What Are The Important Chemical Effects Of Electric Current Class 8 Questions And Answers
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Chemical Effects of Electric Current (2025-26)
1. What are the main chemical effects of electric current explained in NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 11?
The main chemical effects of electric current as per NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 11 include:
- The release of gas bubbles at electrodes when current passes through a solution.
- Deposition of metals or other substances on electrodes, such as copper or silver plating.
- A change in the colour of the solution, indicating a chemical reaction.
These demonstrate how electric current can cause chemical changes in conducting solutions.
2. How does the NCERT Solutions approach the concept of electrolytes and non-electrolytes in Class 8 Science Chapter 11?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 11 define electrolytes as liquids (e.g., acids, bases, salts in water) that conduct electricity due to the presence of ions. Non-electrolytes (like sugar solution) do not conduct electricity because they do not produce ions in solution. The solutions help students recognize examples and test substances to classify them based on their ability to conduct electric current.
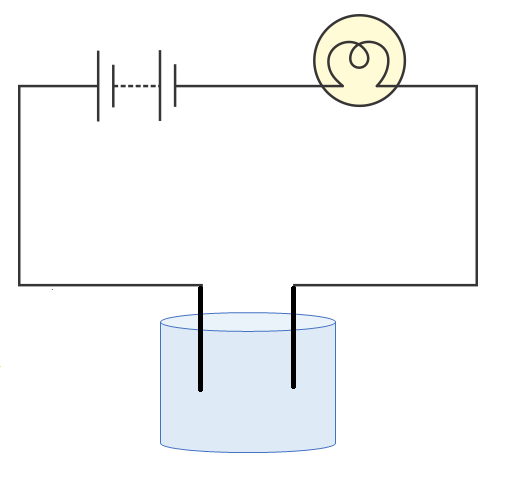
3. Can you explain the stepwise method for testing if a liquid conducts electricity as outlined in the NCERT Solutions?
As per CBSE 2025–26 syllabus, to test if a liquid conducts electricity:
- Connect a circuit with a bulb, battery, and two free ends.
- Dip the free ends into the liquid sample.
- Observe the bulb: if it glows, the liquid conducts electricity; if not, it does not.
- For accuracy, use a magnetic compass near the wire to detect any current flow by needle deflection, especially for weak conductors.
4. Why doesn’t pure distilled water conduct electricity, according to the solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 11?
Pure distilled water does not conduct electricity because it lacks dissolved ions needed for current flow. When a small amount of salt or acid is added, it becomes a conductor as ions are introduced, allowing electric current to pass through the water.
5. What is electroplating and how is it explained in the context of Class 8 Science Chapter 11 NCERT Solutions?
Electroplating is a chemical effect of electric current where a thin layer of a desired metal is deposited onto another object by passing an electric current through a suitable electrolyte. The process is explained with examples like chromium or zinc plating to prevent rust or enhance appearance, making the concept practical and relatable for students.
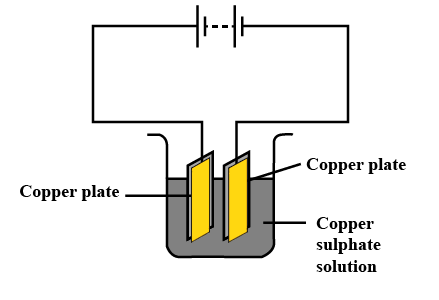
6. How is the process of purification of copper achieved using electric current as described in NCERT Solutions?
The purification of copper is done by electrolysis. An impure copper rod is attached to the positive terminal (anode), and a pure copper plate is attached to the negative terminal (cathode). Passing current through copper sulphate solution causes pure copper to deposit on the cathode, while impurities remain as sludge, aiding purification.
7. What should be done for an electrician’s safety during electrical repairs in rain, based on NCERT guidelines?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science state repairs outdoors during rain are unsafe because rainwater conducts electricity due to dissolved salts. To prevent electric shock, the main electric supply should always be switched off before beginning repairs in wet or rainy conditions.
8. How can you compare the conductivity of two different liquids based on observations from the solutions?
If a bulb connected to a tester glows more brightly in liquid A than in liquid B, liquid A is a better conductor than liquid B. The solution specifies that greater brightness indicates higher conductivity and more current passing through liquid A compared to liquid B.
9. What are some applications of the chemical effects of electric current mentioned in NCERT Solutions?
Applications include:
- Electroplating (e.g., coating jewelry or car parts)
- Electrochemical cells (batteries)
- Purification of metals (like copper)
- Prevention of corrosion via galvanization
These show real-life uses of chemical effects discussed in Class 8 Science Chapter 11.
10. What are common misconceptions students might have about conductors and insulators, as addressed in the solutions?
The NCERT Solutions clarify that it is better to use the terms good conductors and poor conductors rather than just conductors and insulators, since most materials can conduct under certain conditions (e.g., water with dissolved salts). It addresses the misconception that only metals can conduct electricity.
11. Why do dissolved salts in water increase conductivity, as per the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 11?
Dissolved salts introduce free ions into water, which carry electric charge. This ion movement allows water to conduct electricity effectively. The more dissolved salts, the higher the conductivity.
12. What are the key steps recommended in NCERT Solutions for revising important topics in Chemical Effects of Electric Current?
To revise:
- Review definitions of electrolytes, electroplating, and chemical effects.
- Understand experimental setups and diagrams.
- Practice solved examples, especially fill-in-the-blanks and reason-based questions.
- Summarize application-based uses like electroplating and corrosion prevention.
13. How do the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 11 help in understanding real-world phenomena like rust prevention and jewelry making?
The solutions connect theory to practice by explaining that techniques such as galvanization and electroplating prevent rust or add attractiveness to objects, demonstrating how chemical effects of electric current are vital for various industries and daily life.
14. What higher order thinking skills (HOTS) question types are included in the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 11?
The solutions encourage application and analysis by asking students to:
- Predict outcomes when different liquids are tested in a circuit.
- Explain why certain safety procedures are essential in electrical work.
- Reason why pure water is a bad conductor without dissolved ions.
- Apply concepts from the chapter to explain real-world industrial processes.