Process and Control of Reflex Action With Easy Diagram
Reflex action is a fascinating biological process allowing quick, automatic responses to sudden stimuli. This mechanism protects our body from harm in daily life, such as withdrawing your hand from a hot surface. Understanding reflex actions helps students appreciate the interplay between nerves, the spinal cord, and the role of the brain in maintaining safety and bodily coordination.
What is Reflex Action?
Reflex action refers to an involuntary and nearly instantaneous movement in response to a specific stimulus. It does not require conscious thought or decision-making, making it faster than voluntary movements. Reflex actions help organisms survive potentially dangerous situations by allowing immediate protective responses, thus reducing the risk of injury or damage.
Reflex Arc: The Pathway of Reflex Action
The pathway followed by nerve impulses during a reflex action is called a reflex arc. It consists of specialized neurons that conduct messages from the site of a stimulus to the site of response, often bypassing the brain for speed. Understanding the reflex arc is key to appreciating the efficiency of reflex actions in humans and other animals.
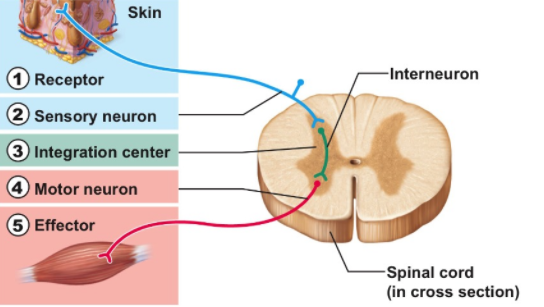
Main Components of the Reflex Arc
There are three primary types of neurons involved in a reflex arc:
- Sensory Neuron: Carries information from the receptor (sensory organ) to the spinal cord.
- Relay (Interneuron): Connects sensory and motor neurons within the spinal cord.
- Motor Neuron: Sends commands from the central nervous system to an effector organ (muscle or gland).
Together, they ensure the reflex is rapid and automatic, skipping the conscious brain in most cases.
Mechanism of Reflex Action
The mechanism of reflex action includes a series of rapid steps that result in immediate movement or response. This process demonstrates how organisms defend themselves from potential harm without requiring thought or prior experience.
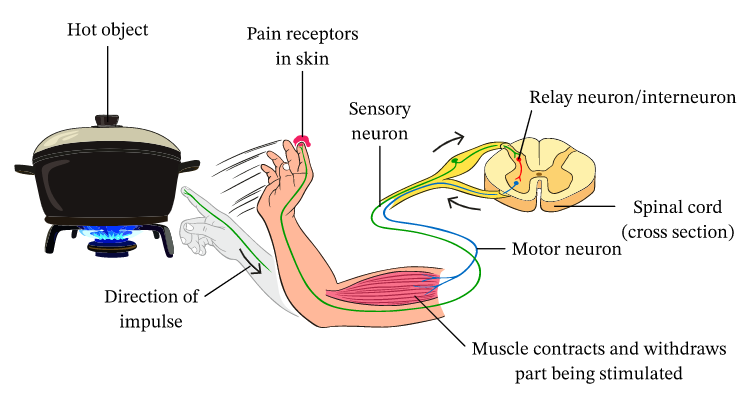
- Stimulus Detection: A receptor, like the skin, detects a change (e.g., heat or pain).
- Message Transmission: The sensory neuron carries the signal to the spinal cord.
- Processing: The interneuron in the spinal cord interprets and relays the signal.
- Response Initiation: A motor neuron sends impulses to the effector organ.
- Action: The muscle contracts or a gland reacts, resulting in a reflex movement like jerking away.
This pathway is designed to be fast for immediate reaction, preventing possible injury.
Types and Examples of Reflex Action
Reflex actions are categorized as either simple or complex, depending on their purpose and complexity. Most occur naturally, but some can be trained with repeated practice.
- Simple Reflexes: Natural, present from birth (e.g., knee-jerk, blinking, salivation when smelling food).
- Conditional Reflexes: Developed through learning (e.g., Pavlov’s dog salivating at a bell’s sound).
Common examples of reflex action include pulling your hand away from something hot, sneezing, coughing, or closing your eyes when something moves near them.
Role of Brain in Reflex Action
A frequent question in biology exams is: What is the role of the brain in reflex action? In most reflex actions, the brain is not directly involved in the process. Instead, the action is coordinated by the spinal cord for faster response. However, the brain does receive information about the reflex afterward, helping us learn or consciously override some reflexes in future situations.
For instance, if repeatedly exposed to a hot object, the brain can help train a person to suppress the urge to drop it—this is more advanced and involves higher nervous processing.
Difference Between Reflex Action and Walking
Many students wonder what is the difference between reflex action and walking? Reflex action is automatic and involuntary, triggered by external stimuli. Walking, in contrast, is a voluntary, controlled process initiated consciously by the brain.
