and gold are present in this group. Transition metals are metals that can conduct electricity. They have high melting and boiling points. Transition metals can form compounds with different colours. Most transition metals are attracted to magnets.
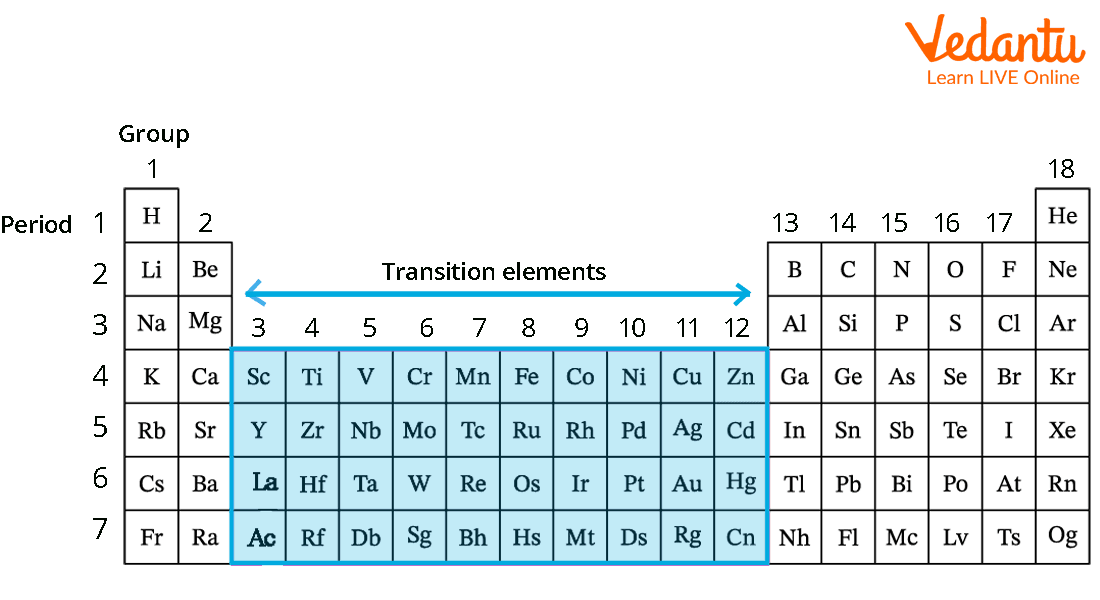
Transition Metals in the Periodic Table
Uses of Transition Metal in Daily Life
Titanium is used in the production of parts and engines of aircraft.
Iron is the most abundant transition element found in the Earth's crust. It is used as a catalyst in Haber's process to produce Ammonia.
Cobalt is used in paints and pigments because of its brilliant blue colour. It is mostly used in rechargeable batteries.
Copper is the best conductor of electricity and is used in electronics as wires. Copper is also a good conductor of heat, making it very useful to make cooking utensils.
Chromium and nickel are used as anti-corrosive coatings because of their corrosion-resistant properties and lustre.
Platinum's colour and durability make it very valuable for jewellery.
Silver is used in jewellery because of its appearance. It is also used in printed circuit boards due to its high electrical conductivity.
Gold is popularly used in jewellery because of its appearance and also because it does not react with air and water.

Gold is Used to Make Jewellery
Uses of Transition Metals
A unique property of transition metals is that they are essential for biological functions.
Iron is used in our body to create haemoglobin which is used to carry oxygen in the blood and not enough Iron in our blood can cause Anaemia.
Platinum is present in the anti-cancer drug, cisplatin and instruments used for surgery.
Copper is important for the proper development of babies in the womb.
Zinc is used in the human body to heal wounds and to store insulin in the pancreas.
Titanium is used in artificial hip replacement and other implants.
Application of Transition Metals
Transition metals are always used in industries as catalysts for various reactions.
Iron mixed with Manganese and Chromium (both elements are also transition metals) gives Steel. Steel is used for construction purposes, building cars and aircraft, etc.
Nickel is used in producing stainless steel.
Copper is used for electrical wiring.
Copper is Used for Electrical Wires
Learning by Doing
Choose the Correct Answer.
Transition metals have high melting and boiling point.
True
False
Which transition metal is used as an anti-cancer drug?
Iron
Platinum
Cooper
None of the above
Solved Questions
1. Why are transition metals important?
Ans: Transition elements are important for life and evolution because, without iron, oxygen would not reach the brain, and life would be impossible.
2. What are the elements used to make Steel?
Ans: Iron, Manganese, and Chromium are used to make Steel.
Summary
Transition elements or the d-block elements are considered as a “transition” or “bridge” between the main group elements on either side of them on the Periodic Table. Transition elements are crucial to life and evolution because, without iron, oxygen would not reach the brain, and life would be impossible.
FAQs on Uses of Transition Metals: Practical Applications for Students
1. What are some common examples of how transition metals are used in our daily lives?
Transition metals are all around us. For example:
- Iron is used to make steel for buildings, bridges, and vehicles.
- Copper is used in electrical wiring and plumbing pipes due to its excellent conductivity.
- Titanium is used in aircraft parts and medical implants because it's strong but lightweight.
- Zinc is used to galvanise steel to prevent rusting.
2. Why are the d-block elements known as 'transition' metals?
They are called 'transition' metals because their properties are intermediate, or transitional, between the highly reactive s-block metals (like sodium) and the less reactive p-block elements (like carbon). Their position in the periodic table literally bridges these two groups, and their chemical behaviours reflect this transition.
3. How do unique properties like variable oxidation states make transition metals so useful?
The ability to have variable oxidation states is a key reason for their usefulness. It allows them to participate in a wide range of chemical reactions, especially as catalysts. For instance, an element like iron can easily switch between Fe²⁺ and Fe³⁺ states, helping to facilitate complex reactions like those in industrial manufacturing or even in our own bodies.
4. Why are transition metals such effective catalysts in industrial processes?
Transition metals are excellent catalysts for two main reasons. First, their ability to adopt multiple oxidation states allows them to form temporary intermediates with reactants, creating a new reaction pathway with lower activation energy. Second, they can provide a large surface area for reactants to adsorb onto, increasing the concentration of reactants and the likelihood of a successful collision. A classic example is iron used in the Haber-Bosch process to produce ammonia.
5. What are some important uses of transition metal complexes?
Transition metal complexes have many specialised uses. For example:
- Cisplatin, a platinum-based complex, is a powerful anti-cancer drug.
- Haemoglobin in our blood is a complex of iron that transports oxygen.
- Silver complexes are used in black-and-white photography to form the image.
- Wilkinson's catalyst, a rhodium complex, is used for the hydrogenation of alkenes.
6. How are transition metals like platinum and titanium used in medicine?
In medicine, transition metals are used for their specific properties. Platinum (in the form of cisplatin) is used in chemotherapy because it can bind to DNA in cancer cells and prevent them from replicating. Titanium is widely used for surgical implants like artificial hip joints and bone screws because it is strong, non-toxic, and resists corrosion inside the body.
7. Do transition metals play any role inside the human body?
Yes, several transition metals are essential for life. They are often found at the active sites of enzymes and proteins. For example, iron is a crucial component of haemoglobin, which carries oxygen in the blood. Zinc is vital for the function of many enzymes, and copper is involved in metabolism. These are known as trace elements because our bodies need them in very small amounts to function correctly.









