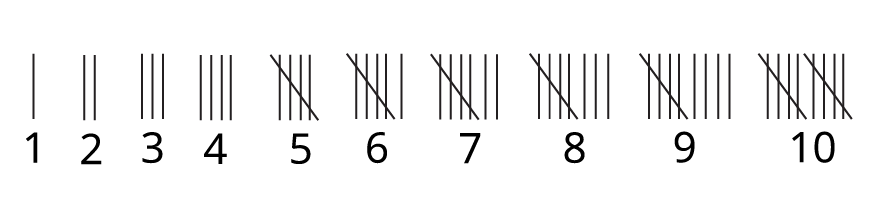Maths Notes for Chapter 13 Smart Charts Class 3 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on Smart Charts Class 3 Maths Chapter 13 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are Smart Charts as explained in Class 3 Maths Chapter 13?
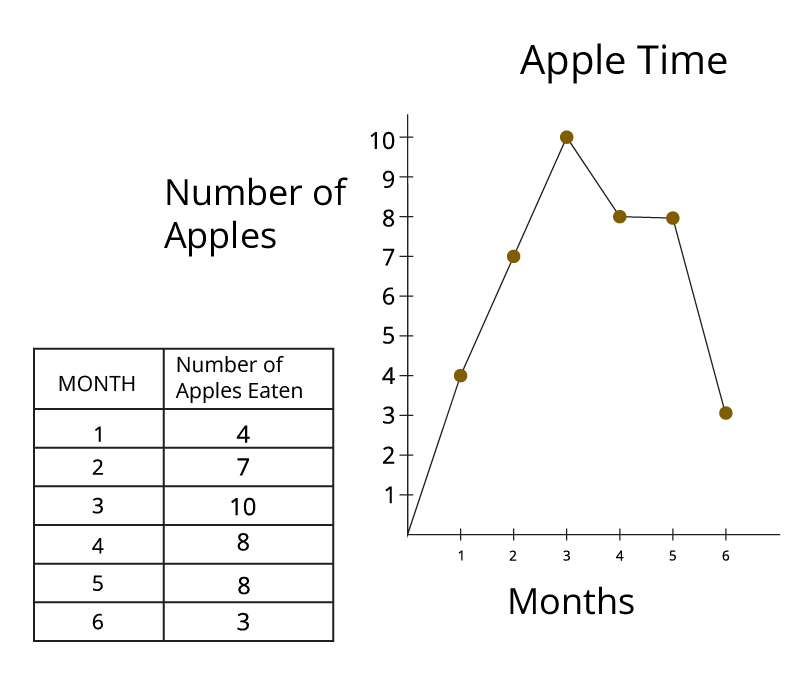
Smart Charts are simple and clever ways to show information, also known as data, in a format that is easy to understand. For Class 3 students, this chapter focuses on creating tables, using tally marks to count, and drawing pictographs to make numbers and facts look clear and organised.
2. What is the main purpose of using revision notes for the 'Smart Charts' chapter?
The main purpose of using revision notes for this chapter is to quickly recall the key concepts. These notes summarise how to collect data, how to organise it into a table, and how to represent it using charts. This helps in building a strong foundation for understanding data handling before exams.
3. How are tally marks used to create a smart chart?
Tally marks are a quick method for counting things. In Chapter 13, you learn to represent numbers by drawing vertical lines. Four lines are drawn vertically, and the fifth line is drawn diagonally across them to form a group of five. This system makes it much easier to count larger numbers of items, like different flowers in a garden, when you are putting them into a table.
