




Common Migraine Symptoms and Triggers
Migraine is defined as throbbing pain in one area of the head that lasts 4 to 72 hours and is coupled with symptoms such as light or sound sensitivity, nausea, and vomiting. Some people have visual disturbances (auras) that appear as flashing lights before or during a migraine.
Despite popular opinion, according to data, migraine headaches affect around 20% of the population. In this article, migraine symptoms and treatment, causes, and types of migraine are discussed.
What is Migraine?
Migraine is a hereditary disorder characterised by persistent headache attacks that vary in intensity, frequency, and duration. Attacks are often unilateral and are accompanied by anorexia, nausea, and vomiting.
What are Migraine Symptoms?
Migraines, which afflict adolescents and teens as well as adults, can go through four stages: prodrome, aura, attack, and post-drome.
Prodrome
The first stage might last a few hours or days. It is possible that one will not encounter it because it does not occur every time. It is referred to as the "preheadache" or "premonitory" phase by others.
Constipation
Changes in mood, from sadness to euphoria
Cravings for food
Stiffness in the neck
Elevated urination
Retention of fluid
Yawning often
Aura
The aura phase might last up to 60 minutes or as little as five minutes. The majority of people do not have an aura, while others have both the aura and the headache at the same time.
Uncontrollable movements
Flashing lights are examples of visual symptoms.
Visual impairment
The feeling of pins and needles in an arm or leg
Numbness
Communication difficulties
Hearing noises that do not exist
Attack
The headache might persist anywhere from four to 72 hours. The word "ache" does not do the agony credit because it can be moderate at times, but it is generally described as drilling, throbbing, or having the sensation of an icepick in your brain. It usually starts on one side of your head and progresses to the other.
It frequently feels like a tremendous throbbing or pulsating ache.
It just affects one side of your head or one of your eyes.
It might last anywhere from 4 to 72 hours.
You are extremely sensitive to light, to the point where you may need to retire to a darker area.
You are also very sensitive to fragrances, noises, and touch.
You may feel sick to your stomach or vomit.
You could feel dizzy or faint.
Your eyesight may get fuzzy.
Postdrome
This stage lasts for a day or two. It is commonly referred to as a migraine "hangover," and it affects 80 per cent of migraine sufferers.
Elated
drained and cleaned
Baffled
Dizzy
Light and sound sensitivity
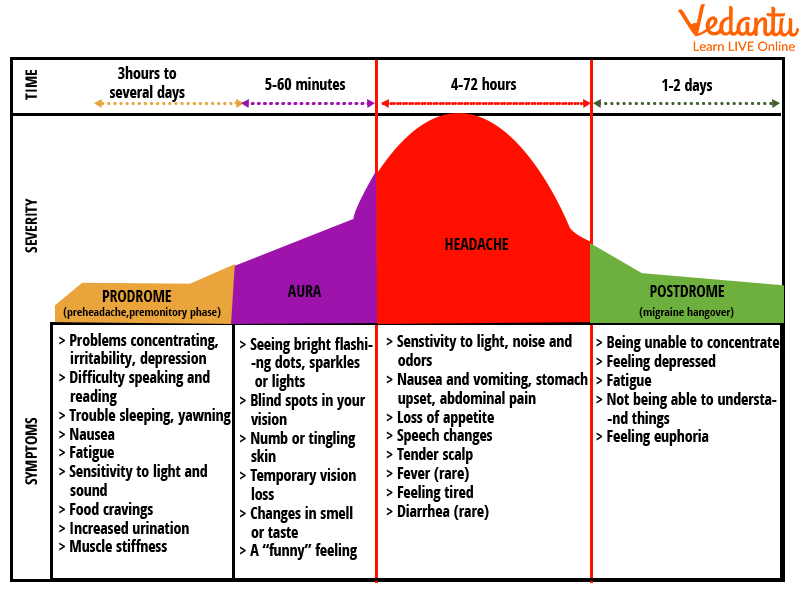
Complete List of Migraine Symptoms
Chronic Migraine Symptoms
A migraine is classified as chronic when it happens at least 15 days per month. The strength of the discomfort and the symptoms may fluctuate on a regular basis. Chronic migraine sufferers may use headache pain relievers more than 10 to 15 days per month, which might, regrettably, contribute to headaches that occur more frequently.
Vestibular Migraine Symptoms
Vestibular migraine can induce vestibular or balance symptoms in addition to or instead of a headache. Vestibular migraines can cause a variety of symptoms, severe migraine symptoms include the following:
A headache that is severe and throbbing, generally on one side of the head.
Vomiting and nausea.
Light, scent, and noise sensitivity.
Migraine Causes
Experts believe that migraine attacks are caused by changes in the brain, brain migraine symptoms are because of that impact on the:
Nerve communication.
Blood vessels.
Chemical equilibrium.
Common Migraine Triggers
Migraine triggers vary for each person, but some common factors include-
Hormonal Changes- Menstruation and hormonal shifts can trigger migraines.
Emotional Factors- Stress, anxiety, depression, and excitement may lead to migraines.
