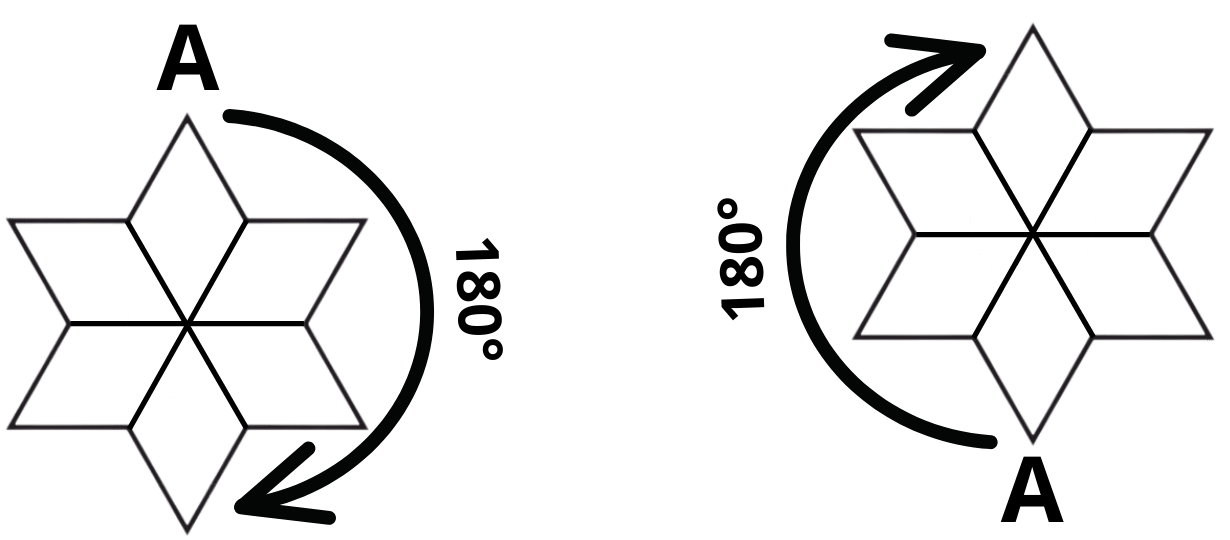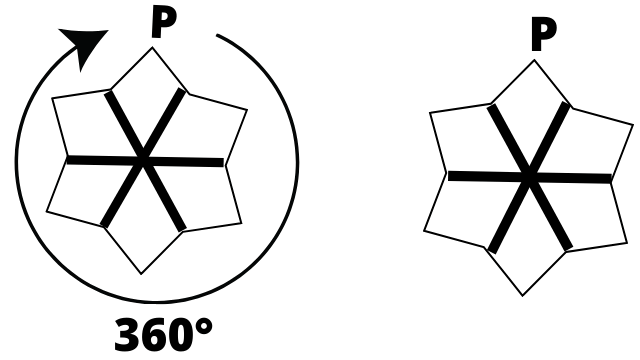Maths Class 7 Chapter 12 Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Maths Chapter 12 Symmetry Exercise 12.3 (2025-26)
1. Where can I find accurate and step-by-step NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 12, Symmetry, for the 2025-26 session?
You can find comprehensive and reliable NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 12 on Vedantu. Our solutions are prepared by subject matter experts and provide a detailed, step-by-step methodology for solving every question as per the latest CBSE 2025-26 guidelines. Each solution focuses on clarity and helps students understand the correct approach to solving problems related to symmetry.
