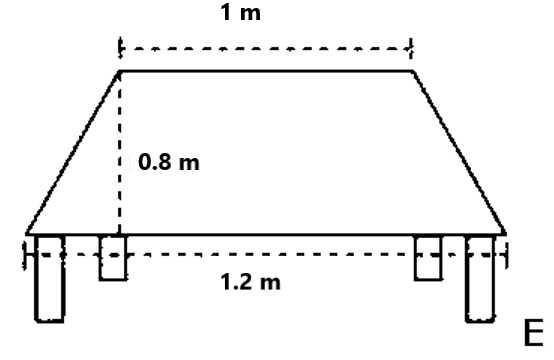
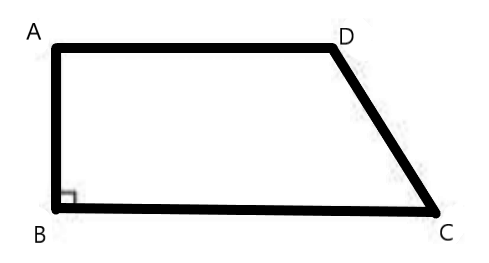
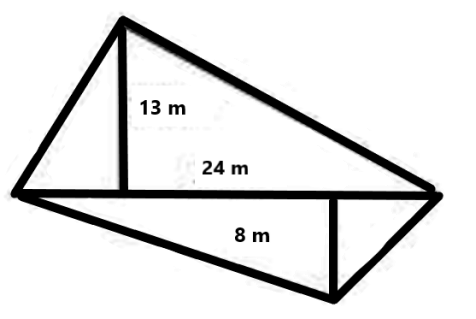
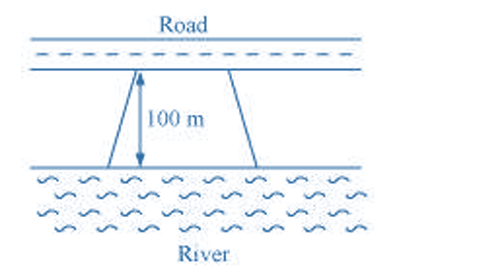
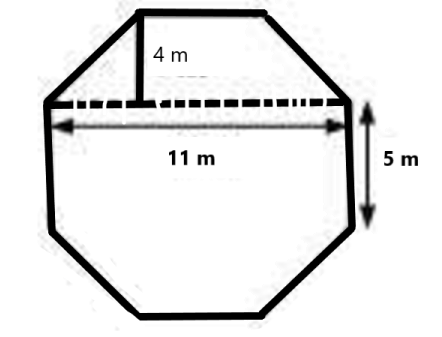
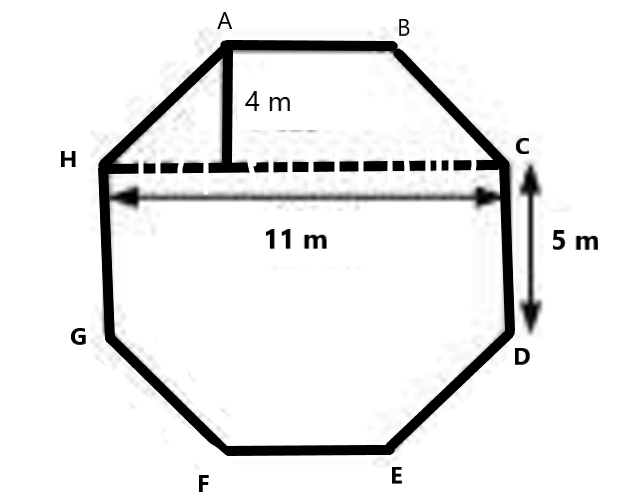
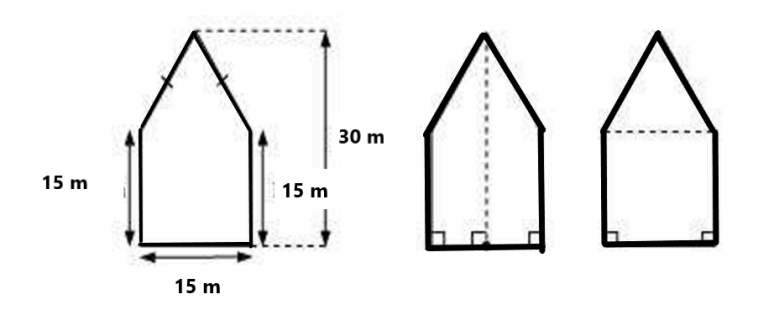
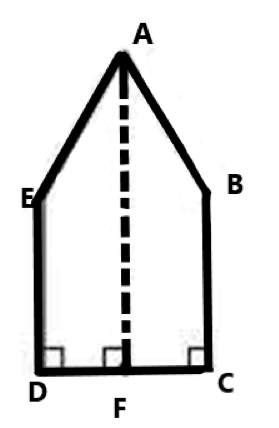
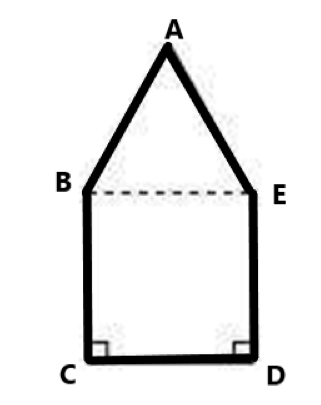
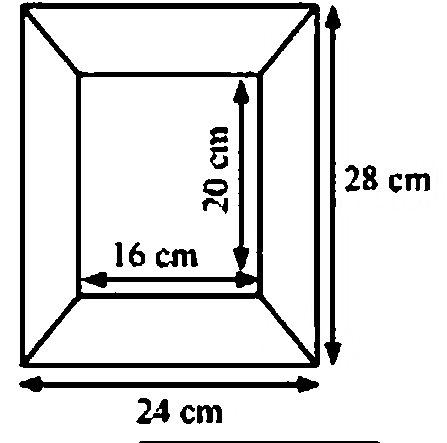
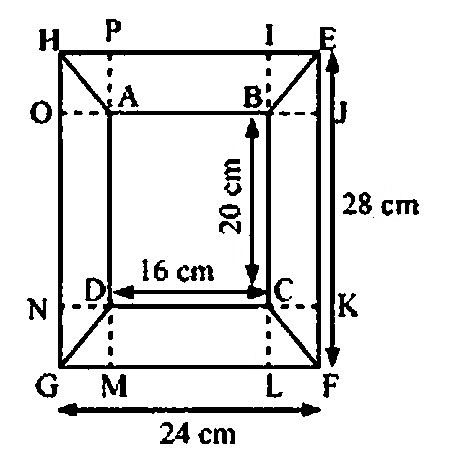
Clear Your Doubts in Class 8 Mensuration 9.1 with Stepwise NCERT Answers
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Mensuration Exercise 9.1 - 2025-26
1. Are Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Exercise 9.1 NCERT Solutions enough for school exams?
Yes, Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Exercise 9.1 NCERT Solutions are sufficient for school exams when students practise textbook questions using the solutions provided on Vedantu.
2. How should students use Class 8 Maths Exercise 9.1 Mensuration NCERT Solutions correctly?
Students should first attempt the questions themselves and then verify their approach using Class 8 Maths Exercise 9.1 Mensuration NCERT Solutions available on Vedantu.
3. Do Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Exercise 9.1 solutions focus on answer presentation?
Yes, Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Exercise 9.1 solutions on Vedantu help students understand proper answer presentation and step structure.
4. Can Class 8 Maths Mensuration Exercise 9.1 NCERT Solutions be used for written practice?
