What Are The Light Class 8 Questions And Answers?
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Light - 2025-26
1. What are the stepwise NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 13, Light, as per latest CBSE 2025–26 exam patterns?
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 13, Light (as per CBSE 2025–26):
- Every answer strictly follows NCERT methodology. For example, when asked to compare regular and diffused reflection, the answer is provided using a table showing the key differences (surface type, ray parallelism).
- Short answers and fill-in-the-blanks are answered directly using correct scientific terms (e.g., the size of the pupil increases in dim light; a person 1 m from a mirror sees his image 2 m away).
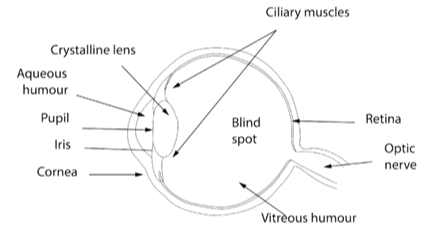
- Diagram questions (like ‘draw the human eye’) are addressed by labelling all key structures (cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, optic nerve) with bullet explanations.
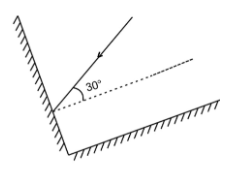
- Numerical/problem-solving (mirror angles, image count between parallel mirrors) uses formulas from the chapter: e.g., angle of incidence if the reflected ray makes 90° with incident ray: i = 45°.
- All reasoning questions explicitly cite the laws of reflection and CBSE-curated concepts.
2. How does the NCERT define and distinguish regular and diffused reflection in Class 8 Science Chapter 13 solutions?
According to Class 8 Science solutions for Chapter 13:
- Regular reflection occurs on smooth and shiny surfaces where parallel incident rays are reflected as parallel rays in a single direction, resulting in a clear image.
- Diffused (irregular) reflection occurs on rough or uneven surfaces where incident rays are reflected in multiple directions, so no clear image is formed. This is not due to failure of the laws of reflection, but due to surface irregularities.
3. What are the key steps to solve image formation questions using NCERT methodology for Class 8 Science Chapter 13, Light?
Steps to solve image formation questions as per NCERT for Class 8 Science Chapter 13:
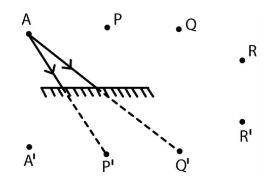
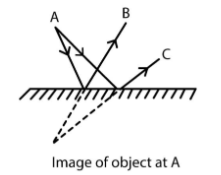
- Identify distance of object from mirror.
- Apply the rule: image appears at the same distance behind the mirror as object is in front.
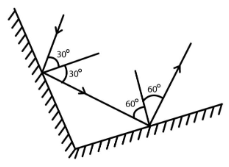
- If between parallel plane mirrors, use the formula: infinite images form due to multiple reflections.
- For diagrams, clearly label rays (incident, reflected, normal) and use the law: angle of incidence = angle of reflection.
4. What are the official NCERT Laws of Reflection covered in Class 8 Science Chapter 13 solutions?
The Laws of Reflection (as per NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 13 solutions):
- First Law: The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
- Second Law: The incident ray, reflected ray, and the normal to the surface all lie in the same plane.
5. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 instruct care of the eyes?
Care of eyes as covered in NCERT Solutions:
- Read in proper lighting to avoid eye strain.
- Wash eyes regularly with clean water.
- Do not rub eyes, especially if dust enters—rinse instead.
- Keep proper distance between book and eyes while reading.
- See a doctor if eye discomfort persists (per CBSE 2025–26 guidelines).
6. According to Class 8 Light NCERT Solutions, what is the role of the pupil and iris in the human eye?
The NCERT Solutions state:
- Pupil acts as the opening that regulates how much light enters the eye—enlarging in dim light and shrinking in bright light.
- Iris surrounds the pupil and controls its size, thus regulating light entering the retina.
7. Why do night birds have more rods than cones, as explained in Class 8 Science Chapter 13 NCERT Solutions?
As per NCERT Solutions: Night birds have more rods than cones in their eyes, which helps them detect dim light and see at night. Rods are sensitive to low light, while cones help in perception of colour and daylight vision.
8. What concept explains the formation of multiple images between two parallel mirrors in the Class 8 Science Light chapter?
NCERT Solutions explain: When two plane mirrors are placed parallel and facing each other, an infinite number of images are formed due to continuous reflection of light between the mirrors. This is an application of the law of multiple reflections.
9. What is white light according to NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 13 solutions?
White light is described as a combination of all colours in the visible spectrum. When passed through a prism, white light splits into its component colors (VIBGYOR), a phenomenon known as dispersion.
10. What are the official NCERT steps to perform the class 8 activity that verifies all reflected rays lie in the same plane?
NCERT steps:
- Place a plane mirror vertically on a sheet of paper.
- Draw an incident ray and mark a normal at the point of incidence.
- Mark the reflected ray using the law that angle of incidence equals angle of reflection.
- Remove the mirror and observe: all rays and the normal lie on the paper—hence in the same plane.
11. What is the Braille system according to NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 13?
NCERT Solutions define Braille: The Braille system is a tactile writing method used by visually impaired individuals; it uses raised dots arranged in cells to represent letters and numbers, enabling reading and writing by touch. It can be adapted for different languages and types of information.
12. How does the CBSE Class 8 Science syllabus define a mirror in the context of the Light chapter NCERT Solutions?
A mirror is defined as a smooth, shiny surface (usually glass with a reflective coating) that forms images by reflecting light rays. NCERT highlights that mirrors are used in optical devices and image formation experiments.
13. FUQ: What misconception do students often have about diffused reflection and its relation to the laws of reflection, and how does the NCERT clarify it in Chapter 13?
Common misconception: Some believe diffused reflection breaks the laws of reflection. NCERT clarifies that the laws of reflection are always obeyed for each ray, even on rough surfaces—the irregularities only scatter rays in different directions.
14. FUQ: How would the solution approach change if a question asks about multiple reflections with non-parallel mirrors, as per Class 8 Light NCERT Solutions?
NCERT Steps: If mirrors are not parallel, use the formula: No. of images = (360°/θ)-1, where θ is the angle between mirrors. If θ divides 360°, images are finite; otherwise, count is adjusted as per NCERT worked examples.
15. FUQ: What if a student looks directly into a laser source during an experiment related to Light in Class 8 NCERT?
The NCERT Solution strictly warns: lasers are highly intense and can permanently damage the retina, potentially causing blindness. Direct eye exposure to laser beams must be avoided during experiments, per CBSE safety guidelines.