Reflex Action vs Walking vs Involuntary Action
| Feature | Reflex Action | Walking | Involuntary Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Involuntary, rapid and automatic | Voluntary, controlled by brain | Involuntary, but not always fast or protective |
| Involvement of Brain | Usually spinal cord, not brain | Brain (cerebrum) initiates and manages | May involve brainstem or autonomic pathways |
| Response to Stimulus | Immediate | Not immediate | Varied, often rhythmic (like heartbeat) |
| Examples | Blinking, knee-jerk | Walking, running | Heartbeat, digestion |
Reflex action is always protective and quick, while walking needs conscious decision-making. Learn more about biological trait differences here.
Difference Between Reflex Action and Involuntary Actions
Involuntary actions are bodily processes not under conscious control (like breathing or digestion). Reflex actions are a special type of involuntary action, but are always rapid and in direct response to a specific stimulus. All reflex actions are involuntary, but not all involuntary actions qualify as reflex actions.
Summary Flowchart: Reflex Action (E.g., Sneezing Reflex)
Many exams ask to “define reflex action with the help of a flowchart”. Here’s a typical sequence using sneezing as an example:
- Dust irritates nasal lining (stimulus).
- Receptor in the nose triggers sensory neuron.
- Sensory neuron sends impulse to spinal cord.
- Relay neuron passes signal to a motor neuron.
- Motor neuron activates muscle contraction—result: sneezing.
This sequence highlights the direct and efficient route that ensures a rapid response, minimizing danger or discomfort.
Real-World Relevance and Importance
Reflex action is essential in daily life. Medical professionals test reflexes to assess nervous system health. In environmental studies, understanding animal reflexes helps with life science research and animal adaptations. Students learning about parts of the brain see how nervous system organization affects body protection and survival.
Explore More in Biology
To further understand biological systems, explore topics like control and coordination, neurons and nerve impulse, or muscular tissue on Vedantu. These concepts build upon reflex actions and explain the complexity of living organisms.
In summary, reflex action is a rapid, involuntary response that protects organisms from sudden harm. It is controlled by specific neural pathways and mostly handled by the spinal cord, while the brain can modify or learn from these actions. Understanding reflex actions builds a strong foundation for further studies in human physiology and life sciences.


FAQs on What Is a Reflex Action?
1. What is a reflex action?
Reflex action is an automatic, rapid response to a stimulus that occurs without conscious thought.
- It helps protect the body from harm.
- It is mediated by the spinal cord and does not involve the brain immediately.
- Examples include blinking, sneezing, and pulling your hand away from something hot.
2. What is a reflex arc?
Reflex arc is the pathway taken by nerve impulses during a reflex action.
- It involves sensory neuron, relay neuron, and motor neuron.
- The impulse travels from receptor to spinal cord and then to effector organ (like a muscle).
- Reflex arc enables fast and involuntary response to stimuli.
3. Why are reflex actions important for survival?
Reflex actions protect the body by providing quick responses to dangers.
- The fast nature of reflexes helps prevent injury.
- Common examples include withdrawing hand from a sharp object or closing eyelids when something approaches the eye suddenly.
- They operate automatically, without waiting for the brain to process the information.
4. Name the components of a reflex arc.
A reflex arc consists of five main components:
- Receptor – detects the stimulus
- Sensory neuron – transmits nerve impulses to the spinal cord
- Relay neuron (interneuron) – processes the signal in the spinal cord
- Motor neuron – carries impulse from the spinal cord
- Effector – performs the response, usually a muscle or gland
5. How do reflex actions differ from voluntary actions?
Reflex actions are automatic and fast, while voluntary actions occur with conscious control.
- Reflexes do not involve the brain immediately; voluntary actions involve decision-making by the brain.
- Reflexes are protective; voluntary actions are based on will and thought.
6. Give two examples of reflex actions in humans.
Common reflex actions in humans include:
- Knee-jerk reaction (patellar reflex) when tapped below the kneecap
- Withdrawl of hand immediately after touching a hot object
7. Explain the role of the spinal cord in reflex action.
The spinal cord acts as the main processing center for reflex actions.
- It receives sensory information and initiates quick motor responses without passing information to the brain first.
- This permits immediate responses, essential for survival.
8. What is the function of ‘effector’ in a reflex arc?
An effector is a muscle or gland that acts in response to nerve impulses in a reflex arc.
- Effectors bring about the quick response like contraction of a muscle or secretion from a gland.
9. Are all involuntary actions reflex actions?
No, not all involuntary actions are reflex actions.
- Reflex actions are immediate and specific responses to external stimuli.
- Other involuntary actions, such as heartbeat or peristalsis, are continuous and controlled by different pathways (like the medulla).
10. Differentiate between conditioned and unconditioned reflexes.
Unconditioned reflexes are natural and present from birth, while conditioned reflexes are learned through experience.
- Unconditioned reflex: Withdrawal from pain, blinking.
- Conditioned reflex: Salivating on the sound of a bell associated with food (Pavlov’s experiment).










