




About Network Topologies in Computers
Network topology refers to the arrangement of elements in a communication network such as links, nodes, and so on. The term network topology refers to the arrangement of various types of telecommunication networks, such as command and control radio networks, industrial field buses, and computer networks. Local area networks, a common computer network installation, contain examples of network topologies.
Network topologies are classified into two types: physical and logical. While logical topology emphasizes the pattern of data transfer between network nodes, physical topology emphasizes the physical layout of the connected devices and nodes
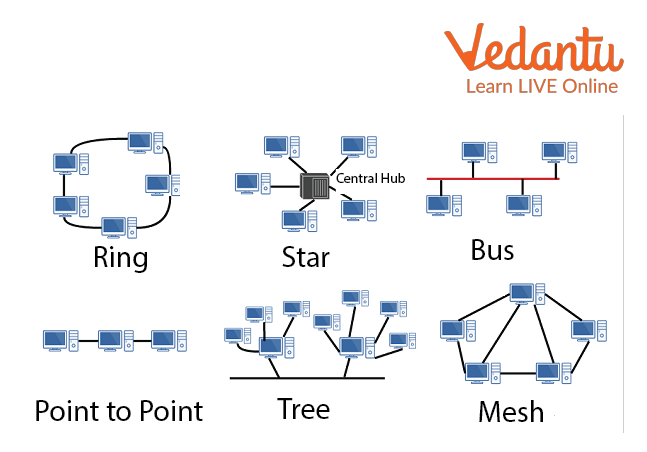
Computer Network Topology
Types of Network Topologies
In computer networks, there are primarily six types of physical topology. They are as follows:
Bus Topology
Ring Topology
Star Topology
Mesh Topology
Tree Topology
Hybrid Topology
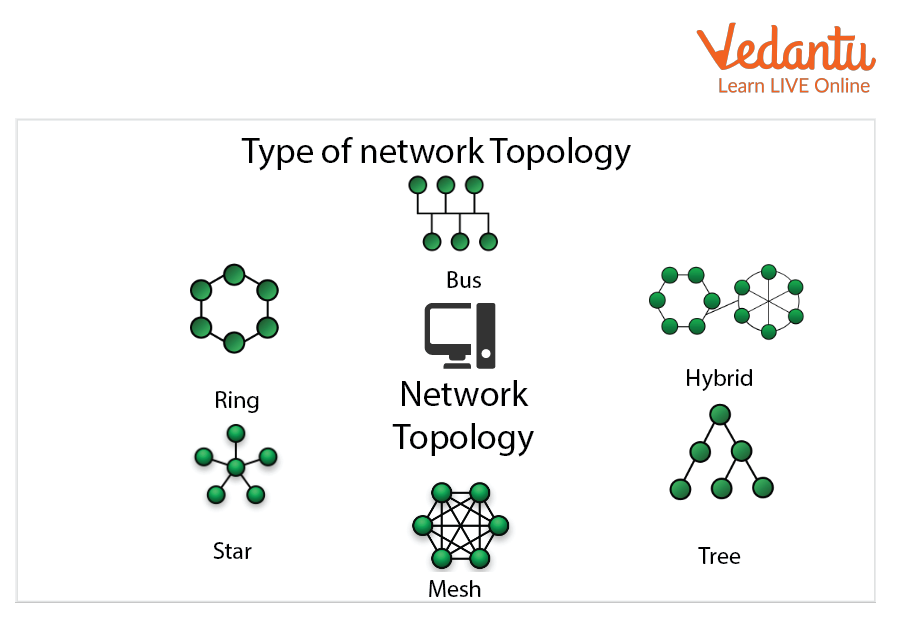
Different Types of Network Topologies
Let us now go over these topologies one by one:
Bus Topology: The simplest type of topology is called a bus topology, in which network communication takes place over a single bus or channel. There are numerous taps and drop lines connected to the bus. Drop Lines are cables that connect the bus to the computer, and taps are connectors. In other words, each node is connected to a single transmission line.
The following are the benefits of Bus topology:
Easy to install and use.
