Master Class 9 Maths Ch 3 Ex 3.2 With Vedantu's Expert Solutions
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 3.2 (2025-26)
1. What are the main concepts covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry?
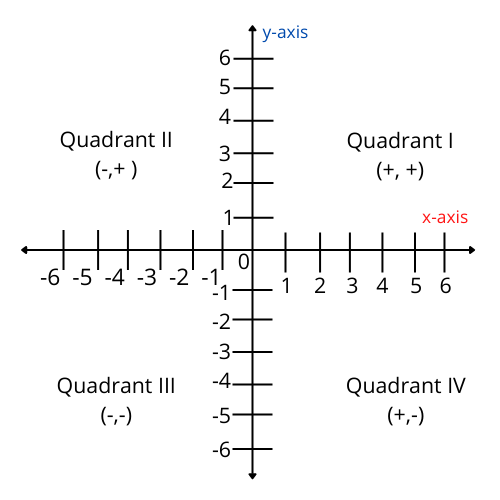
Chapter 3 covers Cartesian coordinates, plotting points in a plane, understanding the x-axis, y-axis, origin, and the four quadrants. You learn to represent locations using ordered pairs and visualize geometric figures in the Cartesian plane, as per the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
2. How can students accurately plot a point on the Cartesian plane as per Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 NCERT Solutions?
To plot a point:
- Start at the origin (0, 0).
- Move x units horizontally (right if positive, left if negative).
- Then move y units vertically (up if positive, down if negative).
- Mark the resulting location; this is your point (x, y).
3. What is the significance of the origin as explained in NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3?
The origin is the meeting point of the x-axis and y-axis, denoted as (0, 0). It serves as the reference point for locating all other points on the Cartesian plane.
4. Why is understanding quadrants essential in Coordinate Geometry for Class 9?
Understanding the four quadrants helps you determine the sign (positive/negative) of x and y coordinates, which is crucial for correct plotting and interpretation of points, as outlined in Class 9 NCERT Solutions.
5. How are abscissa and ordinate defined as per NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3?
The abscissa is the x-coordinate of a point—distance from the y-axis. The ordinate is the y-coordinate—distance from the x-axis. Together, they form the ordered pair (x, y) used to locate points in the Cartesian plane.
6. In what ways does practicing plotting points benefit students, according to NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3?
Practicing plotting points:
- Builds spatial understanding of geometry.
- Improves accuracy in solving coordinate geometry problems.
- Develops a foundation for advanced topics like distance, midpoint, and slope in later classes.
7. What common mistakes should students avoid when working with NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry?
- Reversing the order of coordinates (writing y before x).
- Misidentifying the signs of x and y for each quadrant.
- Incorrectly measuring distances from the wrong axis.
8. How does Coordinate Geometry in Class 9 prepare students for higher-level Maths?
This chapter introduces coordinate representation of geometric figures, a foundation for topics like graphs, linear equations, loci, distance formula, and trigonometry—essential for Class 10 and beyond.
9. What strategy should a student follow to solve CBSE exam questions from Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 effectively?
Follow these strategies:
- Understand the terminology: axis, origin, quadrant, abscissa, ordinate.
- Read the problem thoroughly—draw diagrams where possible.
- Apply the stepwise approach shown in NCERT Solutions.
- Double-check coordinate signs and axes for accuracy.
10. Can NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 help with other subjects or real-life applications?
Yes, mastery in coordinate geometry aids in Physics (motion in a plane), Geography (mapping), and various fields that require spatial analysis, besides preparing you for competitive exams per CBSE curriculum trends.
11. What is the importance of using stepwise solutions as shown in NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3?
Stepwise solutions help students:
- Understand each stage in plotting and interpreting points.
- Build confidence with CBSE exam-style formats.
- Identify and correct logical gaps in their approach.
12. Are there advanced applications or extensions of the Cartesian System beyond this chapter?
Yes. The Cartesian System extends to three dimensions (x, y, z axes) for 3D geometry and is foundational for concepts like vectors, calculus graphs, and computer graphics, all covered in higher grades.
13. How can students distinguish between points lying on the axes versus those in the quadrants?
- Points on the x-axis have y = 0.
- Points on the y-axis have x = 0.
- Points in the quadrants have both x and y non-zero; the sign determines the specific quadrant.
14. What misconceptions about ordered pairs are clarified in Class 9 Coordinate Geometry solutions?
- Ordered pairs (x, y) are always read as x-coordinate followed by y-coordinate.
- Swapping x and y changes both the position and meaning of the point.
- Each ordered pair uniquely identifies one point on the plane.
15. Why are NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 considered reliable for CBSE exam preparation?
NCERT Solutions follow the latest CBSE syllabus, use exam-style language, present step-by-step reasoning, and focus on conceptual clarity. Practicing with them ensures thorough understanding and boosts exam confidence for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry.