




An Overview of Class 12 Biology Identification Of Stages Of Gamete Development Experiment
You might be knowing that sex organs are the organs required for sexual reproduction. But where are these organs located? These organs are present in the reproductive system. Gametogenesis is the process through which gamete formation occurs. Spermatogenesis occurs in males to form sperm and oogenesis occurs in females to produce ovum. These organs are not only primary sex organs but also act as endocrine glands that produce a large number of hormones. Such testosterone is secreted by the testis, and oestrogen and progesterone are secreted by the ovary. To know more about ts of testis and ovary, continue reading the article.
Table of Content
Aim
Articles Required
Theory
Procedure
Observations
Results
Precautions
Lab Manual Questions
Viva Questions
Practical Based Questions
Conclusion
Aim
This experiment aims to identify the stages of gamete development, i.e., T.S. of testes and ovaries through permanent slides from mice.
Articles Required
Permanent slides of T.S of testes
Permanent slides of T.S of the ovary
Compound microscope
Theory
Testes are the primary male sex organ whereas ovaries are the primary female sex organ. Both male and female sex organs are paired structures. Ovaries produce female gametes ovum and testes produce male gametes called sperm.
Ovaries are present in the reproductive system and also act as an endocrine gland that produces some important endocrine hormones. Testes are present outside the abdominal cavity in a pouch called the scrotum to maintain a 2-3°C lower temperature.
Procedure
Place the slides under the microscope. Observe slides both in low as well as high power microscopes.
Observations
