Key Differences Between Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources With Examples
Our planet relies on different types of natural resources that support life and civilization. The two main categories are renewable and non renewable resources. Understanding their differences is essential for sustainable resource management, environmental protection, and future development. Let's explore renewable and non-renewable resources, their examples, uses, and impacts in the real world.
What are Renewable and Non Renewable Resources?
Natural resources are materials or energy sources found in nature, like sunlight, air, water, soil, plants, and minerals. Based on their availability and how quickly they can be replenished, they are classified as either renewable resources or non renewable resources. This classification is crucial for managing human activities and protecting the environment.

Types and Examples of Renewable and Non Renewable Resources
Renewable resources are those that nature replenishes continuously over short periods. Non-renewable resources are finite, formed over millions of years, and cannot be replaced quickly after use. Understanding the difference between renewable and non-renewable resources is important for choosing sustainable options in industries, agriculture, and day-to-day life.
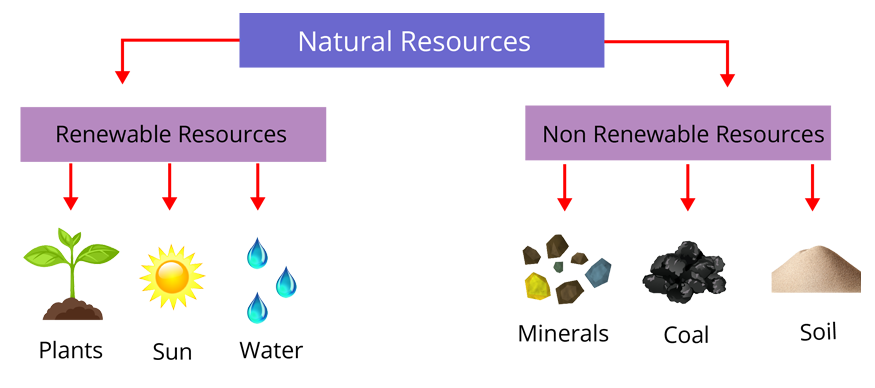
Renewable Resources and Examples
- Solar energy (sunlight)
- Wind energy
- Water (for hydroelectric power, drinking, and irrigation)
- Biomass (plants, crop residue, animal waste)
- Geothermal energy (heat from within the Earth)
These resources can be used again and again, without being depleted, if they are managed responsibly. Renewable and non-renewable resources examples help us understand which energy sources are sustainable in the long run.
Non Renewable Resources and Examples
- Coal
- Petroleum (oil)
- Natural gas
- Minerals (iron, copper, bauxite, gold, etc.)
- Nuclear fuels (uranium, thorium)
Once non-renewable resources are consumed, they cannot be easily replaced in a human lifetime. Using too many non-renewable resources leads to depletion and environmental harm.
Renewable and Non Renewable Energy Resources in Real Life
Energy is one of the most important uses of both resource types. Renewable energy resources like solar panels and wind turbines create electricity in eco-friendly ways. Non renewable energy resources such as coal, oil, and gas power most industries and vehicles. However, burning fossil fuels causes air pollution and climate change. For more on the effects of climate changes, read about climate change impacts.

Difference Between Renewable and Non Renewable Resources
| Aspect | Renewable Resources | Non Renewable Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Naturally replenished and inexhaustible if managed well | Exist in limited quantity and take millions of years to form |
| Availability | Never run out; sustainable | Can be exhausted and are not sustainable long term |
| Main Sources | Sun, wind, water, biomass, geothermal | Coal, petroleum, natural gas, minerals, nuclear fuels |
| Environmental Impact | Low pollution and low carbon footprint | High pollution, greenhouse gas emission, land & air degradation |
| Cost | Higher initial setup, but lower long-term running cost | Often cheaper to start, but costs rise as supplies dwindle |
| Examples | Solar energy, wind energy, hydro power, biomass | Petrol, diesel, coal, iron, copper, uranium |
This table helps to easily differentiate between renewable and non-renewable resources. The key renewable and non-renewable resources difference lies in their ability to replenish and their environmental consequences.
Environmental Impact and Resource Management
Using more renewable energy reduces pollution, greenhouse gases, and health risks. Environmental issues caused by excessive non-renewable resource use include global warming, acid rain, and ecosystem damage. The management of renewable and non renewable resources involves sustainable mining, efficient energy production, and renewable technology adoption.

