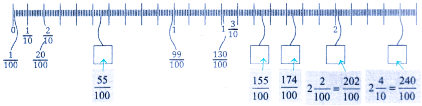
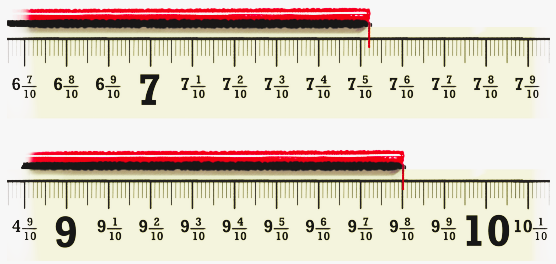
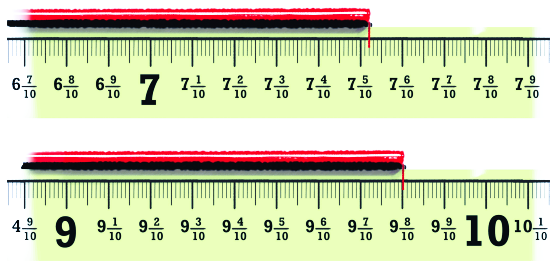
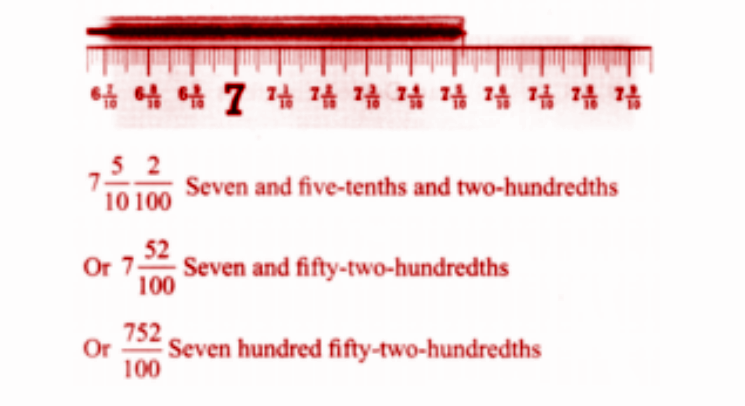
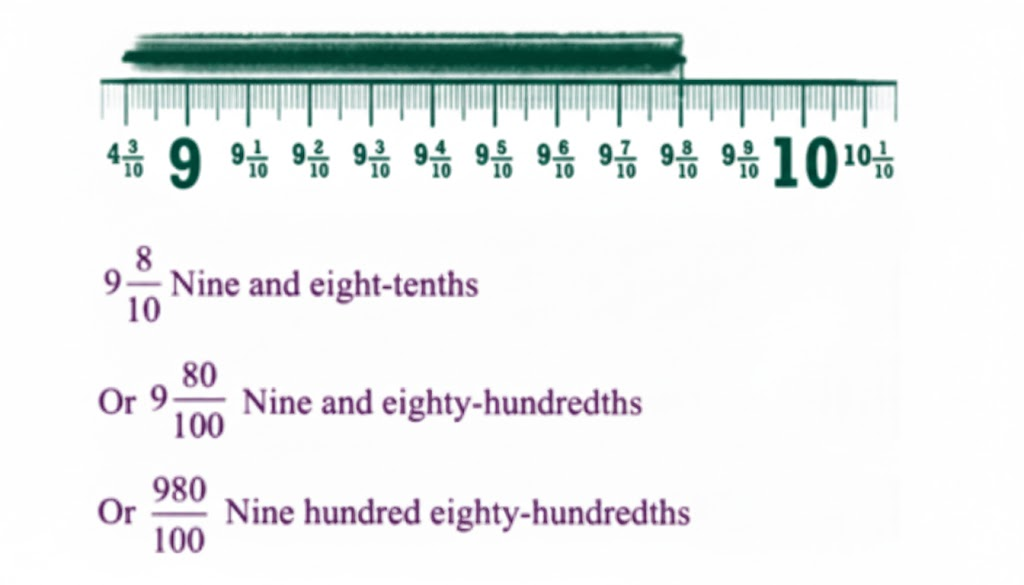
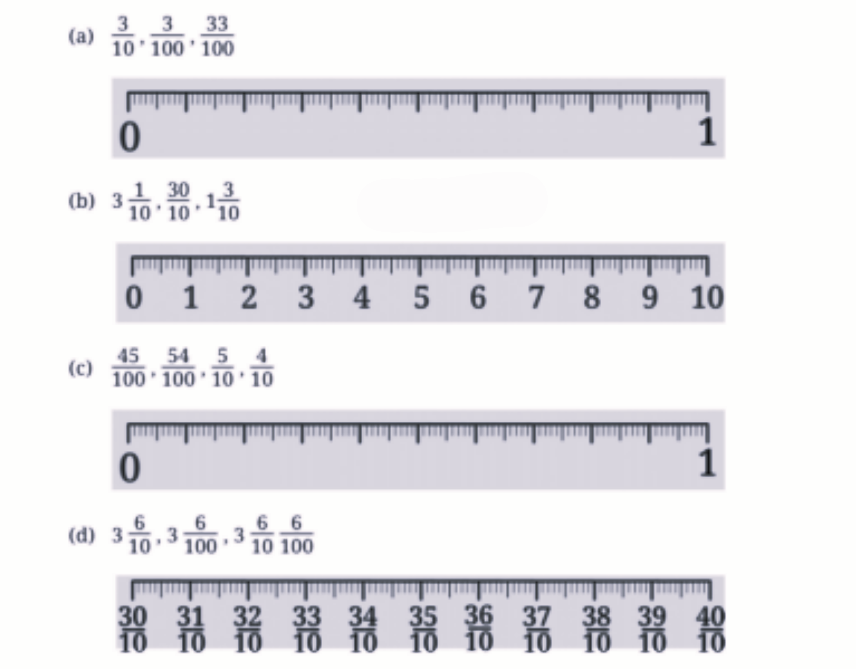
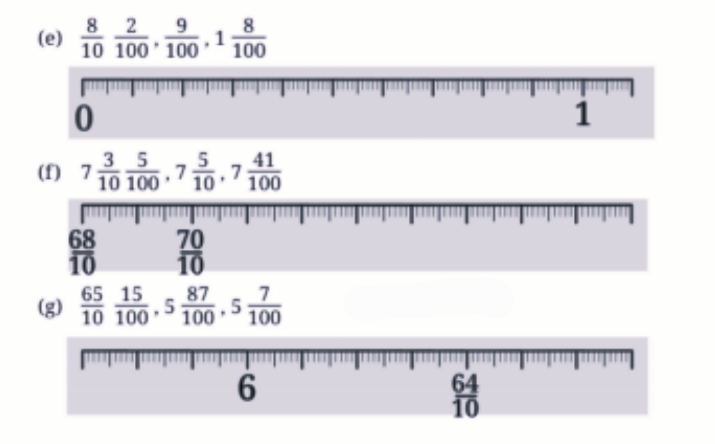
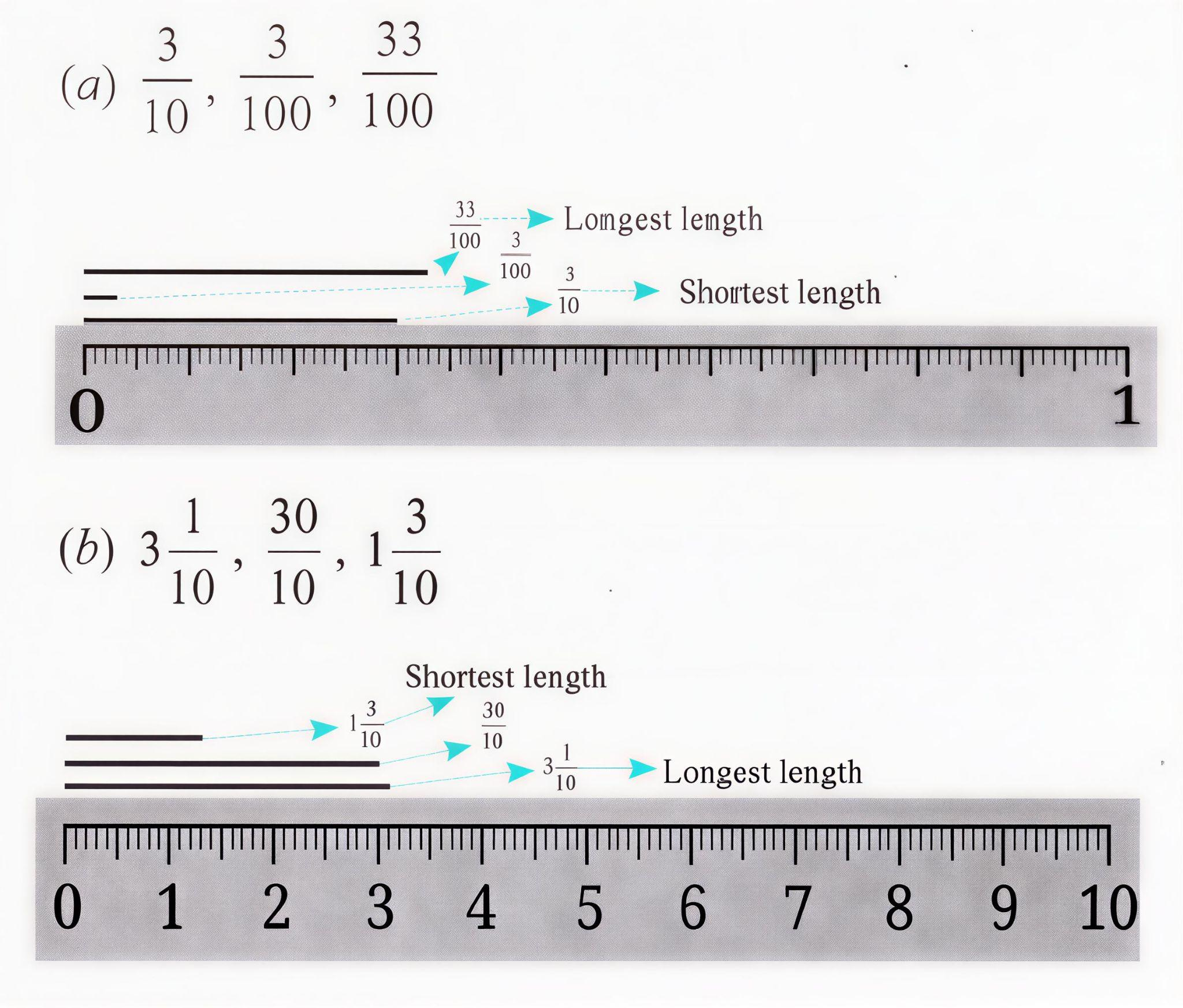
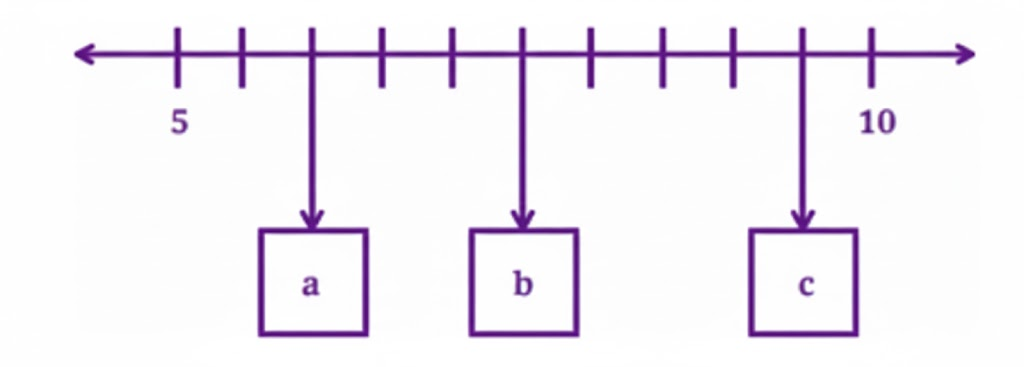
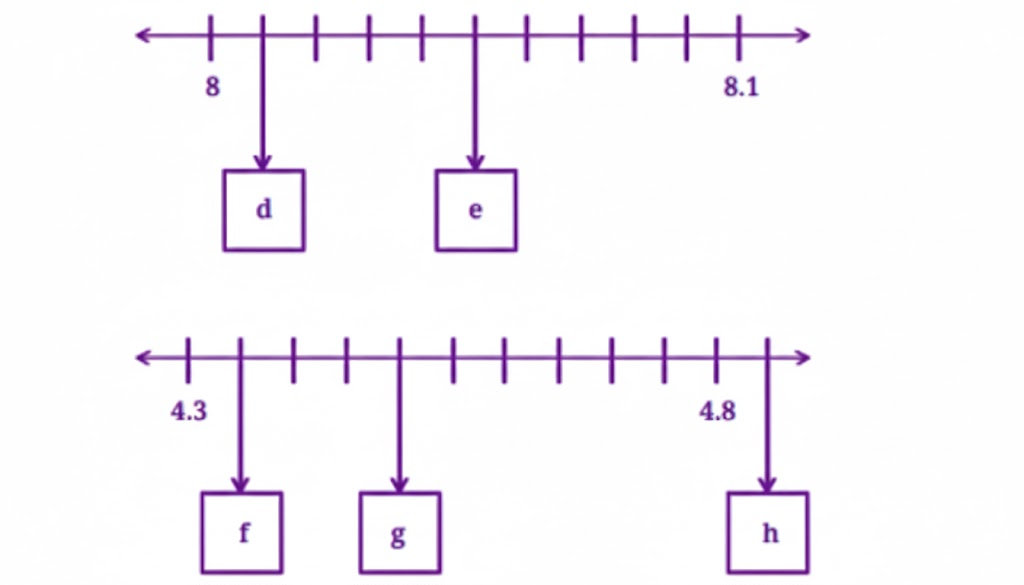
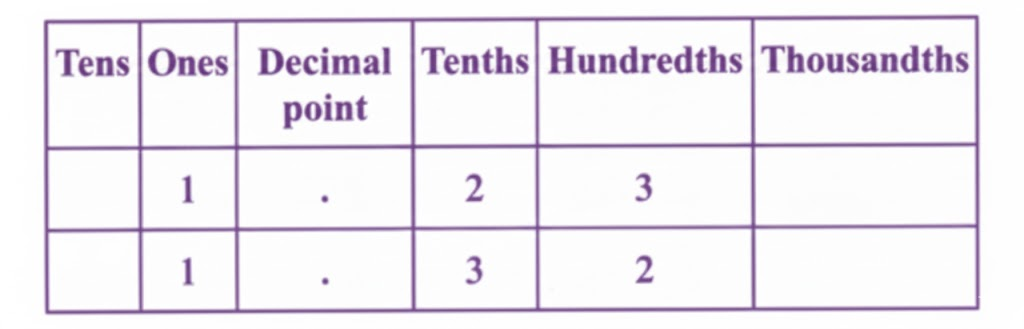
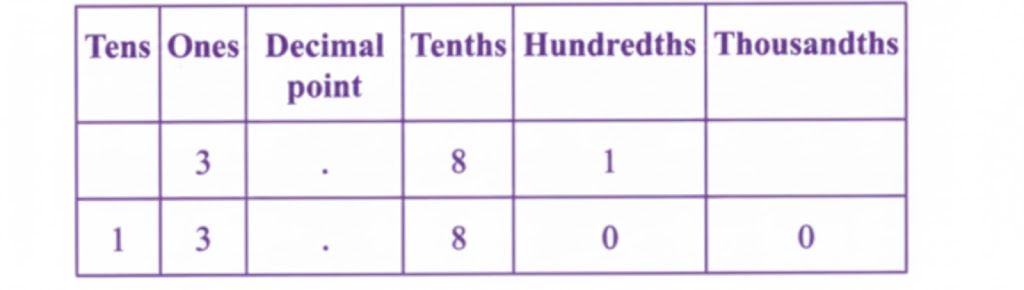
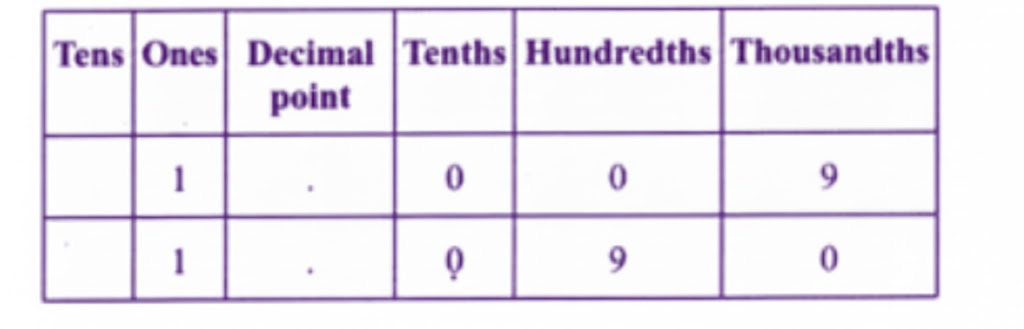
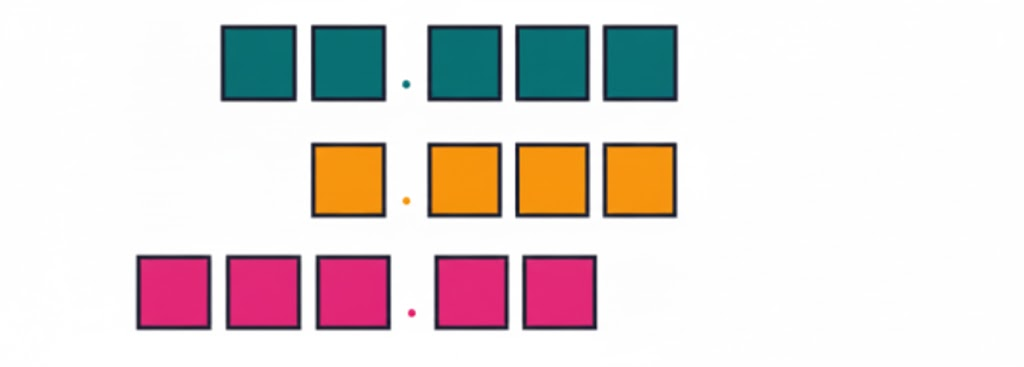
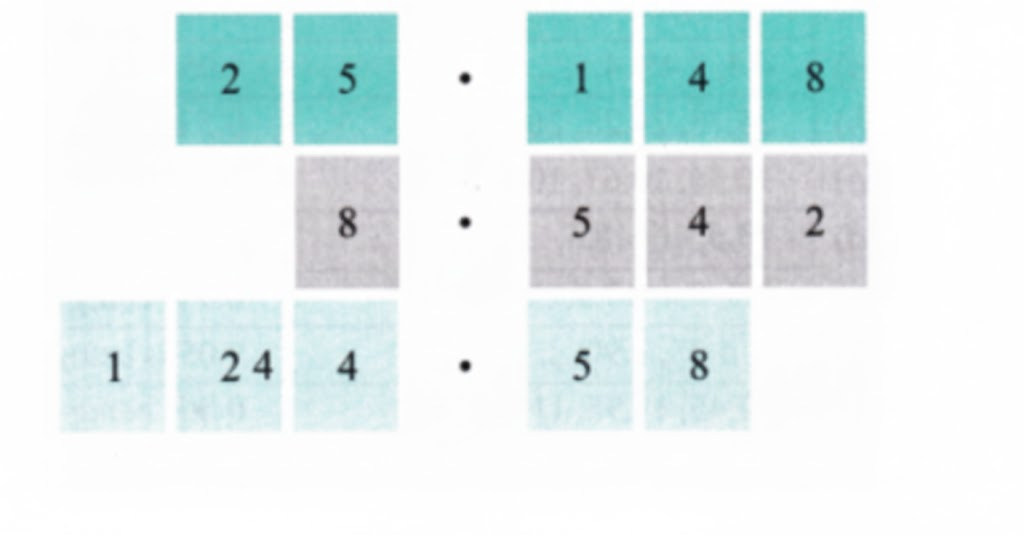
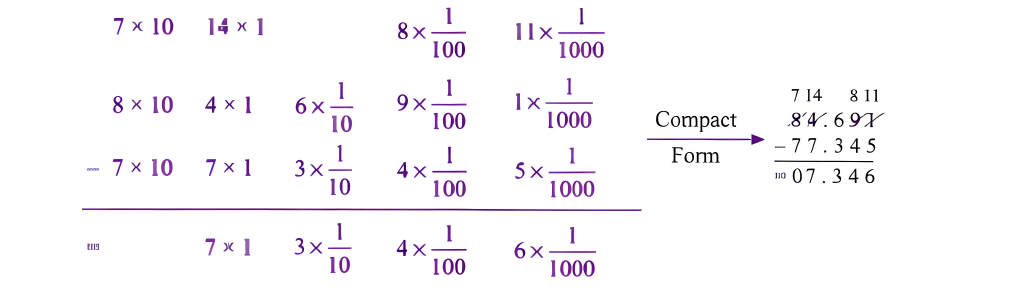
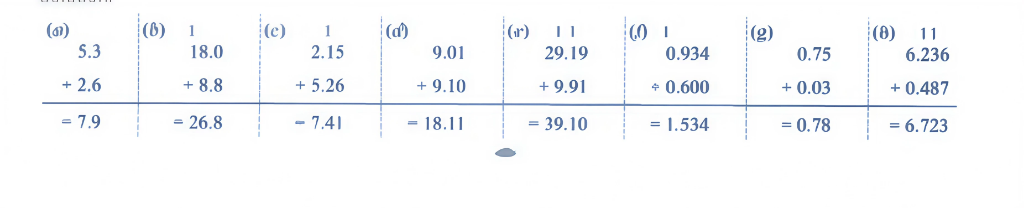
