




Understand What is a Cell and its Types
Cells are considered the fundamental units of life. Every living organism—single-celled or multicellular—is built upon and functions because of cells. The study of cells involves understanding their structure, components (organelles), and how they carry out various life processes.
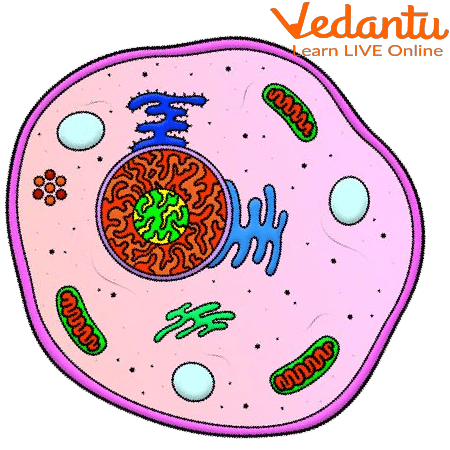
What is a Cell?
The term “cell” was first coined when Robert Hooke observed cork cells.
Cells come in various shapes, sizes, and types, depending on their role within an organism.
The cell membrane controls what enters or leaves the cell, maintaining a balanced internal environment.
Discovery of the Cell
Robert Hooke (1665)- Observed cork cells and introduced the term “cell.”
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek- Improved the microscope, enabling the discovery of bacteria and other microscopic organisms.
Cell Theory- Schwann and Schleiden proposed that all organisms are made up of cells, and cells are the basic unit of life. Rudolf Virchow later added that new cells arise only from existing cells.
Characteristics of a Cell
Structural and Functional Unit-
Cells provide structure to living organisms.
Essential metabolic reactions and gene expression processes occur within cells.
Genetic Material-
Most cells contain DNA, which carries hereditary information and guides protein synthesis.
Cell Membrane-
A selectively permeable boundary that regulates the transport of substances in and out of the cell.
Cytoplasm-
A fluid matrix that holds organelles.
Facilitates chemical reactions.
Types of Cells
Prokaryotic Cells
Definition- Cells without a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles (e.g., bacteria).
Key Features-
Genetic material is in the nucleoid region (not surrounded by a nuclear membrane).
Ribosomes (protein-synthesising structures) float freely in the cytoplasm.
Cell division typically occurs through binary fission.
Eukaryotic Cells
Definition- Cells with a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (e.g., plants, animals, fungi, protists).
Key Features-
The nucleus is encased in a nuclear envelope.
Various organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and so on, each perform specialised functions.
Reproduction can occur asexually (mitosis) or sexually (meiosis).
Cell Organelles
1. Nucleus-
Contains the genetic material (DNA).
Regulates cell growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
2. Mitochondria-
Known as the powerhouse of the cell.
Site of ATP (energy) production.
3. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)-
Rough ER- Studded with ribosomes; synthesises proteins.
Smooth ER- Lacks ribosomes; synthesises lipids and helps detoxify substances.
4. Golgi Apparatus-
Modifies, packages, and transports proteins and lipids.
Forms vesicles that may become lysosomes or secretory vesicles.
5. Lysosomes-
Contain enzymes to break down waste materials or cellular debris.
Play a key role in intracellular digestion.
6. Chloroplasts (in Plant Cells)-
Capture sunlight for photosynthesis.
Contains the green pigment chlorophyll.
7. Vacuoles-
Store nutrients and waste products.
Provide structural support in plant cells (large central vacuole).
Functions of a Cell
Nutrition and Digestion- Intake of nutrients and conversion into energy.
Respiration- Breaking down nutrients to release energy.
Growth and Repair- Cells grow in size or number; damaged cells are replaced.
Reproduction- Ensures the continuation of species (binary fission, mitosis, meiosis).
Response to Stimuli- Cells can respond and adapt to changes in their environment.
Cell Membrane Transport
Passive Transport (Diffusion and Osmosis)- Movement of substances from higher to lower concentration without energy.