2. What is the correct method to solve the questions in Exercise 12.1 of Class 7 Maths Chapter 12?
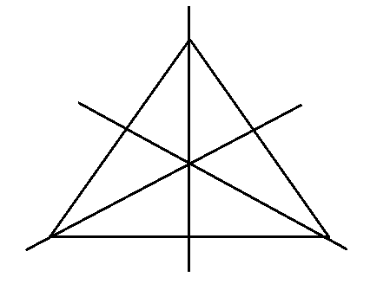
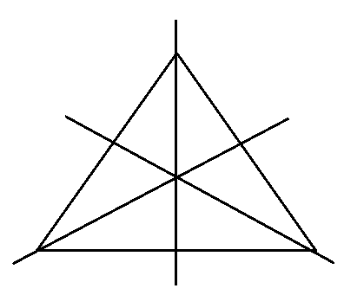
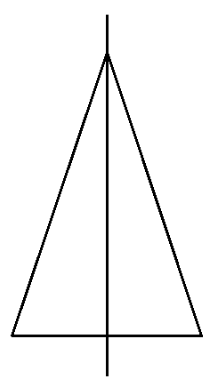
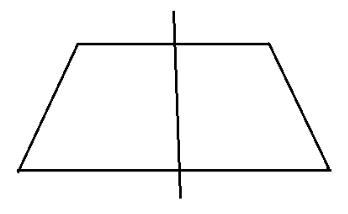
The correct method for solving questions in Exercise 12.1 involves identifying and drawing lines of symmetry for various geometric figures. The step-by-step solutions guide you to:
- Analyse the given shape.
- Identify all possible lines along which the figure can be folded to have two identical halves.
- Draw and count these lines accurately.