Other nodes won't be impacted if one node fails.
Less wiring is needed.
Economical to implement.
The following are Bus topology drawbacks:
Efficiency decreases as nodes increase (strength of signal decreases).
A bus failure will result in network failure.
The bus's limited length means that only a certain number of nodes can connect to it.
As messages are broadcast to all nodes, there are more security concerns and risks.
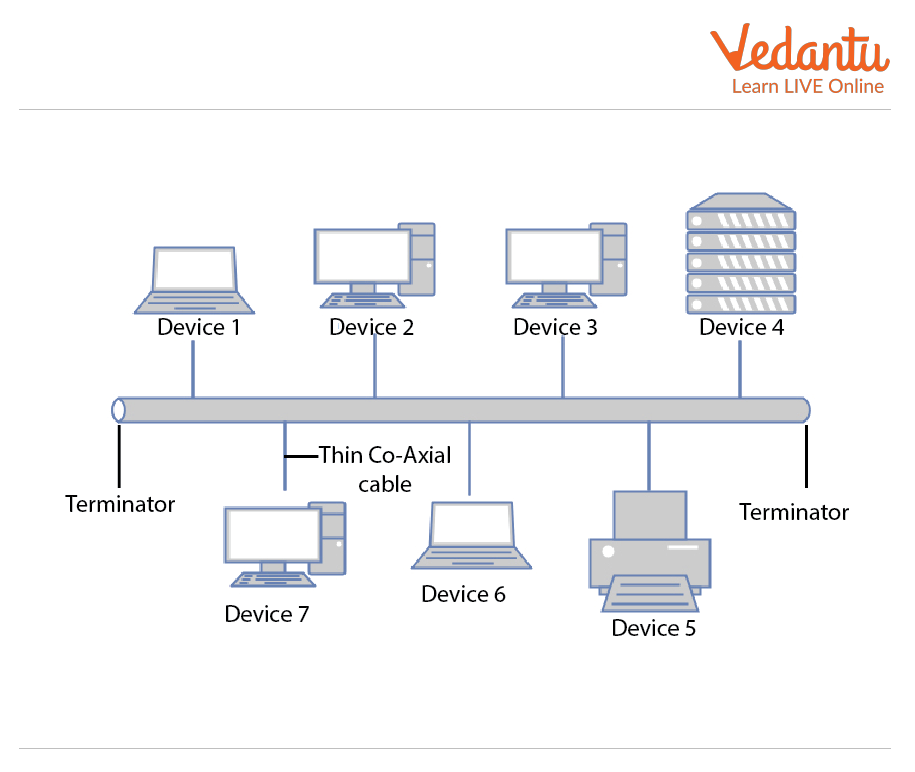
Bus Topology
Ring Topology: When two computers are connected to form a ring, the topology is known as a ring topology. The message passing is circular and unidirectional. A fixed amount of time is allotted for each computer to access the network for transmission in this deterministic network topology. Each node is a part of a closed loop.
Ring topology has the advantages listed below:
Simple installation
Fewer Cables are needed.
Minimizes the possibility of data collision.
An easy problem to solve.
The access time is the same for every node.
The following are some drawbacks to ring topology:
The network as a whole will collapse if one node fails.
Slow data transfer rate as each message has to go through the ring path.
Getting more difficult to reconfigure.
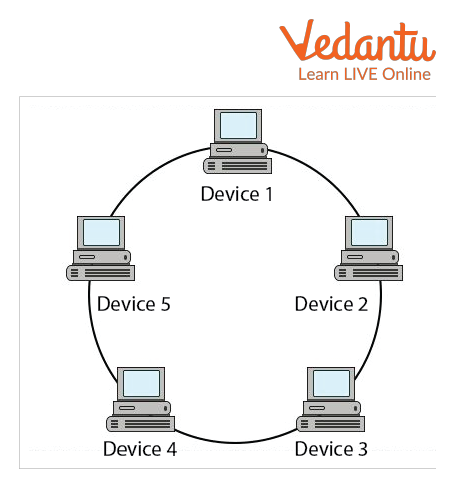
Ring Topology
Star Topology: A computer network topology known as a star topology connects each node to a central hub. The hub or switch acts as a bridge between the nodes. Any node making a service request or offering a service must first get in touch with the hub. The other connected devices function as clients in a star topology, while the hub and switch serve as a server.