Dietary Triggers- Certain foods and drinks can cause migraines, including-
Alcohol and caffeine
Chocolate and nuts
Cheese and citrus fruits
Foods with additives like tyramine and MSG
Medications- Some medicines can trigger migraines, such as-
Sleeping pills
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
Certain birth control pills
Family History- A family history of migraines or even cancer may increase the risk.
Migraine Treatment
Beta-blockers- Propranolol LA 60 mg/d, rising to 160 mg/d as required. Diabetes and reactive airway disease (e.g., asthma) are frequently contraindicated. Beta-blockers may aggravate depression. Nadolol has fewer CNS adverse effects; it is begun at 20 mg/d and gradually raised up to 120 mg/d as needed.
Calcium Channel Blockers- Diltiazem CD 120 mg/d, rising to 240-480 mg total/d as tolerated, sometimes in two split doses. The most common adverse effects are constipation and hypotension, but this is generally the most well-tolerated regimen.
Erenumab (Aimovig)- It is a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor (CGRP-R) antagonist that was licensed in 2018 for use as a monthly injection to prevent migraines.
Summary
Migraine is a common condition with severe headaches, nausea, and sensitivity to light, sound, or movement. However, not everyone with migraines experiences headaches; some may have dizziness, ear pain, sinus pressure, or hearing issues. Treatments for typical migraines also work for these less common symptoms. Migraine affects about 10% of people worldwide, mostly between ages 20-50, and is three times more common in women than men.
Essential Study Materials for NEET UG Success
FAQs on Migraine Symptoms - Understand its Causes & Cures
1. What are the four common types of headaches?
There are four types of headaches- sinus, tension, migraine, and cluster. Primary and secondary headaches are always distinguished. A primary headache is one that is not the result of another ailment or illness. Stress, sleep deprivation, alcohol, missing meals, and certain processed foods are all causes of primary headaches. Secondary headaches are caused by another ailment, such as an accident, infection, or illness, and can range from insignificant to deadly.
2. List the home remedies for migraine pain relief.
Many lifestyle remedies can help lower the frequency and intensity of migraine attacks.
Eating a well-balanced diet.
Exercise on a regular basis.
Caffeine and alcohol should be avoided.
Maintain a consistent sleep routine.
Yoga can aid in pain management and relaxation.
Techniques for stress management and relaxation.
Acupuncture.
Avoid or restrict exposure to recognised triggers.
3. Briefly describe the forms of migraine headaches.
Migraines come in a variety of forms, including-
Common migraine (approximately 80% of all migraines) with no "aura."
Classic migraines (also known as migraines with aura) are more severe than typical migraines and feature an aura before the headache.
Silent (or acephalgic) migraine occurs when there is no head pain, yet there is an aura and other migraine symptoms.
Hemiplegic migraine symptoms, such as weakness on one side of the body, loss of sensation, or a sense of 'pins and needles,’ might resemble a stroke.
Retinal migraine causes transient visual loss in one eye that can last anywhere between minutes and months.
Chronic migraine lasts over an extended period of time.
4. What is a Stage 3 Migraine?
Stage 3- Attack is when the migraine occurs. During this phase, you may experience pain on one or both sides of your head. The pain can last anywhere from a few hours to three days, and it can range from mild discomfort to intense pain that makes it hard to do anything.
5. How can you prevent a migraine from starting?
To stop a migraine before it starts-
Get enough sleep – Rest is essential for preventing migraines.
Don’t skip meals – Missing meals can trigger migraines by affecting your hormones.
Limit caffeine – Try to keep your caffeine intake under 100-200 mLs a day.
Drink plenty of water – Staying hydrated helps prevent migraines.
Exercise regularly – Physical activity can reduce the chances of a migraine.
6. What is the last stage of a migraine?
The last stage of a migraine is called the recovery or postdrome stage. During this phase, you may feel tired, drained, or have a "hangover" feeling. This stage can last for several hours or even a few days as the symptoms gradually fade away.
7. At What Age Do Migraines Stop?
As people get older, especially in their 50s and 60s, many notice that their migraines happen less often and aren’t as intense. However, they might experience new triggers or no longer have some old ones. It's also common for older adults to have silent migraines, which means they experience the aura but not the headache.
8. Where Does Migraine Pain Happen?
Migraine pain can be felt anywhere on the head, neck, and face, but it is most often on just one side. The pain is usually described as throbbing or pulsing. Other symptoms may include nausea, and sensitivity to light, and sound.
9. What foods can trigger migraines?
Certain foods can trigger migraines, such as chocolate, aged cheeses, processed meats, and foods that contain artificial preservatives. Other foods like caffeine, citrus fruits, and foods with MSG can also cause migraines in some people. It's important to pay attention to what you eat and see if certain foods affect you.
10. How Long Do Migraines Last?
A migraine can last anywhere from 4 to 72 hours if not treated. In some cases, migraines can be more intense and last longer, eventually becoming chronic if they continue to occur frequently. Treatment can help reduce the duration and severity of a migraine.
























