Business Studies Notes for Chapter 10 Marketing Class 12 - FREE PDF Download


FAQs on Marketing Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What key topics are summarised in the Class 12 Business Studies notes for Chapter 10, Marketing?
These revision notes for Chapter 10, Marketing, provide a comprehensive summary of essential topics as per the CBSE syllabus. Key areas covered include:
- The fundamental concepts of marketing, needs, and wants.
- The critical difference between the marketing and selling concepts.
- Various marketing management philosophies.
- Core functions of marketing, from market analysis to customer support.
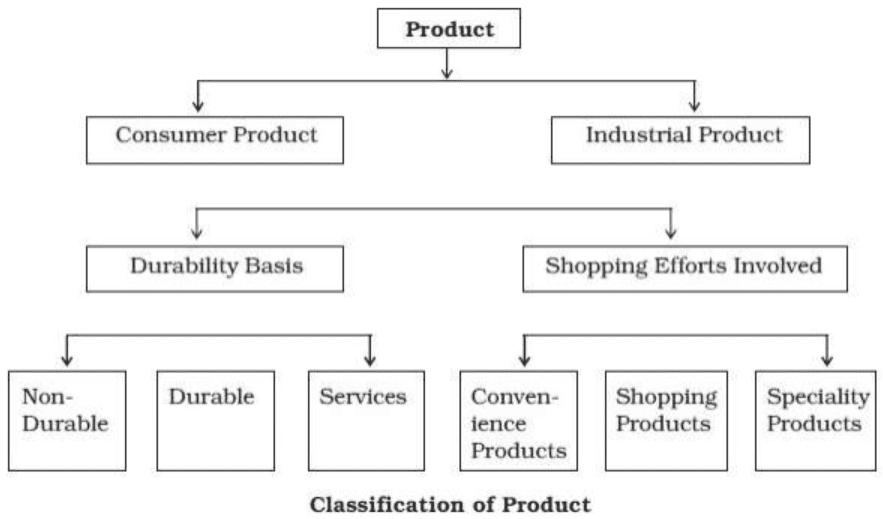
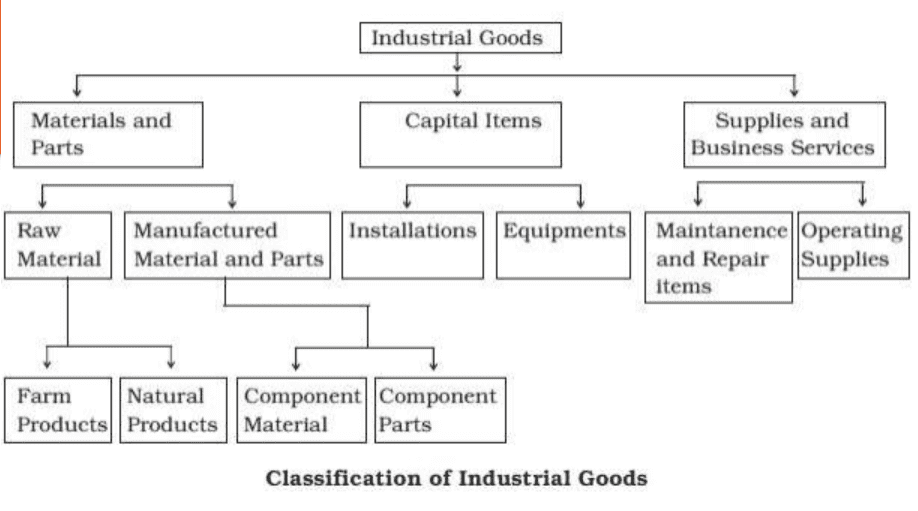
- A detailed breakdown of the marketing mix (the 4 Ps): Product, Price, Place, and Promotion.
2. How does the marketing concept fundamentally differ from the selling concept?
The core difference lies in their starting point and focus. The selling concept focuses on the needs of the seller—to convert existing products into cash. Its activities start after the product is made. In contrast, the marketing concept focuses on the needs of the customer. It begins with identifying customer needs and then developing a product to satisfy them, ensuring long-term profitability through customer satisfaction.
3. What are the 4 Ps of the marketing mix, and how are they interconnected?
The 4 Ps of the marketing mix are the fundamental tools used to achieve marketing objectives. They are:
- Product: The goods or services offered to the target market.
- Price: The amount customers pay for the product.
- Place: The activities that make the product available to target consumers (physical distribution).
- Promotion: The communication activities used to persuade customers to buy the product.
These elements are interconnected because a decision in one area affects the others. For example, a high-quality product (Product) is often sold at a premium (Price), distributed through exclusive outlets (Place), and advertised to highlight its superior features (Promotion).
4. How can I best use these revision notes for a quick recap of the Marketing chapter?
For an effective and quick revision, first scan the main headings to get an overview of the chapter's structure. Then, focus on the definitions of key terms like branding, packaging, and marketing mix. Use the bulleted lists summarising functions and factors to create mental maps. Finally, try explaining a concept like the 'Difference Between Advertising and Personal Selling' in your own words to check your understanding.
5. Why is branding considered more than just giving a product a name or symbol?
Branding is much more than a name because it creates a product's distinct identity and builds a relationship with the consumer. It helps in:
- Product Differentiation: It makes a product stand out from competitors.
- Ensuring Quality: A brand often carries an assurance of a certain quality level.
- Building Customer Loyalty: A strong brand can create loyal customers who prefer it over other options.
- Creating a Status Symbol: Some brands become status symbols, fulfilling psychological needs.
Therefore, a brand is a promise of value, not just an identifier.
6. What is the core idea behind the Societal Marketing Concept, and how does it advance beyond the Marketing Concept?
The Societal Marketing Concept holds that a company's marketing strategy should deliver value to customers in a way that maintains or improves both the consumer's and society's well-being. It advances beyond the standard Marketing Concept by adding a third dimension: societal interests. While the marketing concept focuses on balancing company profits and consumer satisfaction, the societal concept insists that this must be done ethically and with consideration for social welfare, such as environmental protection.
7. What are the primary functions of packaging in marketing?
Packaging serves several crucial functions beyond simply containing the product. It acts as a 'silent salesman' and its primary roles include:
- Product Protection: Guarding the product from damage, spoilage, or leakage.
- Product Identification: Helping customers easily identify the product and brand.
- Facilitating Use: Making the product convenient to transport, store, and use.
- Product Promotion: Using attractive graphics and information to persuade customers to buy.
8. What key factors must a business consider when determining the price of a product?
Determining the right price is critical for success. Key factors include:
- Product Cost: This sets the minimum price, or the floor, as the price must cover costs in the long run.
- Utility and Demand: The value perceived by the customer and the level of demand sets the maximum price, or the ceiling.
- Extent of Competition: Prices of competing products heavily influence a firm's pricing freedom.
- Government and Legal Regulations: The government can intervene to regulate prices of essential commodities.
- Marketing Methods Used: Factors like advertising spend, distribution channels, and sales promotion also impact the final price.
9. How do these Marketing notes align with the CBSE Class 12 syllabus for the 2025-26 session?
These revision notes are carefully structured to align with the latest CBSE syllabus for the 2025-26 academic year. They cover all prescribed topics within Chapter 10, Marketing, ensuring that every concept, from marketing philosophies to the elements of the promotion mix, is explained as per the curriculum's requirements for the board examination.