T.S of Testis
There are two coverings of the testis of mammals. The outer covering is tunica vaginalis and the inner covering is tunica albuginea.
Seminiferous tubules are present in testicular lobules. And interstitial tissues are present between seminiferous tubules.
Different types of cells are present inside seminiferous tubules. The arrangement of cells inside seminiferous tubules is given below:
Spermatogonia, spermatocytes, spermatids, spermatozoa, sperm
Between germinal cells Sertoli cells are also present, these cells provide nutrition to germ cells and gametes.
A large number of spermatozoa with their embedded head in Sertoli cells are present in seminiferous tubules.
Leydig cells are also present in interstitial space and are responsible for making a hormone called testosterone.
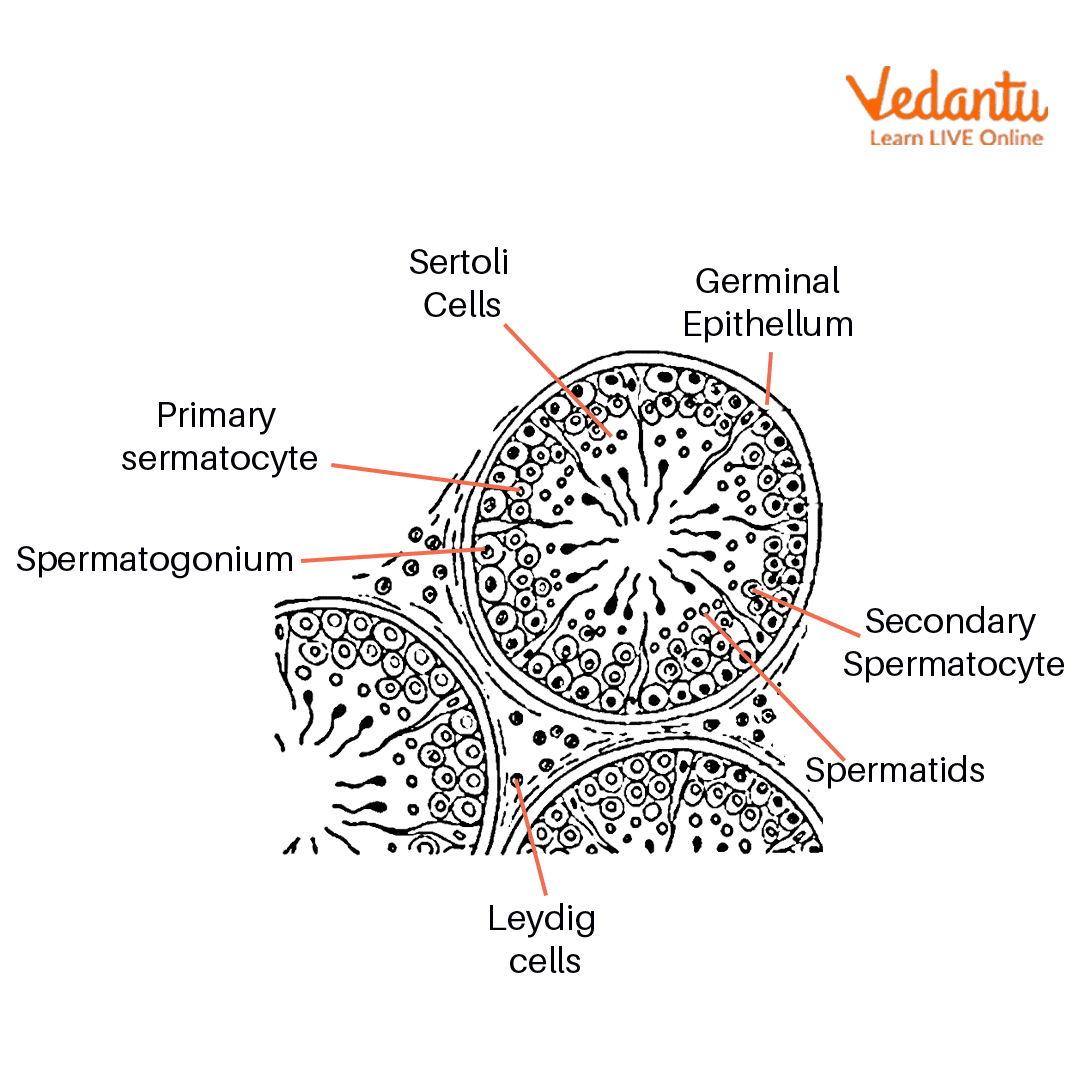
T.S of Testis
T.S of Ovary
The ovary of the mouse is covered by a thick layer of germinal epithelium followed by a layer of tunica albuginea.
The outer part of the ovary is the cortex and the inner part is the medulla. The inner medulla consists of Graafian follicles which are divided into primary, secondary, or tertiary Graafian follicles at various stages of development.
The germinal epithelium of the mammalian ovary is lined by cuboidal epithelium cells.
The medulla also contains blood vessels, nerves, and smooth muscles.
Each follicle contains an ovum which is surrounded by a large number of follicles
The cortex contains young and mature follicles
The cortex also contains corpus lutetium which is a large yellowish body that acts as an endocrine gland in pregnancy.
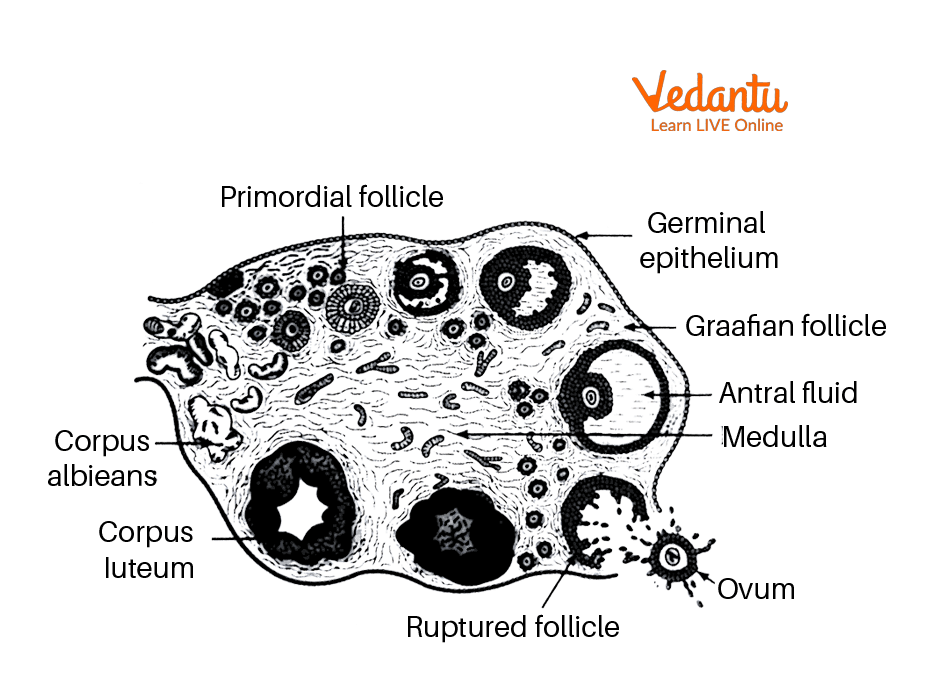
T.S of the Ovary
Results
The various parts of the testis and ovum are seen in this experiment.
