NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026 – Important Chapters and Complete Topic-wise Breakdown
FAQs on NEET 2026 Chemistry Syllabus OUT: Check the Updated Detailed Topics and Subtopics
1. What is the syllabus of NEET in chemistry?
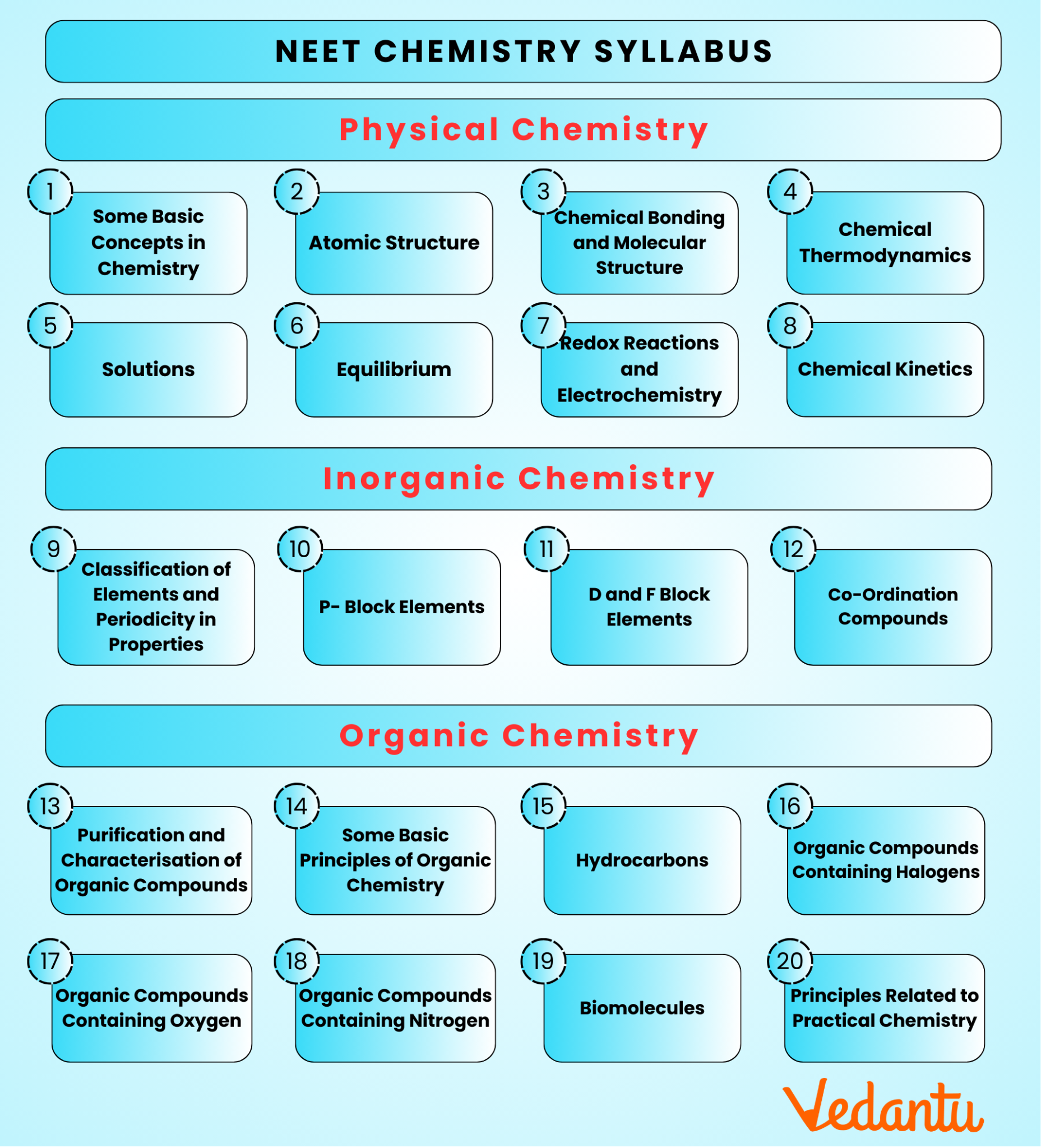
The NEET Chemistry syllabus 2026 is divided into three primary sections:
Physical Chemistry
Organic Chemistry
Inorganic Chemistry
This syllabus includes topics from both Class 11 and Class 12, such as atomic structure, chemical bonding, thermodynamics, organic compounds, and coordination chemistry. Candidates should focus on mastering NEET organic chemistry syllabus, inorganic chemistry NEET syllabus, and NEET physical chemistry syllabus to excel in the exam.
