Molecular Basis of Inheritance Class 12 extra questions and answers free PDF download


FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance - 2025-26
1. What are the most important board exam questions from the chapter Molecular Basis of Inheritance in Class 12 Biology?
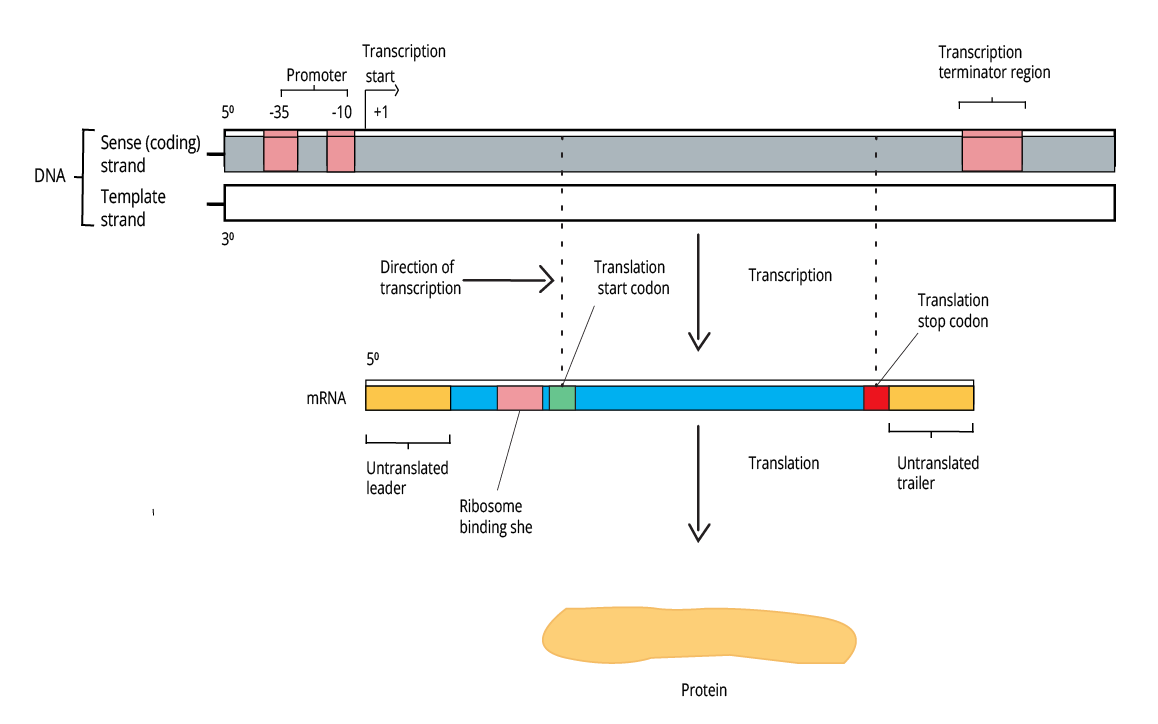
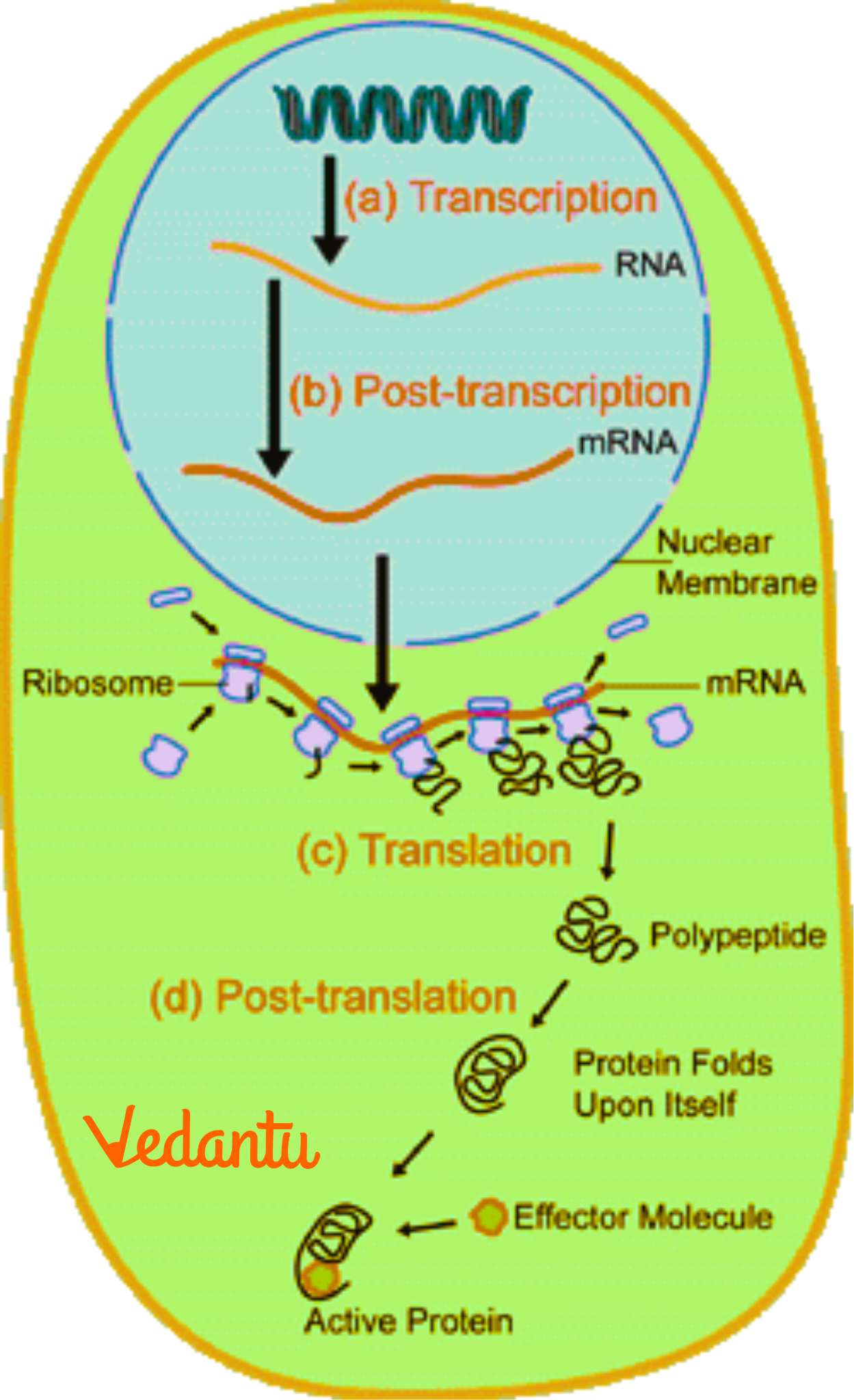
Some high-weightage exam questions from this chapter typically focus on the structure of DNA and RNA, semi-conservative replication, the central dogma (DNA → RNA → Protein), differences between transcription and translation, the genetic code and its features, the Human Genome Project goals, and mechanisms of gene expression such as the lac operon. These topics are frequently asked because they form the conceptual backbone of inheritance at the molecular level.