The benefits of the star topology are as follows:
Less costly.
Centralized management.
Simple to scale.
Other nodes won't be impacted if one node fails.
Easy to upgrade and reconfigure.
The following are some drawbacks of the star topology:
The network will collapse if the primary device faults occur.
There are a limited number of devices in the network.
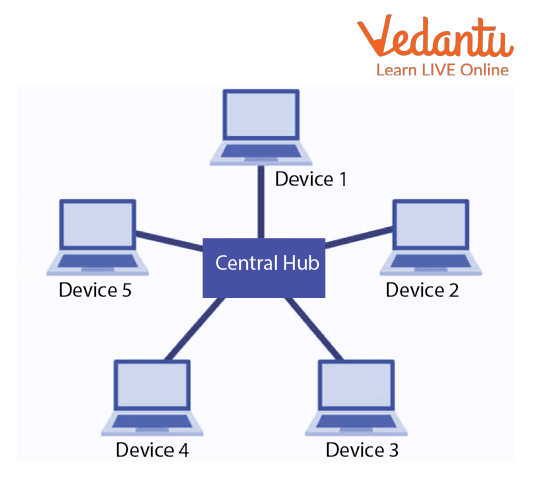
Star Topology
Mesh Topology: Mesh technology is a network configuration in which computers are linked to one another by numerous redundant connections. There are numerous methods for transferring from one computer to another. It lacks a switch, hub, or any other central computer that acts as a communication hub.
Mesh topology has the benefits listed below:
Direct communication is facilitated by dedicated links.
There are no channel traffic issues.
Due to each node having its own dedicated path, fault tolerance is good.
Quick communication.
Maintains security and privacy thanks to a separate communication channel.
There are backup options in the network in case a node fails.
Mesh topology has the following drawbacks:
Extremely high cabling is required.
Implementation is expensive.
The network is difficult to install and takes up a lot of space.
Installation and regular maintenance are extremely difficult.
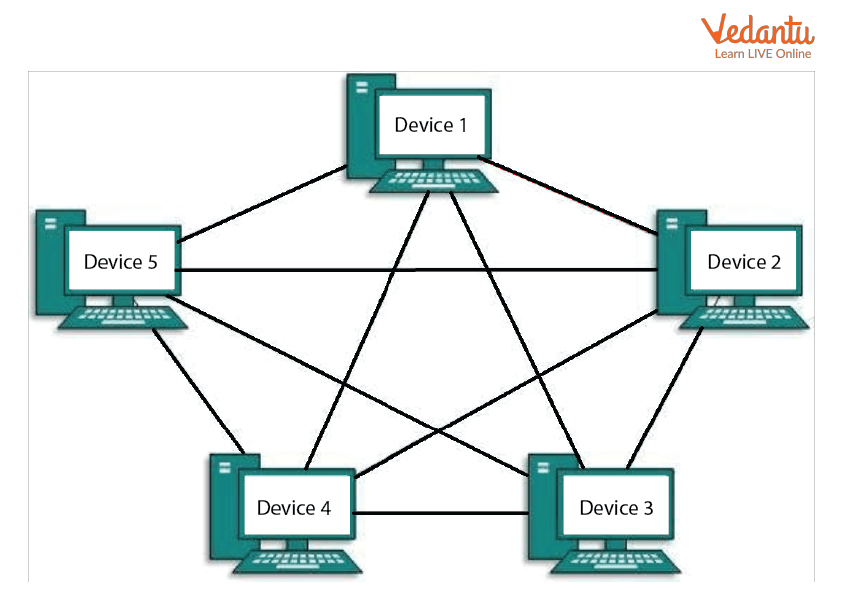
Mesh Topology
Tree Topology: A computer network topology known as a "tree topology" is one in which all nodes are either directly or indirectly connected to the main bus cable. Bus and Star topologies are combined to create tree topology. With a tree topology, the network is split up into manageable segments that can be easily maintained.