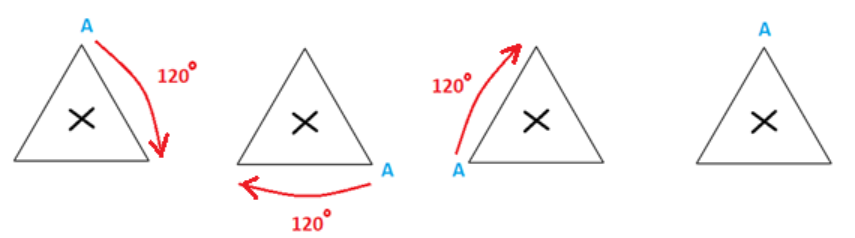
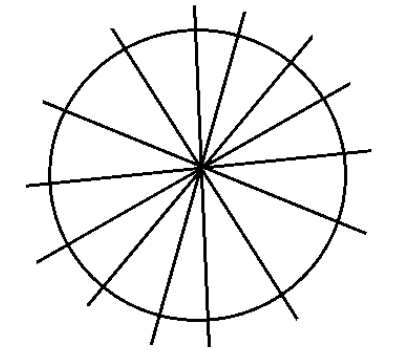
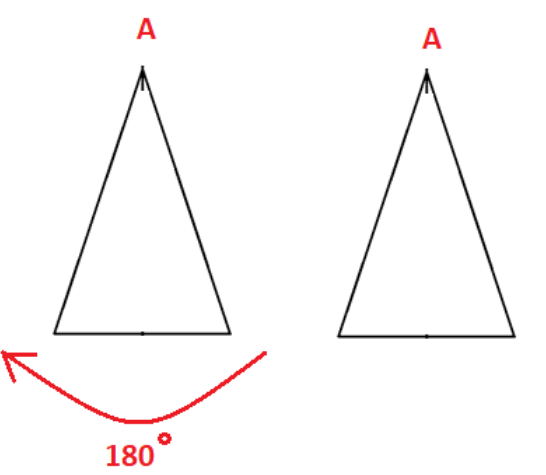
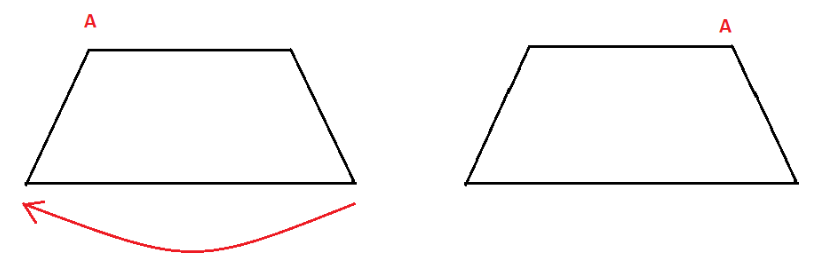
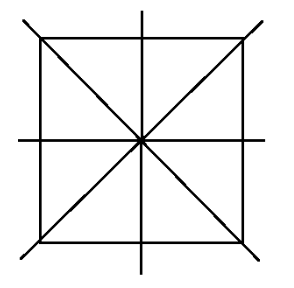
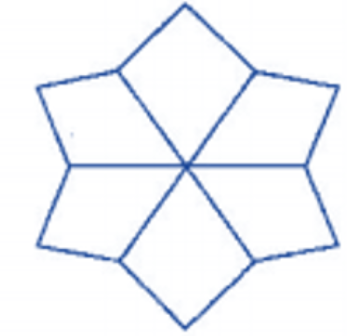
3. How are the problems on rotational symmetry in Exercise 12.2 solved in the NCERT solutions?
The NCERT solutions for Exercise 12.2 provide a systematic approach to solving problems on rotational symmetry. The key steps involve:
- Determining if a figure has rotational symmetry by rotating it around a central point.
- Finding the order of rotational symmetry, which is the number of times the figure looks identical in a full 360° turn.
- Calculating the angle of rotation by dividing 360° by the order of symmetry.
4. What key concepts are covered in the solutions for Exercise 12.3 of Chapter 12?
The solutions for Exercise 12.3 focus on identifying figures that have both line symmetry and rotational symmetry. The problem-solving method involves first checking for lines of symmetry and then checking for rotational symmetry. The solutions clearly explain how to identify the order of rotation and the number of symmetry lines for each shape, helping you understand the relationship between these two types of symmetry.
5. How do I differentiate between line symmetry and rotational symmetry when solving NCERT problems?
To solve NCERT problems correctly, it's crucial to understand the difference. Line symmetry (or reflectional symmetry) is when a figure can be divided by a line into two identical mirror images. You can think of it as folding the shape along a line. Rotational symmetry is when a figure looks the same after being rotated by less than a full 360° turn around a central point. The solution method is to check for 'folding' lines for line symmetry and 'turning' points for rotational symmetry.