4. Why is a chart considered "smarter" than just writing down a list of numbers?
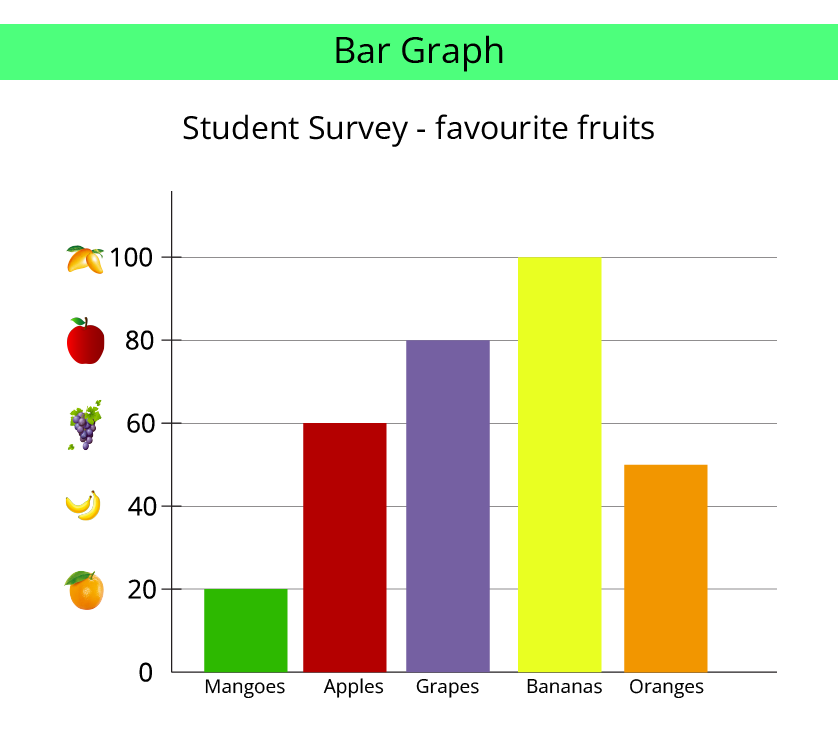
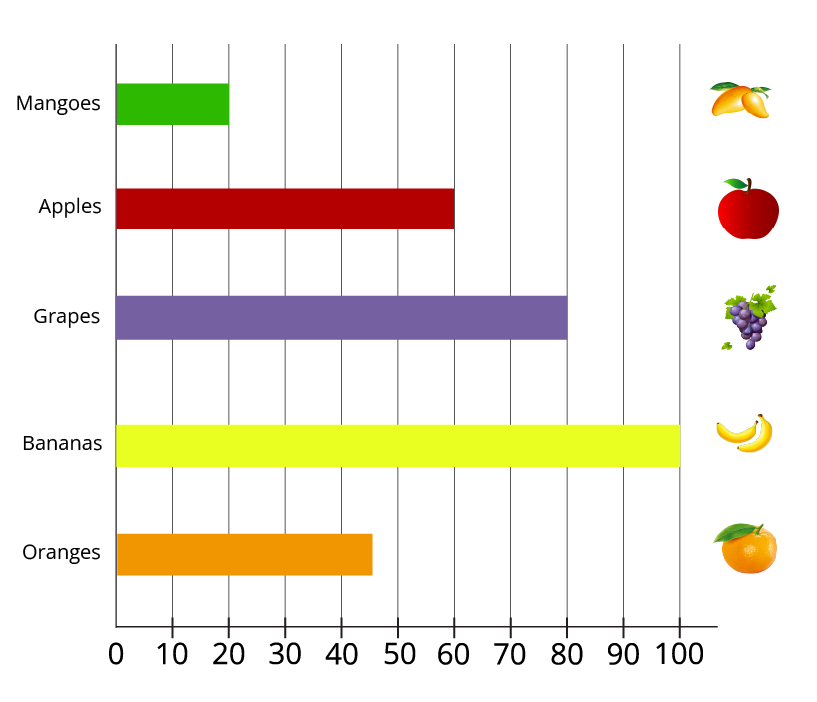
A chart is considered "smarter" because it presents information visually. Instead of reading a long list of numbers, you can understand the data at a single glance. For example, in a pictograph, an item with more symbols is instantly recognisable as the most popular one, which is much faster than comparing numbers in a list. This visual summary helps in making quick comparisons.
5. How can I quickly revise the 'Smart Charts' chapter before an exam?
For a quick revision of 'Smart Charts' as per the 2025-26 CBSE syllabus, focus on the following concepts from your notes:
Review the definitions of a chart and a table.
Practise converting simple data collections into a table using tally marks.
Analyse a few pictographs and answer questions based on them, such as identifying the most or least frequent item.
This approach helps in efficiently revising the core skills taught in the chapter.
6. What is a common mistake to avoid when reading a pictograph?
A very common mistake is forgetting to check the key of the pictograph. The key is crucial as it tells you what each symbol or picture represents (for example, one star might equal 5 students). If you only count the symbols without referring to the key, your calculations will be incorrect. Always check the key first to understand the value of each symbol.
7. How do tables and pictographs work together in this chapter?
In Chapter 13, tables and pictographs work together as a team to manage data. First, you collect information and organise it neatly into a table, often using tally marks to count accurately. Next, you use this organised data from the table to draw a pictograph. In this way, the table ensures the data is accurate, while the pictograph makes the data easy and engaging to read and compare.