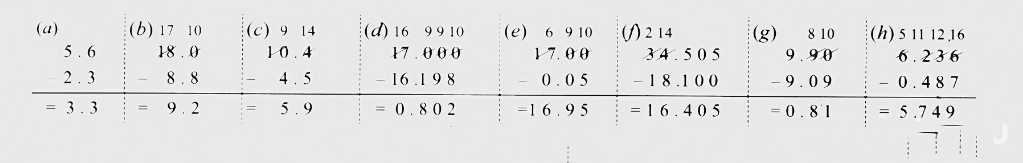
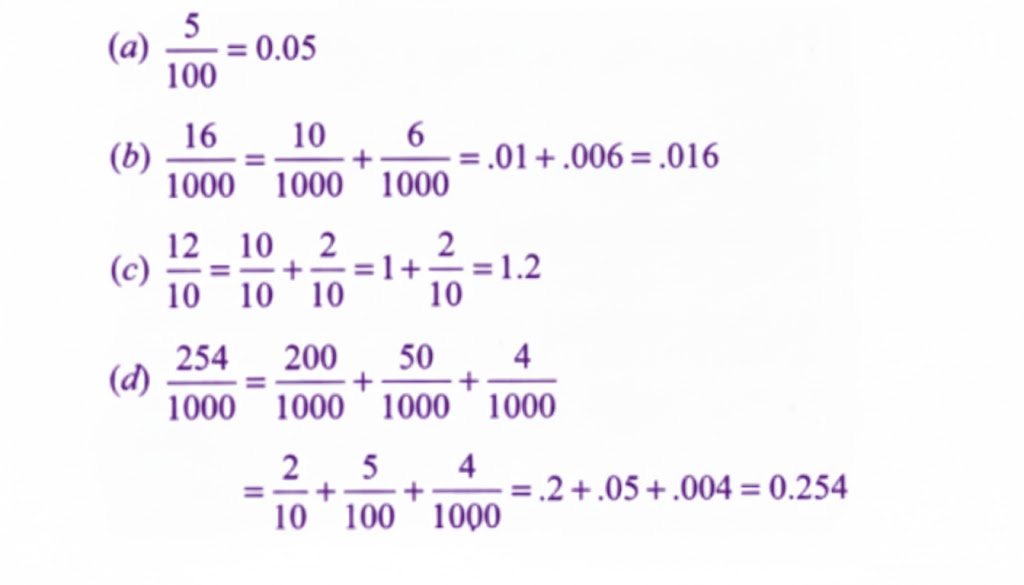
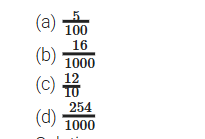Stepwise Answers & PDF for A Peek Beyond the Point Class 7 Maths
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Maths Chapter 3 A Peek Beyond the Point (2025-26)
1. What are NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 3 A Peek Beyond the Point?
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 3 A Peek Beyond the Point are detailed, step-by-step answers to every exercise question for this chapter, helping students score full marks in exams.
- They cover exercise-wise solutions following the latest CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
