Maths Notes for Chapter 11 Areas Related to Circles Class 10 - FREE PDF Download
CBSE Notes Class 10 Maths Chapter 11 - Areas Related to Circles - 2025-26
FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 10 Maths Chapter 11 - Areas Related to Circles - 2025-26
1. What are the key concepts to focus on while revising Areas Related to Circles for CBSE Class 10?
For quick revision of Areas Related to Circles in Class 10 Maths, focus on the following:
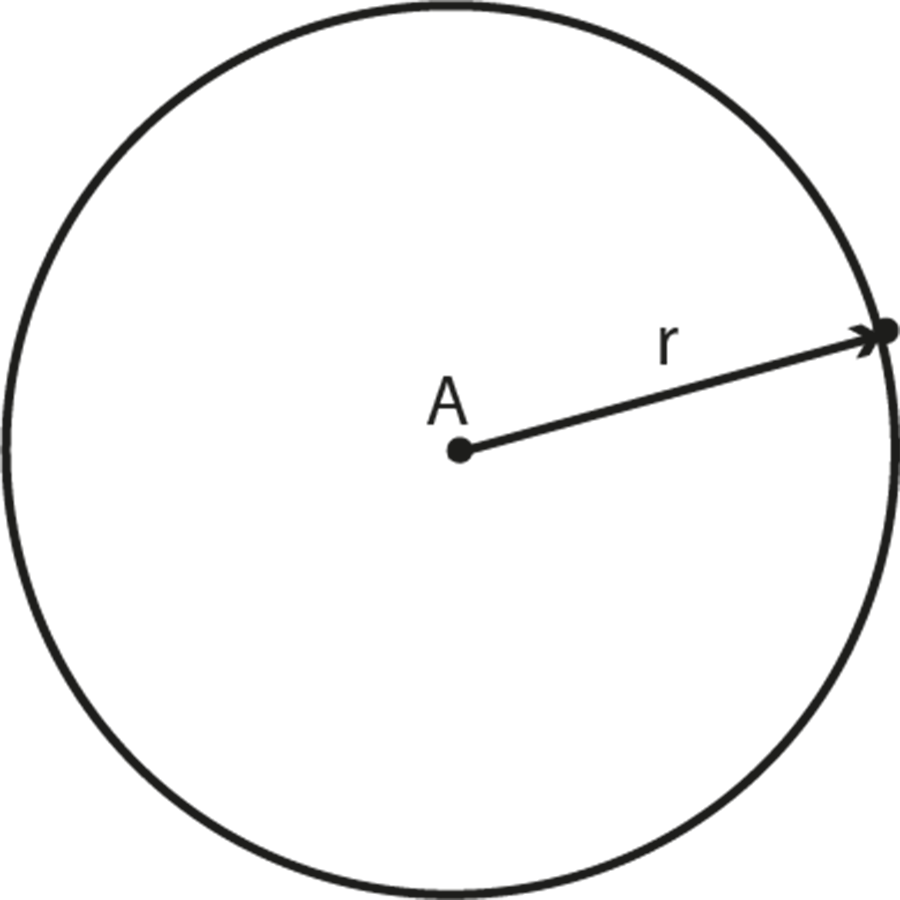
- The definitions of circle, radius, diameter, circumference
- Key formulas: Circumference (2πr), area (πr²), area and perimeter of sectors and segments
- Application-based problems involving combinations of circles with triangles, squares, and rectangles
- Understanding how to calculate area of rings (difference of two circles)
- Properties of arcs, chords, tangents, and sectors
2. How can I revise Areas Related to Circles efficiently before exams?
To revise efficiently, begin by memorizing the main formulas and their derivations. Create a concept map connecting different properties (like area, circumference, and sectors). Practice application-based and HOTS questions, especially on combined plane figures involving circles. Summarize the differences between sector, segment, and arc in your own words for quick recap right before the exam.
3. What is the recommended order to study topics in Chapter 11 for smooth revision?
Start with the basic definitions (circle, radius, diameter), then proceed to circumference and area formulas. Next, cover sectors (including angle, arc length, and area), followed by segments (finding area of minor and major segments). Finally, focus on combined shapes and practical application problems. This sequence helps build understanding progressively as outlined in CBSE Class 10 revision strategies.
