Physics NEET Syllabus 2026 Released - Latest Chapterwise Breakdown FREE PDF
FAQs on NEET Physics Syllabus 2026 Out, Download Official PDF, Chapter-Wise Topics and Weightage
1. What is the syllabus of NEET for 2026?
The NEET 2026 Physics syllabus primarily follows the NCERT curriculum for Classes 11 & 12. It covers key topics such as Mechanics, Electromagnetism, Optics, and Modern Physics, from both Class 11 and Class 12. The syllabus emphasizes conceptual clarity and problem-solving skills in subjects like Thermodynamics, Chemical Bonding, and Human Physiology, ensuring a solid foundation in Physics.
2. What are the chapters of NEET Physics 2026?
The NEET UG 2026 Physics syllabus includes topics from Class 11 and Class 12. Some key chapters are:
Class 11: Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Kinematics, Work, Energy, and Power.
Class 12: Electrostatics, Optics, Modern Physics, and Electromagnetic Induction.
For a complete chapter-wise breakdown, refer to the NEET Physics syllabus 2026.
3. Which chapters are removed from NEET 2026 Physics?
For NEET 2026 Physics, some topics have been deleted based on the updated NCERT curriculum:
Class 11: Rolling friction, Poisson's ratio, some parts of Thermodynamics, and the Doppler effect in Oscillations & Waves.
Class 12: Van de Graaff generator, potentiometer details, cyclotron, Oersted's experiment, and some optics topics like microscopes and telescopes.
These deletions aim to focus on high-yield concepts that are crucial for NEET Physics syllabus 2026.
4. How to score 170+ in Physics NEET?
To score 170+ in NEET Physics, follow these tips:
Focus on conceptual clarity from the NCERT Physics syllabus.
Practice numerical problems regularly from Class 11 and Class 12 topics like Electrostatics, Electromagnetism, and Optics.
Solve Previous Year Questions (PYQs) and take mock tests.
Focus on high-weightage chapters like Laws of Motion, Electrostatics, and Ray Optics.
Build your foundation with NCERT and then practice advanced problems from reference books.
5. Which book is good for NEET 2026 Physics?
Here are some must-have books for NEET 2026 Physics preparation:
NCERT Physics (Class 11 & 12): Core theory, definitions, and diagrams (Mandatory).
Concepts of Physics by H.C. Verma (Vol 1 & 2): Excellent for conceptual clarity and problem-solving (Highly Recommended).
Objective Physics by D.C. Pandey: Chapter-wise MCQs designed for NEET practice (Recommended).
6. Which is the hardest chapter in 12th Physics?
The toughest chapters in Class 12 Physics often include:
Electromagnetic Induction and Electromagnetic Waves: Due to the complex concepts and applications.
Optics (Wave Optics): Involves intricate derivations and detailed numerical problems.
Modern Physics: Quantum Mechanics and Nuclear Physics are difficult due to their abstract nature.
Focus on mastering conceptual understanding to tackle these topics effectively.
7. Which is the easiest chapter in 12th Physics?
Some of the easiest chapters in Class 12 Physics include:
Semiconductor Electronics: Clear concepts with simple formulas.
Atoms and Nuclei: Straightforward theories and equations.
Electromagnetic Waves: Concepts are easy to grasp with practical applications.
Ray Optics: Simple concepts with direct formulas and easy scoring.
8. Which is the easiest chapter in NEET Physics?
Some of the easiest chapters in NEET Physics include:
Units and Measurements: Basic understanding of units and significant figures.
Gravitation: Simple applications of gravitational laws.
Oscillations & Waves: Focus on SHM (Simple Harmonic Motion) and wave basics.
Semiconductor Electronics: Clear theories and straightforward numerical problems.