- Answers include concise definitions, diagrams, and explanations as per CBSE marking scheme.
- Solutions are teacher-reviewed and available as downloadable PDFs for revision.
2. How can I download the PDF for Class 7 Maths Chapter 3 A Peek Beyond the Point solutions?
You can easily download the PDF of Class 7 Maths Chapter 3 A Peek Beyond the Point solutions for offline study.
- Look for a "Free PDF Download" button on the solutions page.
- The PDF contains stepwise answers to all exercises.
- It covers definitions, diagrams, and exam tips as per CBSE 2025–26 requirements.
3. Are stepwise solutions important for scoring full marks in Class 7 Maths Chapter 3?
Yes, presenting stepwise solutions is essential to score full marks in Class 7 Maths Chapter 3.
- Each step ensures you get partial marks even if a final answer is wrong.
- Teachers follow the CBSE marking scheme which rewards proper method.
- Well-structured steps demonstrate understanding and clarity.
4. What are the most important topics in Chapter 3 A Peek Beyond the Point for exams?
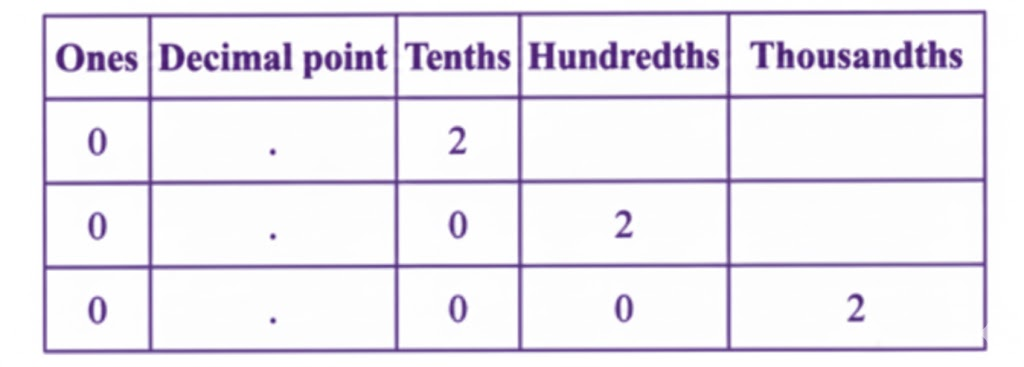
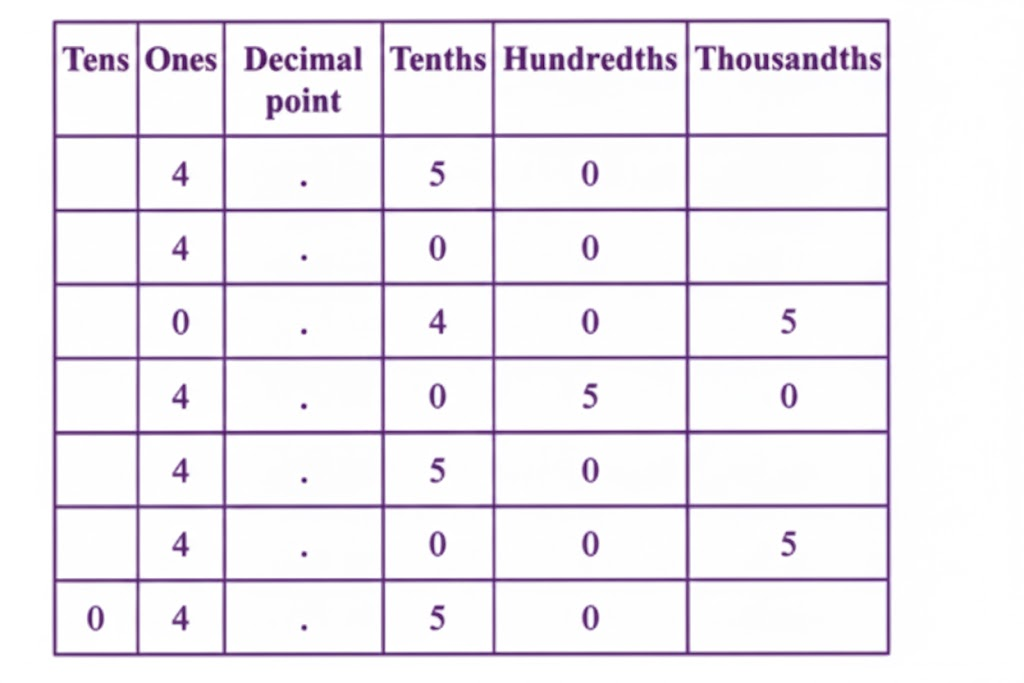
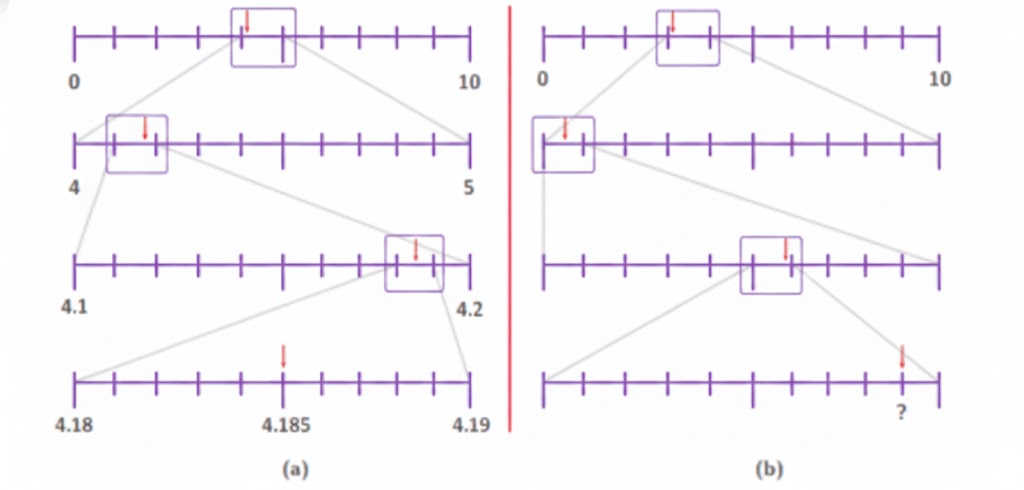
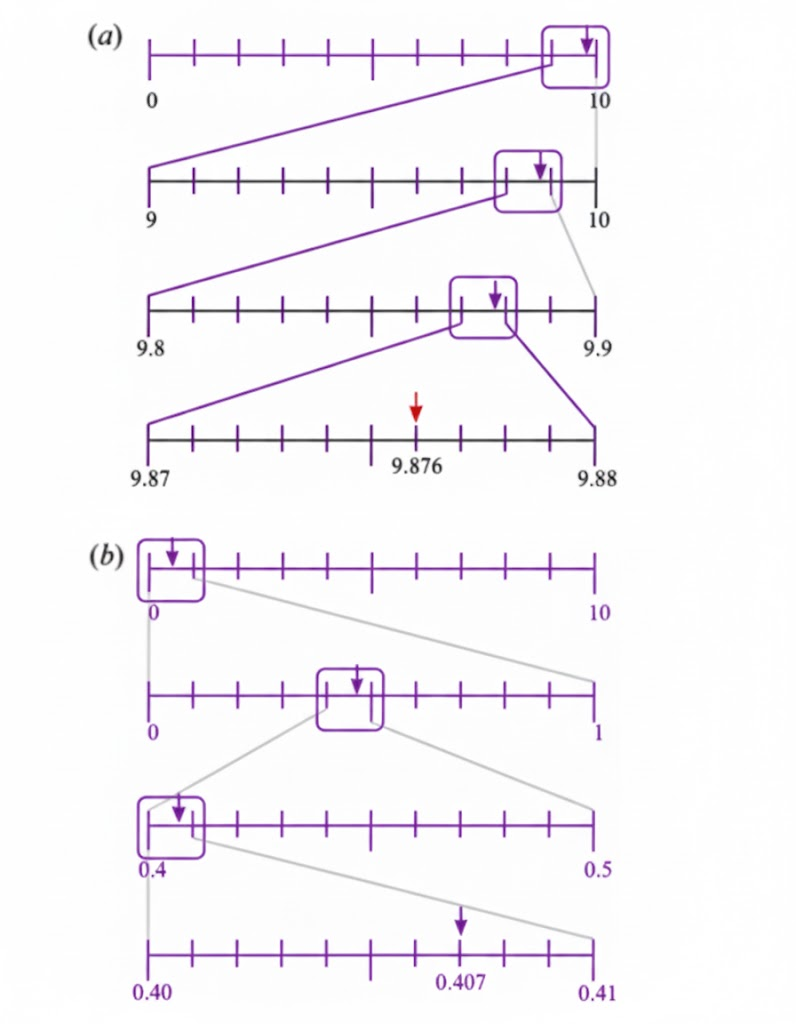
The most important topics in Chapter 3 focus on decimals, place value, and related computations.
- Key concepts include decimal expansion, converting fractions to decimals, and application problems.
