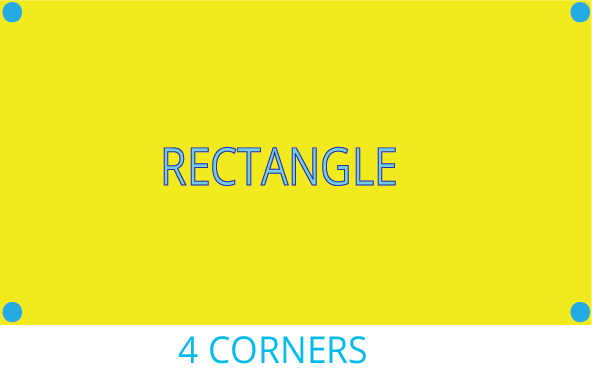Class 3 Maths Chapter 5 Summary Notes PDF Download
FAQs on Shapes and Designs Class 3 Maths Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the main topics to focus on for a quick revision of the CBSE Class 3 Maths Chapter 5, Shapes and Designs?
For a quick and effective revision, you should concentrate on the core concepts. These include:
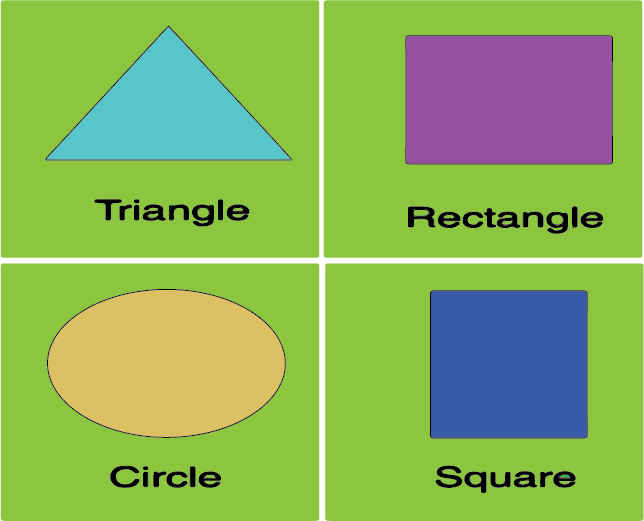
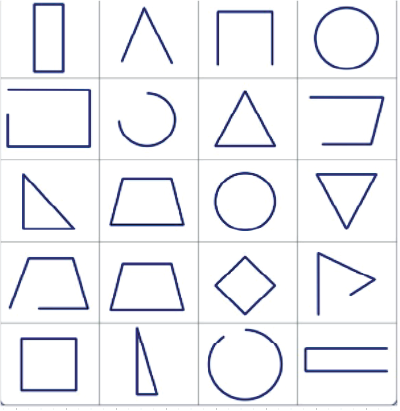
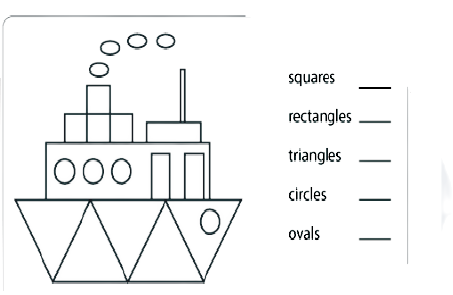
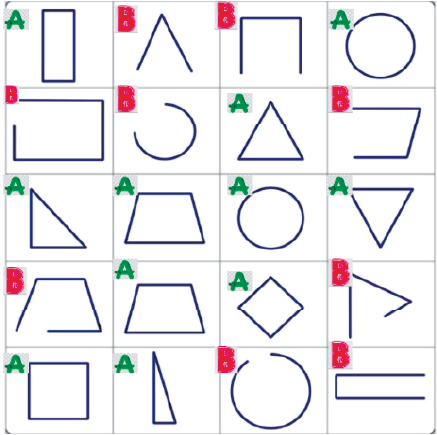
- Identifying 2D shapes (like squares, circles, triangles) and 3D shapes (like cubes, cones, spheres).