Active Transport- Movement of substances against a concentration gradient, requiring energy (ATP).
Some Practise MCQs for Better NEET Preparation
1. Which of the following statements is NOT part of the cell theory?
A. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
B. Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life.
C. All cells arise only from pre-existing cells.
D. Cells can spontaneously generate from non-living matter.
Answer- D
2. Which organelle is primarily responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins in eukaryotic cells?
A. Nucleus
B. Golgi apparatus
C. Lysosome
D. Ribosome
Answer- B
3. In which type of cell would you find a nucleoid region instead of a membrane-bound nucleus?
A. Prokaryotic cell
B. Eukaryotic cell
C. Plant cell
D. Fungal cell
Answer- A
4. Which of the following statements about mitochondria is INCORRECT?
A. They are known as the powerhouses of the cell.
B. They are involved in ATP production.
C. They are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
D. They contain their own genetic material (DNA).
Answer- C
5. The process by which water molecules move across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of higher water potential to lower water potential is called
A. Diffusion
B. Osmosis
C. Active transport
D. Endocytosis
Answer- B
6. Which of the following organelles is involved in photosynthesis and contains the pigment chlorophyll?
A. Ribosome
B. Endoplasmic reticulum
C. Mitochondrion
D. Chloroplast
Answer- D
Essential Study Materials for NEET UG Success
Cell - The Basic Unit of Life

 Share
ShareFAQs on Cell - The Basic Unit of Life
1. What is a cell?
A cell is the basic building block of all living things. It is the smallest unit of life that can exist on its own. Every living thing, from tiny bacteria to big animals, is made up of cells. Cells help the body function by carrying out important tasks like growing, using energy, and reproducing.
2. What are the two main kinds of cells?
There are two main types of cells- prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simple and don’t have a nucleus, like bacteria. Eukaryotic cells are more complex and have a nucleus, like plant and animal cells. These two types make up all living things.
3. What is a vacuole in a cell?
A vacuole is a storage space inside a cell, surrounded by a membrane. It helps store water, nutrients, and waste. Vacuoles are found in both plant and animal cells. In plant cells, they are usually bigger and help maintain the cell's shape.
4. What is cell sap?
Cell sap is a liquid inside the vacuoles of plant cells. It contains water, nutrients, waste, and salts. It helps the cell stay firm and stores important materials. This fluid also plays a role in keeping the plant healthy.
5. What does turgidity mean?
Turgidity is when something, like a plant cell, becomes firm or swollen because it is filled with water. This helps plants stand upright and stay strong. If a plant doesn’t get enough water, it loses turgidity and starts to droop. It’s an important part of how plants stay healthy.
6. What is a special cell?
A special cell is a cell that has a specific job in the body. For example, red blood cells carry oxygen, and nerve cells help muscles move or relax. Each type of special cell is shaped and designed to do its job well.
7. What is the cell theory?
Cell theory is the idea that all living things are made up of cells. It is one of the basic principles of biology. This theory also says that cells are the smallest units of life and that all new cells come from existing cells.
8. What are the main functions of a cell?
A cell does many important jobs to keep living things alive. It gives structure and support, just like bricks in a house. It helps the body grow by making more cells. It moves things in and out, like food and waste. It makes energy so the body can work. It also controls chemical reactions to keep everything running smoothly.
9. What is another name for a cell wall?
In the 1980s, some scientists thought "cell wall" wasn’t the best term for plants. They suggested calling it the "extracellular matrix," like in animal cells. However, not everyone agreed with the change. Many still prefer the original name, "cell wall." So, both terms can be used, but "cell wall" is more common.
10. Do all cells have a nucleus?
Some cells, like the ones in your body, have a nucleus. Others, like bacteria, do not have one. Cells with a nucleus are called eukaryotic cells. "Eukaryotic" means they have special parts inside, like the nucleus. Bacteria and similar cells without a nucleus are called prokaryotic cells.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video