- Definitions, rules for decimal operations, and diagram-based questions are frequently asked.
- Practice all exercise-wise solutions and examples from the NCERT textbook.
5. How should diagrams and definitions be presented in answers for Class 7 Maths Chapter 3?
Diagrams and definitions in Chapter 3 should be clear, labelled, and concise.
- Diagrams must be neatly drawn with proper labels.
- Provide exam-ready definitions exactly as per the NCERT textbook.
- Use rulers for straight lines and explain all terms clearly.
- Well-labeled diagrams can fetch you easy marks as per CBSE guidelines.
6. How do I answer long questions from Class 7 Maths Chapter 3 to match CBSE marking scheme?
Long answers for Chapter 3 should be structured in stepwise format with each step explained.
- Start with a statement of what is given and what is required.
- Write all formulae and definitions used.
- Show each calculation and step clearly.
- End with a final statement and box your answer.
- Use keywords and terms as in the CBSE syllabus.
7. Are NCERT Solutions enough to prepare for Class 7 Maths Chapter 3 for exams?
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 3 are sufficient for covering all important exam topics.
- The solutions follow CBSE patterns and cover intext questions and back exercises.
- For higher-order and competitive questions, refer to NCERT Exemplar problems.
- Regular practice with these solutions ensures you understand all concepts and score well.
8. What are common mistakes students make in Class 7 Maths Chapter 3 A Peek Beyond the Point?
Common mistakes in Chapter 3 include:
- Misplacing the decimal point in calculations.
- Skipping steps in solutions, losing step marks.
- Inaccurate or unlabeled diagrams.
- Forgetting to use correct definitions and formulae.
- Not following the marking scheme for structured answers.
To avoid these errors, follow stepwise NCERT solutions and revise all key concepts.
9. Do examiners award partial marks for correct steps even if the final answer is wrong in Class 7 Maths Chapter 3?
Yes, in CBSE exams for Class 7 Maths Chapter 3, partial marks are awarded for correct steps even if the final answer is incorrect.
- Each step carries marks as per the CBSE marking scheme.
- Always show all workings and calculations to secure maximum marks.
- Stepwise solutions help earn marks even with minor mistakes in the final result.
10. Where can I find extra questions or worksheets for Class 7 Maths Chapter 3?
You can find extra questions and worksheets for Class 7 Maths Chapter 3 A Peek Beyond the Point on various educational platforms.
- Look for materials titled "A Peek Beyond the Point class 7 extra questions" or worksheets.
- Use NCERT Exemplar Solutions and sample papers for additional practice.
- These resources support concept revision and exam preparation.