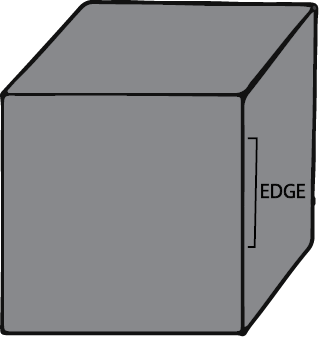
- Counting the number of edges (sides) and corners (vertices) for each shape.
- Understanding the difference between straight and curved lines.
- Recognising simple repeating patterns made from shapes.
2. How can I easily remember the difference between edges and corners for revision?
Think of it this way: Edges are the straight or curved lines that form the boundary of a shape, like the sides of a book. Corners, or vertices, are the points where two or more edges meet, like the sharp point of a triangle. A quick memory trick is 'edges are lines, corners are points'.
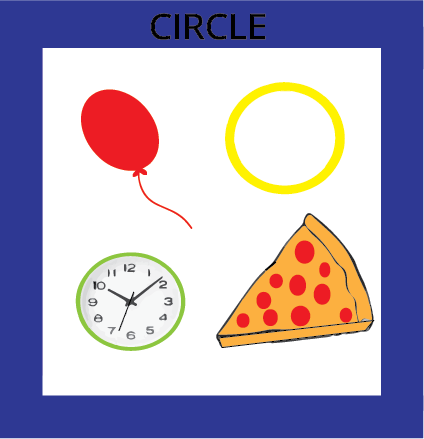
3. What is the key difference between a 2D shape like a circle and a 3D shape like a sphere?
The main difference is that a 2D shape is flat, while a 3D shape is solid and can be held. A circle is a flat drawing, like a picture of the sun. A sphere is a solid object that is round all over, like a real cricket ball. You can only draw a circle, but you can hold a sphere.
4. What is a 'pattern' in the context of this chapter?
In Shapes and Designs, a pattern is a sequence of shapes or lines that repeats in a predictable way. For revision, focus on identifying the rule of the pattern. For example, in the sequence Triangle, Circle, Triangle, Circle..., the rule is that a triangle is always followed by a circle.
5. Why is it important to learn about both 2D and 3D shapes?
It's important because they describe the world around us in different ways. We use 2D shapes to draw and represent things on flat surfaces like paper. We use 3D shapes to understand and describe solid objects we can touch and see from all sides, like a tiffin box (cuboid) or a birthday cap (cone).
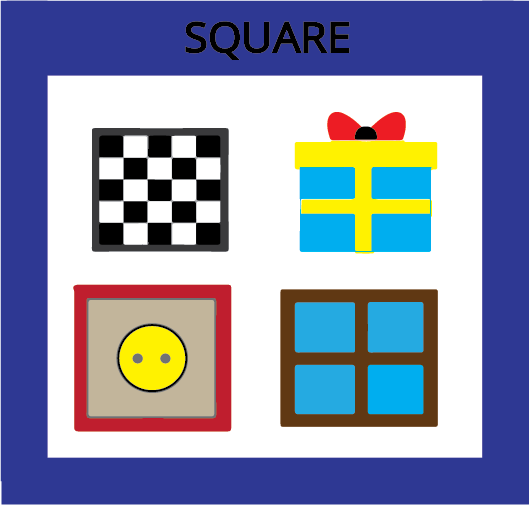
6. How are a square and a cube related? How can I avoid confusing them during revision?
A square is a flat (2D) shape with four equal sides. A cube is a solid (3D) object that is made up of six square faces. A simple way to remember the connection is that a square is just one flat face of a cube. Think of a Rubik's cube; the whole object is a cube, but each coloured tile on it is a square.
7. Can a shape have both straight and curved lines? Please give an example.
Yes, absolutely. Many common objects are made of shapes that combine both. A great example is a cylinder, like a can of soup. It has two flat, circular faces (made with curved lines) and a body that can be seen as having straight sides from one angle. Another example is a semicircle, which has one straight edge and one curved edge.
8. How can a quick summary of this chapter help me solve problems from the NCERT textbook?
A quick summary or revision note helps by reinforcing the fundamental rules. When your textbook asks you to 'find all the triangles in this picture,' your revision helps you instantly recall that a triangle is any shape with 3 sides and 3 corners. This allows you to apply the concept quickly and accurately to solve the problem, instead of guessing.