Precautions
Slides should be washed properly before using
All slides should be handled very carefully
Adjust the lens so that focus would be better.
Lab Manual Questions
Q1. What is gametogenesis?
Ans: Gametogenesis is defined as the process by which males and females make gametes.
Q2. What are the main parts of spermatozoa?
Ans: Head, neck, middle piece, and tail are the main parts of sperm.
Q3. At what stage does the human ovum release from the ovary?
Ans: At the secondary oocyte stage ovum is released from the ovary.
Viva Questions
Q1. What is oogenesis?
Ans: Oogenesis is the process of the formation of the ovum from germ cells. This process occurs inside the ovum which is a female sex organ.
Q2. What is spermatogenesis?
Ans: Spermatogenesis is the process of the formation of sperm from male germ cells. This process occurs in the testis which is a male sex organ.
Q3. What are the functions of the testis?
Ans: The main function of the testis is to make sperm which is a male gamete and it also acts as an endocrine gland that makes testosterone.
Q4. Explain the functions of the ovary.
Ans: Ovary is the primary sex organ that makes female gametes ovum. It also acts as an endocrine gland and produces several hormones such as oestrogen and progesterone.
Q5. What are secondary sex organs?
Ans: Secondary sex organs are the organs that facilitate the conduction and transport of gametes and these organs include ducts and glands.
Q6. What is the spermatid?
Ans: Spermatids are haploid cells that are formed by a division in secondary spermatocytes. It further undergoes development to form sperm.
Q7. What is the ploidy of primary spermatocytes?
Ans: Primary spermatocytes are diploid cells that undergo meiosis to form sperm.
Q8. What is the ploidy of spermatids?
Ans: Spermatids are haploid cells formed by meiotic division.
Practical Based Questions
Q1. Which of the following is part of male reproductive system?
Testis
Breast
Stomach
None of the above
Ans: 1. Testis
Q2. Which stain is used in ts of the ovary?
Safranin
Methylene blue
Iodine
None of the above
Ans: 1. Safranin
Q3. What is the colour of the ovary?
Black
Organ
Grey
Green
Ans: 4. Grey
Q4. Which of the following is the secondary reproductive organ in male
Breast
Testis
Ovary
Epididymis
Ans: 4. Epididymis
Q5. What is the normal shape of the testis?
Rectangular
Oval
Circular
None of the above
Ans: 2. Oval
Q6. Where is sperm stored?
Epididymis
Bulbourethral gland
Prostate gland
None of the above
Ans: 1. Epididymis
Q7. What are the functions of testis?
Sperm production
Hormone production
Both of the above
None of the above
Ans: 3. Both of the above
Q8. Which hormone is produced by the ovary?
Oestrogen
Progesterone
Both of the above
None of the above
Ans: 3. Both of the above
Conclusion
In this article, we have studied an experiment on the identification of stages of gamete development.