Yes, Class 8 Maths Mensuration Exercise 9.1 NCERT Solutions on Vedantu are suitable for notebook practice and written preparation.
5. Do Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Exercise 9.1 solutions maintain NCERT answer length?
Yes, the Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Exercise 9.1 solutions on Vedantu maintain the appropriate answer length expected in school evaluations.
6. Are Class 8 Maths Exercise 9.1 Mensuration solutions useful before unit tests?
Yes, Class 8 Maths Exercise 9.1 Mensuration solutions available on Vedantu are useful for last-stage preparation before unit tests.
7. Do Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Exercise 9.1 NCERT Solutions follow a consistent solving format?
Yes, Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Exercise 9.1 NCERT Solutions on Vedantu follow a consistent step-by-step solving format.
8. Can parents rely on Class 8 Maths Exercise 9.1 NCERT Solutions for accuracy?
Yes, parents can rely on Class 8 Maths Exercise 9.1 NCERT Solutions provided on Vedantu, as they are aligned with the NCERT textbook.
9. Are Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Exercise 9.1 solutions suitable for self-checking answers?
Yes, Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Exercise 9.1 solutions on Vedantu are suitable for self-checking answers after practice.
10. How do Class 8 Maths Mensuration Exercise 9.1 NCERT Solutions help students avoid mistakes?
Class 8 Maths Mensuration Exercise 9.1 NCERT Solutions help students avoid mistakes by showing the correct solving steps and final presentation on Vedantu.