4. Which formulas from Areas Related to Circles are crucial for last-minute revision?
The most important formulas include:
- Circumference = 2πr
- Area of a circle = πr²
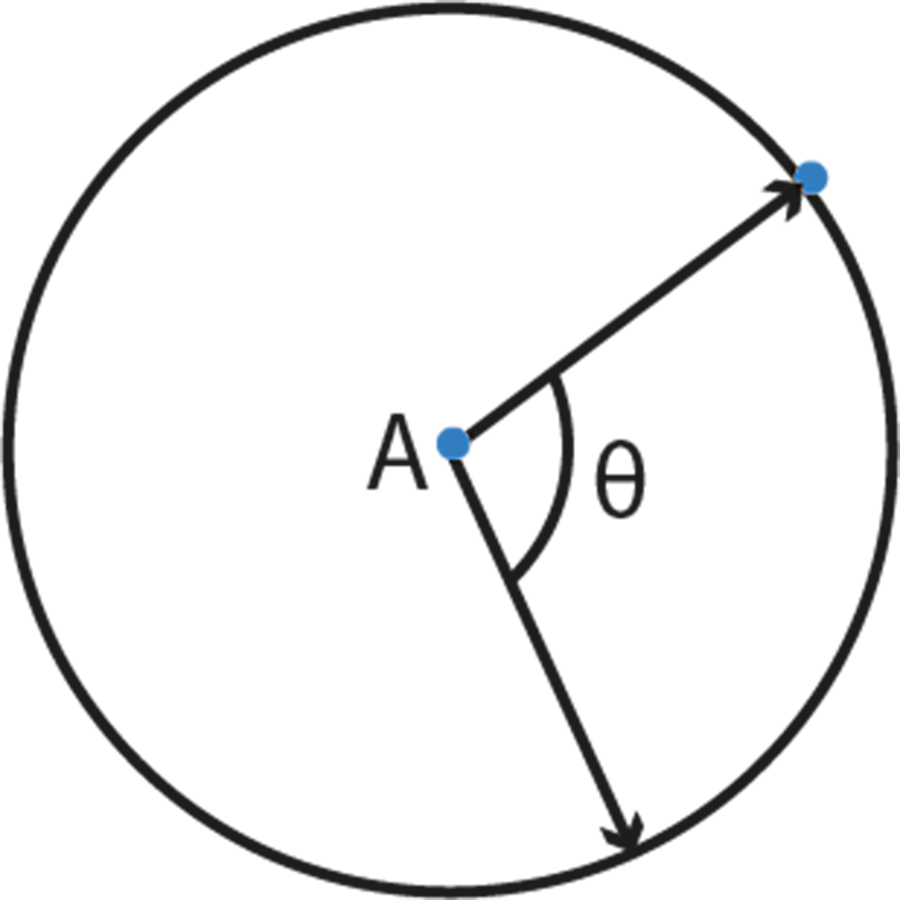
- Length of an arc = (θ/360°) × 2πr
- Area of a sector = (θ/360°) × πr²
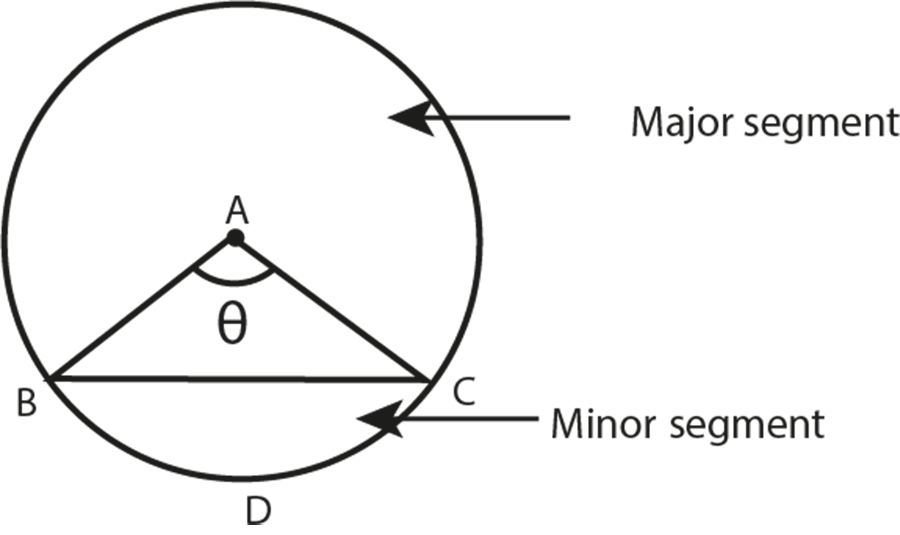
- Area of a segment = Area of sector − Area of triangle
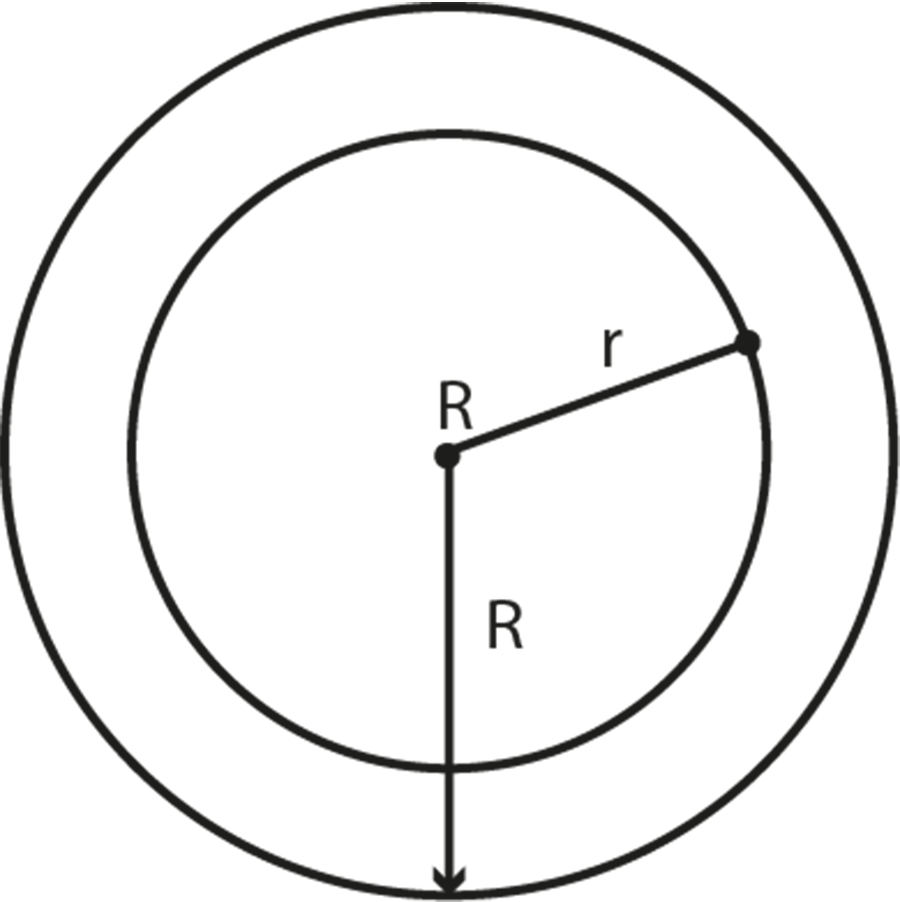
- Area of a ring = π(R² − r²)
5. What are the common mistakes to avoid when revising this chapter?
Common errors include:
- Confusing radius with diameter (remember: diameter = 2 × radius).
- Forgetting to convert degrees to radians (if required) or using the wrong value for θ.
- Not adding the length of the straight edge (diameter) when calculating perimeters of semicircles or sectors.
- Mixing up area formulas for segments and sectors.
- Ignoring units or using inconsistent units.
6. How do visualizations and diagrams help in understanding Areas Related to Circles?
Visual diagrams make it easier to identify sectors, segments, and arcs and clarify their differences. Drawing combined figures (like circles inscribed in squares or part of rectangles) enables a better grasp of how to apply area and perimeter formulas in practical geometry questions, a key part of quick revision and board exam preparation.
7. What strategy should I use for concept mapping in this chapter?