We have seen the t.s of mammalian ovaries and t.s of mammalian testis under a microscope.
Various stages of development have been seen in ts section
Spermatogonia, spermatocytes, and spermatids are visible in ts of the testis.
Different follicular cells of ovaries are also seen in ts of ovaries.
FAQs on Class 12 Biology Identification Of Stages Of Gamete Development Experiment
1. What are the key stages of gamete development identified in CBSE Class 12 Biology practicals?
In CBSE Class 12 Biology, the key stages of gamete development are identified as follows:
- Spermatogenesis: involves spermatogonia, primary spermatocytes, secondary spermatocytes, spermatids, and spermatozoa (in males).
- Oogenesis: includes oogonia, primary oocytes, secondary oocytes, and the mature ovum (in females).
2. What makes the identification of gamete development stages important for board exams?
Identification of gamete development stages is frequently asked in CBSE practical and theory exams because it tests conceptual understanding of reproductive biology, cellular processes like meiosis, and the ability to relate structure to function. Board trends show this topic appears in both 3-mark and 5-mark exam sections for its high biological significance and diagrammatic skill assessment.
3. List the differences between T.S. of testis and T.S. of ovary as required for exam answers.
- Testis: Contains numerous seminiferous tubules; main cell types include spermatogonia, spermatocytes, spermatids, spermatozoa, and Sertoli cells; produces sperm and testosterone.
- Ovary: Shows multiple Graafian follicles at various stages; main structures include primordial, primary, secondary, tertiary follicles, corpus luteum, and ovum; produces ova, oestrogen, and progesterone.
4. How does the location and structure of testis help in gamete development according to CBSE marking guidelines?
The testis is located outside the abdominal cavity in a scrotal pouch to maintain a temperature 2-3°C lower than body temperature, which is crucial for spermatogenesis. The seminiferous tubules provide a protected site for germ cell development. Proper mention of structural adaptations, as per CBSE guidelines, helps secure marks in exam answers.
5. Explain the significance of secondary oocyte stage in oogenesis with respect to ovum release.
The secondary oocyte is released from the ovary during ovulation. This stage is important as it is ready for fertilisation if it meets a sperm cell. In the context of exam answers, highlighting this stage shows understanding of sequential events in female gamete development as per CBSE curriculum expectations.
6. Why are Sertoli cells and Leydig cells important for spermatogenesis, and how can misconceptions about their roles be avoided in exams?
Sertoli cells provide nutrition and support to developing germ cells, while Leydig cells produce testosterone, which is essential for spermatogenesis. A common misconception is to mix up their roles. Clearly stating their distinct functions is crucial for 1-mark or 2-mark exam answers in the CBSE Biology paper.
7. What common precautions must students take during the identification of gamete stages experiment in the lab exam?
- Handle permanent slides carefully to avoid breakage.
- Clean slides before and after observation.
- Adjust the microscope lens for proper focus to clearly see stages of development.
8. Compare the hormone production roles of the testis and ovary as expected in important board exam questions.
- Testis: Produces the hormone testosterone, which supports male secondary sexual characteristics and spermatogenesis.
- Ovary: Produces oestrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle, female secondary sexual characteristics, and support pregnancy.
9. How can students ensure their exam diagrams for gamete development are CBSE-score compliant?
To ensure diagrams meet CBSE scoring criteria:
- Use clear labels for all cell stages and major structures.
- Draw neatly with accurate proportions for testis and ovary sections.
- Mention slide magnification or identifying stains when relevant (e.g., safranin for ovary).
10. What are some higher-order thinking questions (HOTS) that may be asked on identification of gamete development stages in recent CBSE board trends?
CBSE is increasingly focusing on application-based HOTS questions, such as:
- Predicting the effects of hormonal imbalance on gametogenesis.
- Evaluating what would happen if the temperature of the scrotum rose to body temperature.
- Comparing the consequences of spermatogenesis and oogenesis errors on fertility.
