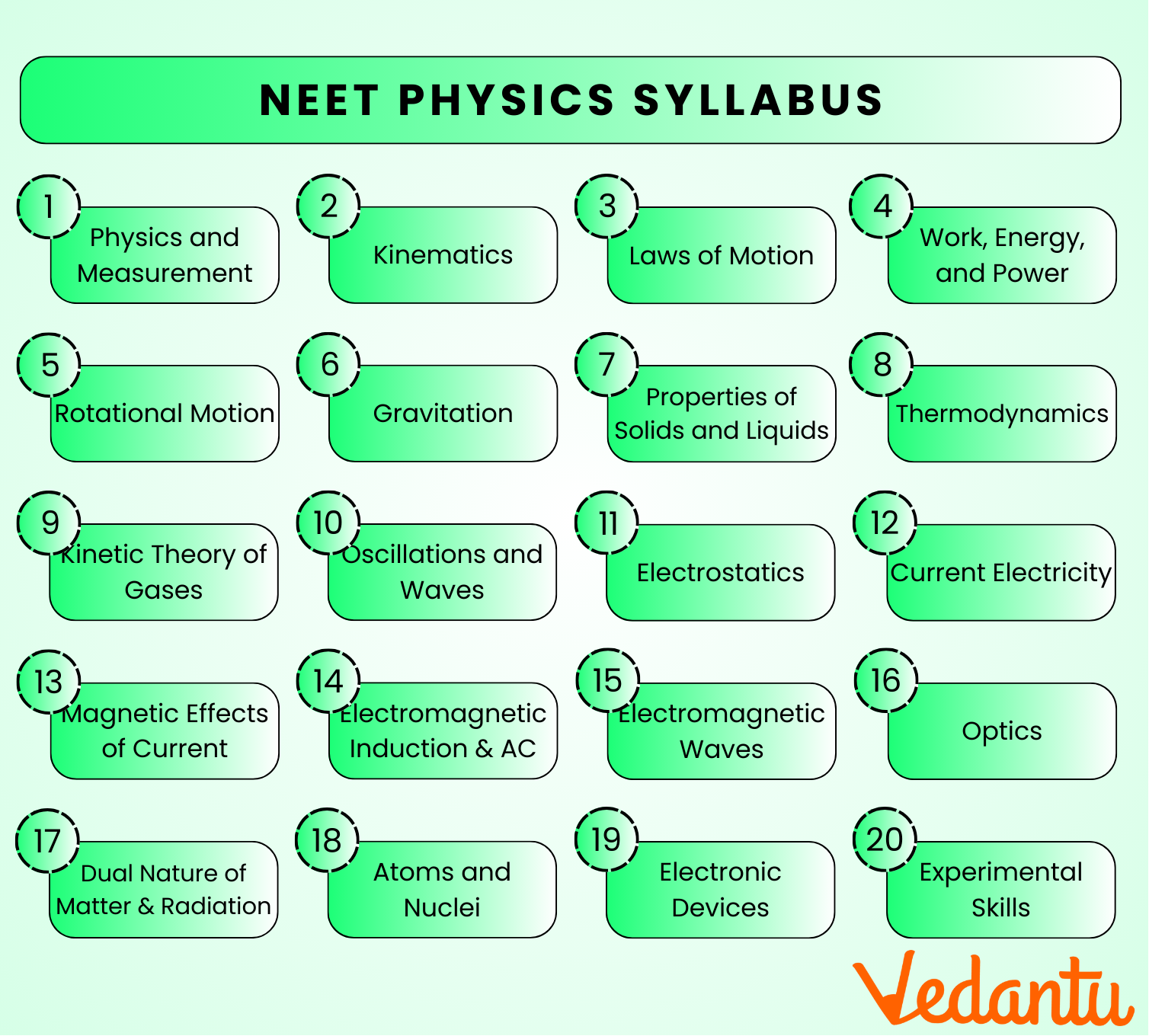
9. How many chapters are there in NEET Physics?
The NEET Physics syllabus is divided into Class 11 and Class 12 chapters, with approximately 20 key chapters covering essential concepts from Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Optics, and more. Refer to the NEET Physics syllabus chapter-wise breakdown for detailed information.
10. Where can I download the NEET Physics Syllabus 2026?
You can download the official NEET Physics Syllabus 2026 from the National Testing Agency (NTA) official website or from Vedantu’s dedicated page. The syllabus is available in PDF format, which provides a detailed breakdown of all the chapters, important topics, and deleted sections.