Link each concept (like area, sector, segment) with its formula, related properties, and at least one solved example. Use arrows to indicate relationships (e.g., how area of a segment depends on both sector and triangle areas) for rapid recall during exams. A concept map reduces revision load and enhances understanding of interconnections.
8. In what ways do Areas Related to Circles connect with other geometry topics in Class 10?
This chapter interrelates with Triangles (area calculation using sine rule), Quadrilaterals (combining shapes), and Coordinate Geometry (finding distance, area). These connections are important for solving compound figure questions and reinforce the use of formulas and geometric reasoning needed across the CBSE syllabus.
9. Why is understanding sectors and segments vital for circle-based problems?
Sectors and segments help break down complex circle-related figures into manageable calculations. Most exam questions involve areas of shaded regions or combination of circle parts with other shapes. Understanding how to partition the circle is crucial for accurate and efficient problem-solving in CBSE exams.
10. What types of higher-order thinking questions can be formed from this chapter for revision?
HOTS for revision may include:
- Comparing areas of overlapping circles
- Creative use of sector and segment formulas in real-life scenarios (e.g., designing a circular park with flower beds or pathways)
- Reasoning about minimum/maximum area configurations
- Combining algebraic and geometric methods to find unknown lengths or areas




















 Watch Video
Watch Video