The following are the benefits of Tree topology:
Network coverage over a long distance.
Checking each hierarchy makes fault finding simple.
There should be little or no data loss.
A large number of nodes can be directly or indirectly connected.
If one of the hierarchical networks fails, the others are unaffected.
The following are the drawbacks of Tree topology:
The cost of cabling and hardware is high.
Implementation is difficult.
Hub cabling is also necessary.
A large network with a tree topology is difficult to manage.
It necessitates a lot of maintenance.
The network will fail if the main bus fails.
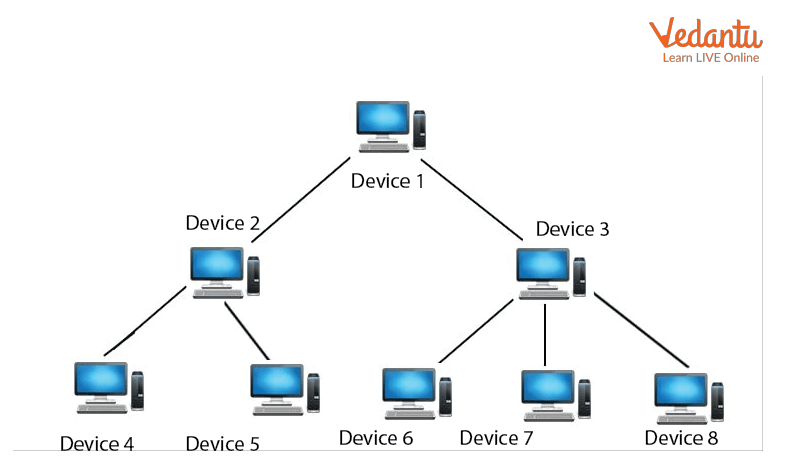
Tree Topology
Hybrid Topology: A hybrid topology is a computer topology made up of two or more topologies. All topologies in this topology are interconnected based on their needs to form a hybrid.
The following are the benefits of hybrid topology:
It can support a large number of nodes.
It allows us to modify the network to meet our specific requirements.
Very Dependable.
The following are the drawbacks of hybrid topology:
The design is complicated.
Implementation is costly.
MSAL (Multistation Access Unit) is required.
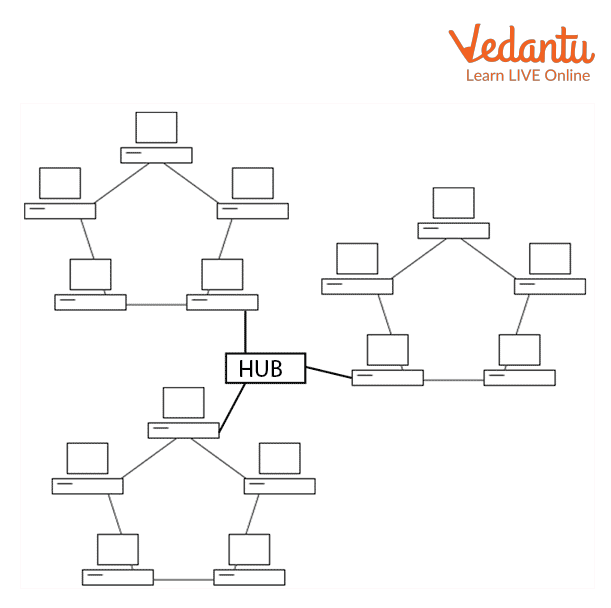
Hybrid Topology
Summary
As a result of learning about the various computer network topologies, we can conclude that the following factors must be considered when choosing a physical topology:
Installation is simple.
Tolerance for Errors.
The cost of implementation.
Cabling is needed.
Regular maintenance is required.
Reconfiguration and upgrade are simple.
