What Are the Main Steps of Nutrition in Amoeba with Diagram?
Nutrition in Amoeba is a fascinating example of how single-celled organisms manage complex life processes without specialized organs. Understanding this process helps us grasp the basics of nutrition in unicellular organisms and how they utilize food for survival. This topic is especially important for students studying life processes and cell functions in biology.
Nutrition In Amoeba: Definition and Overview
Nutrition in Amoeba refers to the process by which this unicellular protozoan acquires, digests, absorbs, and utilizes food for energy and growth. Amoeba shows a type of heterotrophic nutrition called holozoic nutrition, where it engulfs solid food particles directly from its environment. Studying this provides a clear model for how basic life processes occur even in the simplest living beings.
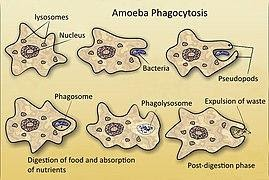
Steps of Nutrition in Amoeba
The nutrition in Amoeba occurs through a series of well-coordinated steps. These essential stages are similar, at a basic level, to those in more complex organisms and are often discussed in class 12 nutrition in amoeba notes.
- Ingestion: Amoeba approaches a food particle and extends finger-like projections, called pseudopodia, around it. This process is called phagocytosis or cell eating. The food particle becomes enclosed in a bubble called the food vacuole.
- Digestion: Enzymes from the amoeba’s cytoplasm enter the food vacuole. These enzymes break down large, complex food molecules into simpler, soluble forms, making them easier to absorb.
- Absorption: The digested, soluble food diffuses from the food vacuole into the cytoplasm. This absorbed nutrition provides the materials needed for various cellular functions.
- Assimilation: The Amoeba uses the absorbed nutrients for energy, growth, and cell repair. This process is vital for routine activities and the overall maintenance of the cell.
- Egestion: Undigested food particles are expelled from the cell. The vacuole containing waste moves towards the cell membrane, merges with it, and releases its contents to the outside.
Key Features of Nutrition in Amoeba
Some unique aspects make nutrition in amoeba a valuable example for biology topics and MCQs. These features highlight its significance for understanding basic nutrition processes in living organisms.
- Simple, single-celled organism: Amoeba manages all processes, including nutrition, inside one cell.
- No digestive organs: Nutrition takes place with the help of pseudopodia and food vacuoles rather than specialized systems.
- Flexible process: The amoeba adapts its nutrition method quickly depending on food availability in its surroundings.
- Use of enzymes: Enzymes play a key role in digestion, similar to the human digestive system, though on a simpler scale.
Nutrition in Amoeba: Diagram (Explained)
Although this page does not include a nutrition in amoeba diagram, many textbooks illustrate the series of steps: the amoeba surrounds a food particle with its pseudopodia, forming a food vacuole, where digestion and absorption occur. These diagrams are essential for class 12 board exams and entrance tests.
Examples and Applications
Nutrition in amoeba examples are found in aquatic ecosystems, where amoebas play a role in decomposing organic matter. Their nutrition process is also vital for research in cellular biology and medicine, helping scientists understand basic cell functions. Learning about amoeba nutrition enhances our awareness of nutrient cycles and cell-level digestion, alongside other organisms like fungi (see nutrition in fungi).
Comparison: Nutrition in Amoeba vs. Higher Organisms
| Feature | Amoeba | Higher Animals (e.g. Humans) |
|---|---|---|
| Body Structure | Single-celled organism | Multicellular, complex systems |
| Nutrition Type | Holozoic (engulfs food) | Holozoic (ingestion, digestion in organs) |
| Digestion Site | Food vacuole (intracellular) | Stomach and intestines (extracellular) |
| Absorption | Direct into cytoplasm | Through intestinal walls to blood |
| Egestion | Cell membrane expels waste | Specialized organs (anus/rectum) |
The table above shows that while the processes are similar in principle, amoeba conducts all nutrition steps within a single cell, whereas higher animals have specialized organs for each function.