2. Which chapters are removed from NEET 2026 Chemistry?
For NEET 2026 Chemistry, certain chapters have been excluded, such as:
States of Matter
Hydrogen
s-Block Elements
Environmental Chemistry
Polymers
Chemistry in Everyday Life
Some specific topics, such as the third law of thermodynamics and parts of experimental chemistry, have also been removed. The focus has shifted to core conceptual understanding, based on the chemistry syllabus for NEET 2026.
3. How to score 150+ in Chemistry NEET?
To score 150+ in NEET Chemistry, follow these steps:
Master NCERT for both Inorganic and Organic Chemistry basics.
Practice Physical Chemistry numericals using formulas from NCERT and reference books.
Solve Previous Year Questions (PYQs) and take regular mock tests.
Focus on name reactions and exceptions in Organic Chemistry.
Revise essential chapters like Chemical Bonding and Periodic Table.
Build conceptual clarity through practice, avoiding rote learning.
Make short notes for quick revision.
This approach ensures thorough preparation for the NEET Chemistry syllabus 2026.
4. Which is the hardest chapter in 12th Chemistry?
The hardest chapters in Class 12 Chemistry are:
Electrochemistry
Chemical Kinetics
Coordination Compounds
Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids (Organic Chemistry)
These chapters often involve complex numericals (Electrochemistry, Kinetics), abstract concepts like isomerism (Coordination Compounds), and detailed reaction mechanisms (Organic), which require strong conceptual understanding.
5. Which chapter is most important in chemistry?
Some of the most important chapters in NEET Chemistry include:
Chemical Bonding
Thermodynamics
Organic Chemistry basics (especially Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids)
Electrochemistry
Equilibrium
Kinetics
These chapters are essential for both building a solid foundation and scoring well in the exam, and are covered extensively in the NEET 2026 chemistry syllabus.
6. Which is the easiest subject in chemistry?
Chemistry is often considered the easiest-scoring subject in NEET.
The questions are generally direct and based on standard concepts, especially from the NEET organic chemistry syllabus and inorganic chemistry NEET syllabus.
7. What are the five topics for chemistry NEET 2026?
The five major topics in NEET Chemistry are:
Physical Chemistry
Organic Chemistry
Inorganic Chemistry
Biochemistry
Analytical Chemistry
These topics are all covered in the NEET Chemistry syllabus 2026 and essential for thorough preparation.
8. How many total chapters of Chemistry are in NEET 2026?
For NEET 2026, there are approximately 20 main chapters in Chemistry, divided into the following categories:
Physical Chemistry: 8 chapters
Inorganic Chemistry: 5 chapters
Organic Chemistry: 7 chapters
The total number of questions in Chemistry is 45, with a focus on high-yield chapters like Stoichiometry, Atomic Structure, Chemical Bonding, Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, and Coordination Compounds. For detailed preparation, download the NEET Chemistry syllabus PDF.
9. How to score 150+ in Chemistry NEET?
To score 150+ in NEET Chemistry, follow this strategy:
Master key topics like Chemical Bonding, Thermodynamics, and Organic Chemistry basics.
Regularly solve mock tests and previous year’s questions (PYQs).
Focus on Physical Chemistry numericals and ensure conceptual clarity.
Prioritize high-weightage topics such as Electrochemistry and Equilibrium.
By adhering to this focused strategy aligned with the NEET Chemistry syllabus 2026, you can easily score 150+ marks.