2. Which topics from Molecular Basis of Inheritance should be given priority for 3- and 5-mark questions in the CBSE board exams?
Focus on these priority areas for 3- and 5-mark questions:
- Semi-conservative DNA replication and its experimental proof
- Key differences between DNA and RNA
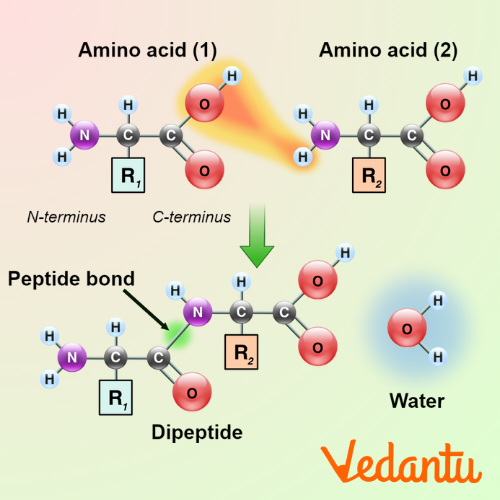
- Steps of transcription and translation
- Structure and importance of nucleosomes
- Process and significance of DNA fingerprinting
- Details about the lac operon and its regulation
- Human Genome Project milestones
These are often targeted for long-answer questions as they test both understanding and application.