6. Why is finding the 'order of rotational symmetry' an important step in solving Chapter 12 questions?
Finding the order of rotational symmetry is a critical step because it quantifies the symmetry of a shape. It tells you exactly how many positions a figure can be rotated to and still look identical. This value is essential for fully describing a shape's properties as required by the NCERT curriculum and is also used to calculate the angle of rotation (360° ÷ order), which is another key parameter in solving these problems.
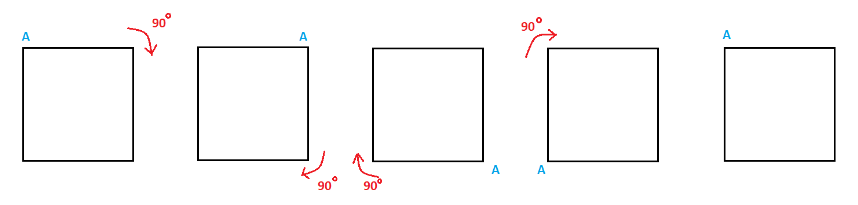
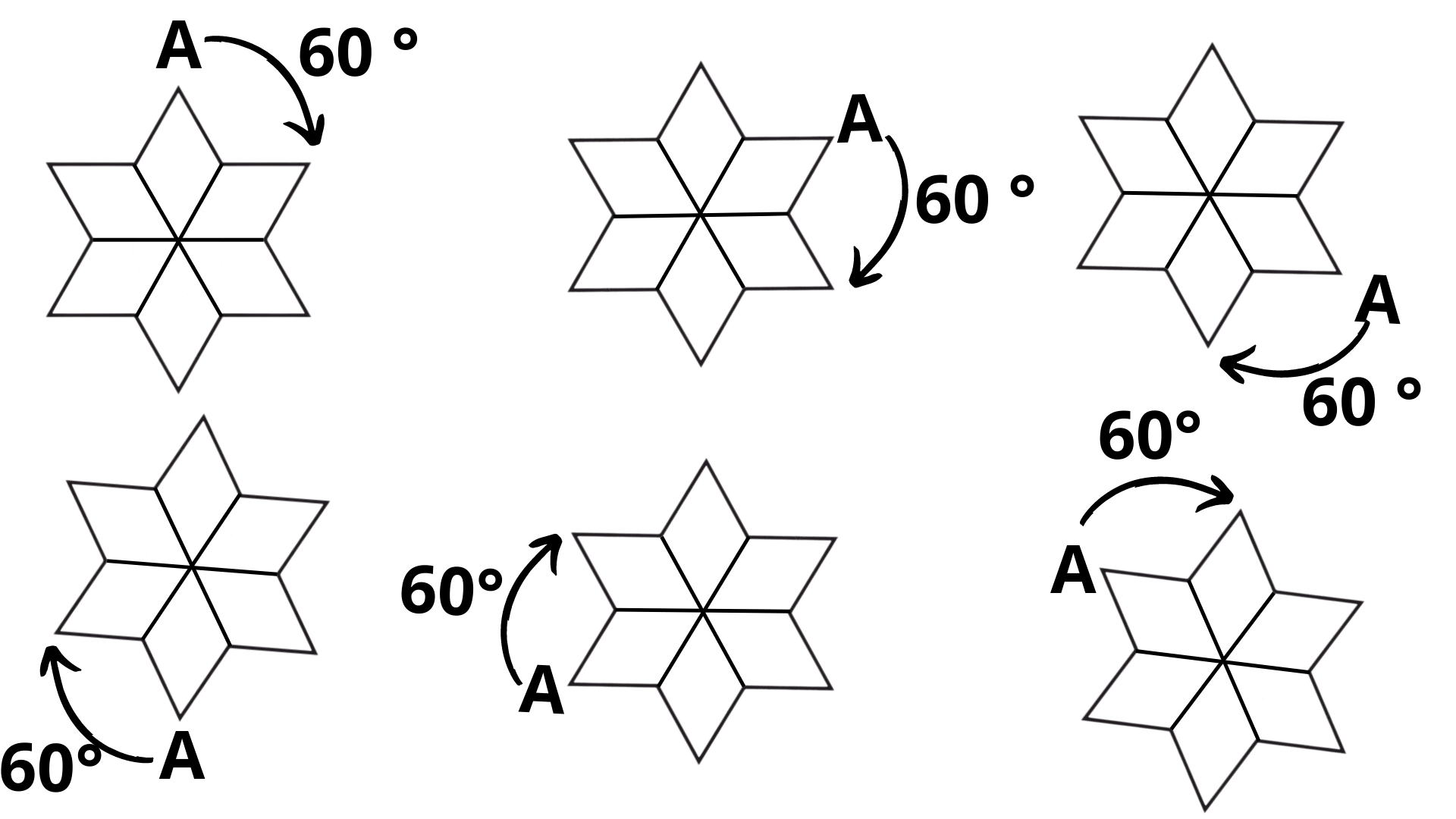
7. How can I determine the angle of rotation for any shape as per the CBSE method?
According to the CBSE method for solving problems in Chapter 12, the angle of rotation is found using a simple two-step process:
- First, determine the order of rotational symmetry by counting how many times the shape matches its original position during a 360° turn.
- Second, use the formula: Angle of Rotation = 360° / Order of Rotational Symmetry.
8. What common mistakes should be avoided when solving problems on symmetry in the Class 7 Maths NCERT book?
When solving symmetry problems, students often make a few common mistakes. You should be careful to:
- Not confuse a diagonal with a line of symmetry in all quadrilaterals (e.g., a rectangle's diagonals are not lines of symmetry).
- Correctly count the order of rotational symmetry. An order of 1 means there is no rotational symmetry.
- Ensure that for line symmetry, the two halves are perfect mirror images.