Why Study Nutrition in Amoeba?
Nutrition in Amoeba forms an essential base for more advanced biology topics, such as cell theory, metabolism, and health. It also aids in understanding how various nutrients affect cellular and body functions. Students can link this topic to broader concepts like life processes and environmental studies, such as effects of climate changes.
Summary
Nutrition in Amoeba demonstrates how even simple organisms follow a systematic process to ingest, digest, absorb, and utilize food. It highlights essential steps of holozoic nutrition within a single cell and forms a crucial foundation for understanding more advanced biological systems. Learning about amoeba’s nutrition strengthens core biology concepts and their applications across science, medicine, and the environment.


FAQs on Nutrition in Amoeba: Process and Steps
1. What is nutrition in Amoeba?
Nutrition in Amoeba refers to how the organism obtains and utilizes food for its survival.
Amoeba demonstrates holozoic nutrition, involving ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion. The process includes:
- Ingestion: Capturing food using pseudopodia
- Digestion: Breaking down food inside the food vacuole by enzymes
- Absorption: Absorbing digested nutrients into the cytoplasm
- Assimilation: Utilizing nutrients for energy and growth
- Egestion: Expelling undigested food outside the body
2. Describe the steps of nutrition in Amoeba with a diagram.
Amoeba follows five key steps in nutrition: ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion.
These steps are:
- Ingestion: Amoeba engulfs food by forming pseudopodia.
- Digestion: Enzymes in the food vacuole break down the food.
- Absorption: Nutrients are absorbed into the cytoplasm.
- Assimilation: Absorbed nutrients are used for energy and growth.
- Egestion: Undigested waste is removed from the cell.
3. What is the role of pseudopodia in the nutrition of Amoeba?
Pseudopodia help Amoeba capture and engulf food particles.
The functions include:
- Extending outward to surround the food particle
- Enclosing the food to form a food vacuole
- Ingesting the particle for digestion inside the cell
4. How does digestion occur in Amoeba?
Digestion in Amoeba takes place inside the food vacuole by enzymatic action.
The key steps are:
- Digestive enzymes are released into the food vacuole
- Enzymes break down complex food into simpler, absorbable molecules
- The digested nutrients diffuse into the cytoplasm for assimilation
5. Explain the difference between holozoic nutrition and saprophytic nutrition with reference to Amoeba.
Amoeba shows holozoic nutrition, while saprophytic nutrition is seen in fungi and bacteria.
Differences:
- Holozoic nutrition involves ingesting solid food and internal digestion (as in Amoeba)
- Saprophytic nutrition involves absorption of dissolved organic matter from decaying substances (not seen in Amoeba)
6. Write a short note on the process of egestion in Amoeba.
Egestion in Amoeba is the process of removing undigested food material.
- After digestion, waste remains in the food vacuole
- The vacuole moves towards the surface of the cell
- Undigested material is expelled out by rupturing the cell membrane at any place
7. Which type of nutrition is found in Amoeba? Name the steps involved in this process.
Holozoic nutrition is found in Amoeba.
The steps involved are:
- Ingestion
- Digestion
- Absorption
- Assimilation
- Egestion
8. How does Amoeba obtain its food?
Amoeba obtains its food by a process called phagocytosis.
- It moves towards food using pseudopodia
- Engulfs the food particle forming a food vacuole
- Digests and absorbs nutrients inside the cytoplasm
- Expels undigested waste
9. Why does Amoeba not have a fixed shape, and how does this help in its nutrition?
Amoeba does not have a fixed shape because it constantly changes form using pseudopodia.
This flexibility allows Amoeba to:
- Move towards and capture food particles easily
- Adjust its body to engulf different types and sizes of food
- Efficiently adapt to its environment for survival
10. List the main functions of food vacuole in Amoeba.
Food vacuole in Amoeba is responsible for managing all steps of food processing.
The main functions are:
- Storage of engulfed food particles
- Absorption of nutrients into the cytoplasm
- Collection and egestion of waste