3. Are HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills) questions included in the Molecular Basis of Inheritance important questions, and what types can be expected?
Yes, HOTS questions are increasingly featured. They often ask students to analyze experimental data (for example, interpreting results of Meselson-Stahl or Griffith’s experiments), predict outcomes of mutations or changes in genetic code, or compare molecular processes such as transcription in prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes. Students should be prepared for application-based scenarios and reasoning questions.
4. What common conceptual mistakes do students make in answering important questions from Molecular Basis of Inheritance?
Students often confuse leading and lagging strand synthesis, mix up roles of different RNAs (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA), or incorrectly explain why only one DNA strand is used for transcription. Another frequent error is misunderstanding the difference between codons and anticodons, or not clearly stating the evidence for semi-conservative replication. Clear, concise answers with correct terminology are essential.
5. How are board exam important questions structured in terms of marks for the Molecular Basis of Inheritance chapter?
According to the CBSE 2025–26 blueprint, questions may be:
- 1-mark – Direct definition or term-based (e.g., What is a codon?)
- 2/3-mark – Short explanations or differences (e.g., State two differences between DNA and RNA)
- 5-mark – Detailed processes, experimental descriptions, or multi-part reasoning (e.g., Describe the steps of Griffith’s experiment and its significance)
Board exam papers typically balance these types to assess both memory and understanding.
6. Why does the CBSE Board stress the importance of understanding the central dogma in molecular genetics exam questions?
The central dogma (DNA → RNA → Protein) summarises the flow of genetic information in all living cells. It is foundational for understanding mutations, gene expression, and biotechnology applications, which is why it is a frequent and important exam focus. A clear grasp of these steps allows students to connect inheritance concepts from molecular to organismal levels.
7. What kind of diagram-based questions are commonly asked in Molecular Basis of Inheritance important questions?
Diagram-based questions often require students to:
- Label the structure of DNA and nucleotides
- Depict and explain stages of DNA replication, transcription, or translation
- Interpret or create diagrams showing the lac operon, the process of genetic fingerprinting, or steps of the Human Genome Project
Well-labelled and neat diagrams can help score full marks in such questions.
8. What strategies should students use to tackle expected important questions in this chapter for the best exam results?
Effective strategies include:
- Reviewing previous years’ board exam questions for recurring topics
- Practicing precise definitions and labelled diagrams
- Writing short, clear, and pointwise answers for long questions
- Memorising and understanding key experiments (Griffith, Meselson-Stahl, Hershey-Chase)
- Linking conceptual knowledge to real-life applications such as genetic testing or biotechnology
9. What is the significance of practicing important questions from the chapter rather than just reading the theory?
Practicing important questions helps students:
- Identify frequently tested concepts
- Develop skills to frame exam-appropriate answers
- Improve time management during the exam
- Spot conceptual gaps and address common errors ahead of time
- Build confidence in applying knowledge to both direct and applied questions
10. How do board trends influence the selection of important questions in the Molecular Basis of Inheritance chapter?
Board trends are analyzed by reviewing past years’ exam questions to determine which topics are frequently repeated or have high-scoring potential. This influences the selection of important questions toward key experiments, processes, and concepts that the CBSE Board tends to emphasize. Keeping track of trends helps both students and teachers to prioritize specific areas within the chapter.
11. If a gene mutation changes the codon UAU to UAA in a gene, why is this significant for protein synthesis and which type of question tests this concept?
This mutation changes a codon for the amino acid tyrosine (UAU) to a stop codon (UAA), leading to premature termination of translation and a truncated, likely nonfunctional protein. This concept is usually tested through application-based or HOTS questions, assessing students’ understanding of the consequences of point mutations at the molecular level.
12. What key skills do students develop by solving important questions from the CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 5?
Solving such questions develops:
- Conceptual clarity on core processes (replication, transcription, translation)
- Scientific reasoning for experiments and evidence interpretation
- Answer structuring for both short and long-form responses
- Ability to apply theory to practice and real-life situations (like DNA fingerprinting)