Renewable energy industries also generate more jobs compared to fossil fuel sectors. Effective management ensures resources remain available for future generations and helps solve pressing environmental problems.
Utilization in Real Life: Medicine, Agriculture, and More
Non-renewable resources like minerals and petroleum are used to make medicines, fertilizer, plastics, and technology devices. Renewable resources, such as plant products and solar power, sustain agriculture and green innovation. You can learn about food science and the role of nutrients in improving health.

From medicines to machinery, both resources are integral. However, increased reliance on non-renewable resources poses risks, making it necessary to transition towards renewables.
Why is the Difference Important?
Understanding the renewable and non-renewable resources difference is key to making choices that protect the environment and human society. As renewable resources and non renewable resources impact everything from economy to health, shifting towards sustainable options ensures resources, clean air, and healthy ecosystems for future generations. To explore more science concepts, visit Vedantu's Biological Science or related topics like traits inheritance and air and water.
In summary, renewable and non renewable resources define how we power our world, develop technologies, and improve lives. Understanding their differences and managing them wisely enables sustainable progress. Prioritizing renewables and efficient resource use protects nature and secures a better future for people and the planet.


FAQs on Understanding Renewable And Non Renewable Resources
1. What are renewable and non-renewable resources?
Renewable resources are natural resources that can be replenished naturally over time, while non-renewable resources are those that exist in a fixed amount and cannot be replaced once used up.
Examples:
- Renewable resources: solar energy, wind energy, biomass, hydroelectric power
- Non-renewable resources: coal, petroleum, natural gas, minerals
2. Give examples of renewable resources.
Some common renewable resources include:
- Solar energy — energy from the sun
- Wind energy — harnessed by wind turbines
- Hydroelectric energy — produced from flowing water
- Biomass — organic materials like plants and waste
- Geothermal energy — from heat within the earth
3. List some non-renewable resources.
Common non-renewable resources are natural reserves that cannot be replaced on a human timescale. Examples include:
- Coal
- Petroleum (crude oil)
- Natural gas
- Minerals like iron, copper, bauxite
- Nuclear fuels (uranium)
4. What are the differences between renewable and non-renewable resources?
The main difference is renewable resources can be naturally replenished, while non-renewable resources get depleted over time.
Key differences include:
- Renewable: Inexhaustible, environmentally friendly, sustainable
- Non-renewable: Limited supply, causes pollution, not sustainable
- Examples: Sun (renewable), coal (non-renewable)
5. Why is it important to conserve non-renewable resources?
Conserving non-renewable resources ensures their availability for future generations and reduces environmental problems.
- They take millions of years to form and can’t be replaced quickly
- Overuse leads to their depletion
- Reduces pollution and environmental damage
- Encourages the use of alternative renewable resources
6. How can we conserve resources for sustainable development?
To ensure sustainable development, resources should be used wisely and conserved for future generations.
- Use energy efficiently
- Switch to renewable energy sources
- Recycle and reuse materials
- Use public transport and reduce wastage
- Spread awareness about conservation
7. What are the advantages of using renewable resources over non-renewable resources?
Using renewable resources is more beneficial as they are sustainable and environmentally friendly.
- Unlimited supply (e.g., sunlight, wind)
- Less pollution and greenhouse gas emissions
- Reduce dependence on fossil fuels
- Promote sustainable future and green jobs
8. What is the role of humans in conserving natural resources?
Humans play a crucial role in the conservation of natural resources by making sustainable choices.
- Minimise resource waste
- Participate in recycling and afforestation
- Switch to renewable energy
- Educate others about conservation practices
9. What is the impact of excessive use of non-renewable resources?
Excessive use of non-renewable resources leads to environmental and economic problems.
- Depletion of reserves
- Increased pollution and global warming
- Rise in prices and scarcity
- Decrease in natural biodiversity
10. Differentiate between exhaustible and inexhaustible resources with examples.
Exhaustible resources are limited and can be exhausted by human use, while inexhaustible resources are available in unlimited quantity.
- Exhaustible: Coal, petroleum, minerals (non-renewable)
- Inexhaustible: Sunlight, wind, water (renewable)