Learning by Doing
Choose the Correct Answer:
1. If a star topology is used, the network will fail if..
the switch/hub breaks
one of the numerous computers system failures
the printer break
All of the above
2. The entire setup will be affected by a bus defect.
True
False
3. Tree topology combines the features of ______________topology.
Ring and Star
Star and Bus
Mesh and Bus
None of the above
Solved Questions
1. Identify the category of topology in which all nodes are linked to a central system.
Ans: Star Topology
2. The single backbone connects all computers. What kind of topology is that?
Star Topology
Bus Topology
Ring Topology
All of the above
Ans: B) Bus Topology
3. Describe a node.
Ans: A node on a network is any computer or other device that can communicate with other devices.
FAQs on Network Topologies
1. What is a network topology in the context of computer science?
A network topology refers to the physical or logical arrangement of nodes (like computers, printers, and servers) and the connections between them within a network. The physical topology describes the actual layout of the hardware and cables, while the logical topology describes the path that data signals take to travel from one device to another.
2. What are the main types of physical network topologies as per the CBSE syllabus?
The main types of physical network topologies commonly studied in computer networks are:
- Bus Topology: All devices are connected to a single central cable, known as the bus or backbone.
- Star Topology: All devices are connected to a central device, such as a hub or a switch.
- Ring Topology: Each device is connected to exactly two other devices, forming a circular pathway for signals.
- Tree Topology: A hybrid structure that combines characteristics of bus and star topologies.
- Mesh Topology: Every device is directly or indirectly connected to every other device, offering high redundancy.
- Hybrid Topology: A network that integrates two or more different topologies.
3. How does a Star topology work, and what is its main point of failure?
In a Star topology, every node on the network is connected to a central device, like a hub or a switch. All communication between devices must pass through this central point. While this design makes it easy to add or remove devices without disrupting the network, its main vulnerability is the central device itself. If the central hub or switch fails, the entire network becomes inoperable.
4. What is the difference between a Bus and a Ring topology?
The key difference lies in their structure and data flow. In a Bus topology, all devices connect to a single shared cable (backbone), and data is broadcast to all nodes, but only the intended recipient accepts it. In a Ring topology, devices are connected in a closed loop, and data travels in one direction from node to node until it reaches its destination. A failure in the main cable of a bus affects the whole network, while in a simple ring, the failure of one node can also bring down the entire network.
5. Why is a Mesh topology considered the most reliable but also the most expensive?
A Mesh topology is highly reliable because it provides multiple paths for data between any two nodes. If one link or node fails, the network can automatically reroute traffic through an alternate path, ensuring constant connectivity. This is known as high fault tolerance. However, this reliability comes at a high cost. It requires a significant amount of cabling and complex configuration because every device is interconnected, making it expensive and difficult to install and manage, especially in large networks.
6. In what specific real-world scenario would a Tree topology be an ideal choice?
A Tree topology is ideal for large, hierarchical organisations like universities or corporations with multiple departments. For example, a central 'root' switch can be on the main campus server floor, connecting to secondary switches in different buildings (the 'branches'). Each of these building switches can then connect to individual department networks, which might be set up as star topologies. This structure allows for easy expansion and segmented network management.
7. What are the primary factors a network administrator must consider when selecting a network topology?
A network administrator must evaluate several key factors to choose the right topology:
- Cost: The budget for cabling, hardware (hubs, switches), and installation.
- Scalability: How easily new devices can be added to the network in the future.
- Reliability & Fault Tolerance: The network's ability to withstand a device or cable failure without collapsing.
- Ease of Installation & Maintenance: The complexity and effort required to set up and manage the network.
- Performance: The required speed and efficiency of data transfer, considering potential bottlenecks.
8. How does a Hybrid topology offer the 'best of both worlds'?
A Hybrid topology provides flexibility by combining the strengths of two or more different topologies to meet specific needs. For example, a company might use a Star topology within its individual departments for easy management and then connect the central hubs of each department to a Bus topology backbone that runs through the building. This approach allows the network to be scalable and reliable in a cost-effective manner, leveraging the advantages of each topology while mitigating their weaknesses.











